Plant responses to climate are lagged
Climate drivers outside of the growing season may have stronger effects on plants than previously assumed.
2021-02-22
(Press-News.org) Two in five of the world's plant species are at risk of extinction. In the face of climate change, understanding why certain plant species are vulnerable to extinction while others prevail is more urgent than ever before. Previous studies linking climate and plant vital rates have found relatively modest effects, sometimes leading to the conclusion that other threats, such as land use change, may still be more important than climate drivers. However, these conclusions could result from wrong assumptions about which times of the year (which "time window") climate drivers such as temperature and precipitation influence plant species. "Most researchers assume that plant populations respond to the climate within twelve months and only use this time window in their models to analyse plant responses," says first author Sanne Evers from iDiv and MLU.
Climate conditions during dormant seasons often neglected
For their study, the team of researchers led by iDiv, MLU and UFZ analysed 76 studies performed on 104 plant species that link climate drivers with demographic responses. They found that 85% of all studies considered 1-year time windows, and often focus on the growing season (e.g. spring and/or summer). However: "There are many ways in which climate during the dormant season, or climate that occurred few years in the past, can influence the survivorship, growth, and reproduction of plants. For example, species can grow substantially during the cold season, at least where the cold season temperature does not fall below 5° Celsius. In addition, it might take multiple years for plants to die after physiological damage from drought has occurred," says Aldo Compagnoni from iDiv and MLU and senior author of the paper.
To investigate which combination of climate drivers and temporal window have the best predictive ability, the researchers used four exceptionally long-term data sets: the montane plants Helianthella quinquenervis and Frasera speciosa and the arid plants Cylindropuntia imbricata, and Cryptantha flava. "For these plant species, 15 to 47 years of data was available. And even though they are all perennials, they come from very different habitats with clearly marked seasons," Sanne Evers explains.
Climate stress may become visible only years later
The results were clear: In many cases, it can take several years for plants to respond to climate. "Plant responses to climate drivers that are lagged and/or outside of the growing season are the rule rather than the exception," says co-author Tiffany Knight, professor at MLU and UFZ and head of a research group at iDiv. "This could be explained by the physiological features of some plants: For instance, in alpine environments, it may take up to four years until leaves and flowers of plants such as F. speciosa reach maturity." Accordingly, the effects of an extreme climate event may only become visible in the number of leaves and flowers four years after that event influenced the formation of these structures.
While this study focuses on examining the effects of past climate on plants, there are important implications for understanding how plants will be affected by future climate change. This study highlights that plant responses to climate are more complex than was previously appreciated. We need to prioritize experiments and observations of terrestrial ecosystems in order to create robust scenarios for the plant species that are critical to human well-being.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-22
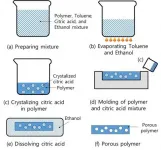
- A silicone membrane for wearable devices is more comfortable and breathable thanks to better-sized pores made with the help of citric acid crystals. -
A new preparation technique fabricates thin, silicone-based patches that rapidly wick water away from the skin. The technique could reduce the redness and itching caused by wearable biosensors that trap sweat beneath them. The technique was developed by bioengineer and professor Young-Ho Cho and his colleagues at KAIST and reported in the journal Scientific Reports last month.
"Wearable bioelectronics are becoming more attractive for the day-to-day monitoring of biological compounds ...
2021-02-22
"The lengthy groundwork is finally complete," says Jouko Rikkinen, Professor of Botany at the University of Helsinki, Finland, giving a sigh of relief.
The research article just published focuses on species diversity in the genus Leptogium, a group of jelly lichens that are common in the mountain forests of East Africa. Thousands of lichen specimens were collected from Kenya and Tanzania in 2009-2017, including nearly 600 Leptogium specimens.
DNA analyses revealed that the dataset on Leptogium included more than 70 different species, of which no more than a dozen or so are previously known. DNA analyses were necessary, as ...
2021-02-22
The course and severity of COVID-19 in individual patients is largely influenced by the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus and the human immune system. Normally, the antiviral immune response of natural killer cells (NK cells) is an important step in combating viral replication in the early phase of the infection. On their surface, these killer cells have special, activating receptors, including the NKG2C receptor, which communicates with an infected cell via one of its specialised surface structures, HLA-E. This interaction results in the destruction of virus-infected cells. However, due to a genetic ...
2021-02-22
Professor Jeremy Michalek and his Ph.D student Matthew Bruchon have published a study investigating what vehicle electrification would look like in a world where ridesourcing companies like Uber and Lyft were held responsible for the air pollution and carbon emissions created by their business.
Ridesourcing has changed the way people travel, affecting air emissions in the process. Researchers like those at the Center for Air, Climate and Energy Solutions (CACES) have quantified the negative health effects of airborne particulates created by cars in rates of cardiovascular and respiratory disease, and they're also the largest source of greenhouse gasses in the US. With public sector fleets such as the US Postal Service ...
2021-02-22
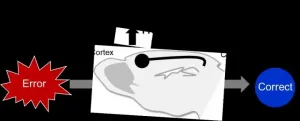
Mount Sinai researchers have identified a neural pathway through which the brain detects errors and guides subsequent behavioral improvement. This process, called cognitive control, is frequently dysregulated in a wide range of psychiatric disorders. The team's research, published February 19 in Neuron, also suggests that neurostimulation of this brain pathway could provide an important mechanism for attention adjustments following behavioral errors.
When errors are committed, such as missing a stop sign or running a red light while driving, it's important for our survival to immediately adapt behavior by paying more attention to prevent further errors. This ability to adapt behavior after erroneous actions is one of the key components of human cognitive control.
"Deficits ...
2021-02-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Converting the ground under electrical transmission towers into spaces for wildlife can enable fragmented populations to connect with one another, increasing local biodiversity and providing animals around the globe an important tool for adapting to climate change, a new study found.
"The most common way species respond to climate change is to try to shift their range - i.e., go live somewhere else," Oregon State University scientist Virginia Morandini said. "When landscapes become fragmented, usually because of human activity, it greatly hinders animals' ability to move their range. That's why it's so important for biodiversity conservation to try to get their environments connected."
For this study, Morandini ...
2021-02-22
The latest star data from the Gaia space observatory has for the first time allowed astronomers to generate a massive 3D atlas of widely separated binary stars within about 3,000 light years of Earth -- 1.3 million of them.
The one-of-a-kind atlas, created by Kareem El-Badry, an astrophysics Ph.D. student from the University of California, Berkeley, should be a boon for those who study binary stars -- which make up at least half of all sunlike stars -- and white dwarfs, exoplanets and stellar evolution, in general. Before Gaia, the last compilation of nearby binary stars, assembled using data from the now-defunct Hipparcos satellite, included about 200 ...
2021-02-22
BOSTON - Chronic inflammation drives the development of various cancers, including those of the skin, colon and pancreas. Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) who previously demonstrated high expression levels of an immune molecule called interleukin-33 (IL-33) during cancer-promoting inflammation have now uncovered the details behind the molecule's effects. The research, which is published in The EMBO Journal, could lead to new strategies to prevent certain cancers.
When epithelial cells that line the surfaces of the body are stressed or injured, they release IL-33 to alarm the immune system, leading to a robust inflammatory response. In addition to being secreted from cells, IL-33 also acts within a cell's nucleus, where ...
2021-02-22
DALLAS, Feb. 22, 2021 -- Exposure to what is considered low levels of air pollution over a long period of time can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, atrial fibrillation and pneumonia among people ages 65 and older, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation.
Air pollution can cause harm to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems due to its effect on inflammation in the heart and throughout the body. Newer studies on the impact of air pollution on health are focused on ...
2021-02-22
DALLAS, Feb. 22, 2021 -- Twelve weeks of exercise training improved artery health and function in middle-aged and older men (ages 50-70 years) with low-to-normal testosterone levels, while testosterone therapy provided no benefits to the arteries, according to new research published today in Hypertension, an American Heart Association journal.
The natural aging process for men includes decreased testosterone and physical activity levels decline with age, leading to declines in artery health and function. Testosterone replacement therapy is often used to combat the symptoms of decreasing testosterone levels, including low energy, reduced muscle mass and reduced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Plant responses to climate are lagged
Climate drivers outside of the growing season may have stronger effects on plants than previously assumed.