Big Data to model the evolution of the cosmic web
2021-02-22
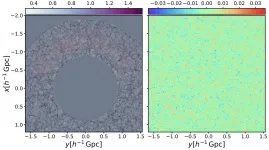
(Press-News.org) The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has led an international team which has developed an algorithm called COSMIC BIRTH to analyse large scale cosmic structures. This new computation method will permit the analysis of the evolution of the structure of dark matter from the early universe until the formation of present day galaxies. This work was recently published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
The IAC researcher, a co-author of the article and leader of the group of Cosmology and Large Scale Structure (LSS) Francisco-Shu Kitaura explains that one of the key aspects of this algorithm "consists in expressing the observations as if they had been detected in the early universe, which simplifies many of the calculations".
"Our algorithm uses sampling techniques designed to deal with high dimensional spaces, and is the product of more than four years of development. That is why I thank the funding programmes Ramon y Cajal and Excelencia Severo Ochoa which have allowed us to make scientific journeys which are such a challenge and a risk", he adds.
"It is fascinating to use the methods of classical mechanics to reconstruct the large scale structure of huge cosmic volumes", says Mónica Hernández Sánchez, a doctoral student at the IAC and the University of La Laguna (ULL), and first author of another linked article, who has shown that an idea of the particle physicists from 30 years ago has proved useful in the present context.
"It has been exciting to explore, using Big Data techniques, the structures which include the formation of galaxy clusters emerging at "cosmic noon". That is the moment when the Universe lit up the galaxies with stars", notes Metin Ata, a researcher at the Kavli Institute for Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (IPMU), in Japan, and leader of the application of the COSMIC BIRTH algorithm to the combination of five studies of distant clusters in the COSMOS (Cosmic Evolution Survey) fields.
The authors have dedicated this last work to the French astrophysicist Olivier Le Fèver, who participated in the study and who unfortunately died while it was being completed.
INFORMATION:
Main article: Kitaura et al. "COSMIC BIRTH: Efficient Bayesian Inference of the Evolving Cosmic Web from Galaxy Surveys, MNRAS, 2021. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020MNRAS.tmp.3630K/abstract
- Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.00284.pdf
Related articles:
1) Hernández-Sánchez, Kitaura et al 2021:
https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021MNRAS.tmp..185H/abstract
2) Ata, Kitaura et al 2021:
https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021MNRAS.500.3194A/abstract
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-22
Moralities of Intelligent Machines is a project that investigates people's attitudes towards moral choices made by artificial intelligence. In the latest study completed under the project, study participants read short narratives where either a robot, a somewhat humanoid robot known as iRobot, a robot with a strong humanoid appearance called iClooney or a human being encounters a moral problem along the lines of the trolley dilemma, making a specific decision. The participants were also shown images of these agents, after which they assessed the morality of their decisions. The study was funded by the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation and the Academy of Finland.
The trolley dilemma is a problem ...
2021-02-22
Electric current is deflected by a magnetic field - in conducting materials this leads to the so-called Hall effect. This effect is often used to measure magnetic fields. A surprising discovery has now been made at TU Wien, in collaboration with scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute (Switzerland), McMater University (Canada), and Rice University (USA): an exotic metal made of cerium, bismuth and palladium was examined and a giant Hall effect was found to be produced by the material, in the total absence of any magnetic field. The reason for this unexpected result lies in the unusual properties of the electrons: They behave as if magnetic ...
2021-02-22
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized endocrine gland composed of two structurally and functionally separate parts known as anterior and posterior lobes. The pituitary gland's anterior lobe secretes six hormones essential to growth, reproduction, and other basic physiological functions. Abnormal development of the pituitary gland, or hypopituitarism, can cause mild or complete deficiency of one or more pituitary hormones, which manifests as highly varying symptoms. Tumours mainly cause hypopituitarism in humans, but a congenital factor can also be associated with the disorder.
The POU1F1 gene regulates the development of the ...
2021-02-22
In Sweden, approximately one in five adults suffers from dental anxiety or phobia. The number has decreased over time, but still an important part of the population have major problems, according to a recent doctoral thesis from the University of Gothenburg.
The thesis includes a nationwide interview study involving 3,500 adult individuals, randomly selected from the general population of Sweden. Nineteen percent of the participants reported some degree of dental anxiety, fear or phobia.
The results showed that 4.7% of the respondents described their dental anxiety as severe, 4.5% as moderate and 9.8% as low. The remaining 80.9% reported no dental anxiety. The proportion with no dental ...
2021-02-22
Scientists of the P. N. Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (LPI RAS), the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) and the Institute for Nuclear Research of RAS (INR RAS) studied the arrival directions of astrophysical neutrinos with energies more than a trillion electronvolts (TeV) and came to an unexpected conclusion: all of them are born near black holes in the centers of distant active galaxies powerful radio sources. Previously, only neutrinos with the highest energies were assumed to be obtained in sources of this class.
It is believed that there are massive black holes in the centers ...
2021-02-22
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is a type of breast cancer that begins in the milk-producing glands (lobules) of the breast. It covers 10-15% of all breast cancer cases, has a high risk of late recurrence, unique metastatic sites, high sensitivity to hormones, unpredictable responses to therapies, unique histopathology, distinctive biology, and resists chemotherapy. More than 90% of ILC tumors also contain estrogen receptors, meaning that they can receive hormone signals from the body e.g. estradiol, that can spur their growth and metastasis.
Despite all this, ILC is relatively understudied compared to other breast cancers, and as a result, there have been very few models developed to study it. The reason is ...
2021-02-22
Water is an essential element for all living things. Understanding the dynamics of water in trees is crucial for understanding the consequences of climate change and altered water availability for forest ecosystems. This study, which is a product of a joint research project with Samuli Junttila PhD, and Professor Masato Katoh of Shinshu University's Institute for Mountain Science and others demonstrates a new laser scanning based method that can be used to monitor changes in leaf water content of tree communities.
Lasers can be used to measure and monitor the leaf water content of trees and plants, because the reflection of laser light at the shortwave infrared region is changed due to varying leaf water ...
2021-02-22
Two in five of the world's plant species are at risk of extinction. In the face of climate change, understanding why certain plant species are vulnerable to extinction while others prevail is more urgent than ever before. Previous studies linking climate and plant vital rates have found relatively modest effects, sometimes leading to the conclusion that other threats, such as land use change, may still be more important than climate drivers. However, these conclusions could result from wrong assumptions about which times of the year (which "time window") climate ...
2021-02-22
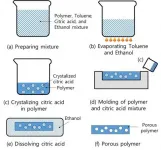
- A silicone membrane for wearable devices is more comfortable and breathable thanks to better-sized pores made with the help of citric acid crystals. -
A new preparation technique fabricates thin, silicone-based patches that rapidly wick water away from the skin. The technique could reduce the redness and itching caused by wearable biosensors that trap sweat beneath them. The technique was developed by bioengineer and professor Young-Ho Cho and his colleagues at KAIST and reported in the journal Scientific Reports last month.
"Wearable bioelectronics are becoming more attractive for the day-to-day monitoring of biological compounds ...
2021-02-22
"The lengthy groundwork is finally complete," says Jouko Rikkinen, Professor of Botany at the University of Helsinki, Finland, giving a sigh of relief.
The research article just published focuses on species diversity in the genus Leptogium, a group of jelly lichens that are common in the mountain forests of East Africa. Thousands of lichen specimens were collected from Kenya and Tanzania in 2009-2017, including nearly 600 Leptogium specimens.
DNA analyses revealed that the dataset on Leptogium included more than 70 different species, of which no more than a dozen or so are previously known. DNA analyses were necessary, as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Big Data to model the evolution of the cosmic web