(Press-News.org) Loneliness is a risk factor associated with adolescents being drawn into compulsive internet use. The risk of compulsive use has grown in the coronavirus pandemic: loneliness has become increasingly prevalent among adolescents, who spend longer and longer periods of time online.
A study investigating detrimental internet use by adolescents involved a total of 1,750 Finnish study subjects, who were studied at three points in time: at 16, 17 and 18 years of age. The results have been published in the Child Development journal.
Adolescents' net use is a two-edged sword: while the consequences of moderate use are positive, the effects of compulsive use can be detrimental. Compulsive use denotes, among other things, gaming addiction or the constant monitoring of likes on social media and comparisons to others.
"In the coronavirus period, loneliness has increased markedly among adolescents. They look for a sense of belonging from the internet. Lonely adolescents head to the internet and are at risk of becoming addicted. Internet addiction can further aggravate their malaise, such as depression," says Professor of Education and study lead Katariina Salmela-Aro from the University of Helsinki.
Highest risk for 16-year-old boys
The risk of being drawn into problematic internet use was at its highest among 16-year-old adolescents, with the phenomenon being more common among boys.
For some, the problem persists into adulthood, but for others it eases up as they grow older. The reduction of problematic internet use is often associated with adolescent development where their self-regulation and control improve, their brains adapt and assignments related to education direct their attention.
"It's comforting to know that problematic internet use is adaptive and often changes in late adolescence and during the transition to adulthood. Consequently, attention should be paid to the matter both in school and at home. Addressing loneliness too serves as a significant channel for preventing excessive internet use," Salmela-Aro notes.
It was found in the study that the household climate and parenting also matter: the children of distant parents have a higher risk of drifting into detrimental internet use. If parents are not very interested in the lives of their adolescents, the latter may have difficulty drawing the lines for their actions.
Problematic net use and depression form a cycle
In the study participants, compulsive internet use had a link to depression. Depression predicted problematic internet use, while problematic use further increased depressive symptoms.
Additionally, problematic use was predictive of poorer academic success, which may be associated with the fact that internet use consumes a great deal of time and can disrupt adolescents' sleep rhythm and recovery, consequently eating up the time available for academic effort and performance.
INFORMATION:
Information about the publication:
Toth-Kiraly, Istvan, Morin, Alex, Hietajärvi, Lauri & Salmela-Aro, Katariina (2021). Longitudinal trajectories, social antecedents, and outcomes of problematic internet use among late adolescents. Child Development, Early View
https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13525
The University of Helsinki researchers conducted the study in cooperation with researchers from Concordia University, Canada.
The study was supported by the Academy of Finland, Horizon 2020 (ySKILLS), Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada and Concordia University.
Contact information:
Professor Katariina Salmela-Aro,
University of Helsinki,
katariina.salmela-aro@helsinki.fi,
phone +358 504155283
Strategies based on the use of gene therapy to mitigate the effects of mutations that cause blindness are undergoing rapid development. Novel gene vectors now achieve widespread gene delivery and reduce the risks associated with these approaches.
The incidence of genetic mutations that result in rapid deterioration of the ability to see is larger than is generally supposed. For example, on the order of five million people around the world suffer from congenital retinal dystrophies, which often lead to blindness at an early age. These diseases are caused by defects in specific genes, which direct the production of proteins that play an essential role ...
WASHINGTON (Feb. 22, 2021) --- People living with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who have a history of severe immunosuppression and at least one copy of the Alzheimer's disease-related gene variant APOE4, might see a compounded adverse effect on the circuitry that impacts memory. This could eventually lead to an increased risk for dementia after age 65, according to Georgetown University Medical Center investigators and colleagues.
The researchers used MRI scans to examine the brain, with a focus on two regions - the hippocampus, which is critical for memory and is often affected in Alzheimer's disease, and the caudate ...
Cancer cells acquire growth advantages over normal cells in myriad ways. Changes in cell programming allow these cells to grow in an uncontrolled fashion, thereby forming the cancer mass. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), being highly malignant and invasive with a high recurrence rate and drug resistant phenotype, is one of the most dreadful cancers. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms is crucial to design therapeutic interventions and to predict patient prognosis.
Cancer cells use metabolic, immunogenic, or growth-related strategies, which can be controlled by a number of alterations in the cell process. Of these, "post-transcriptional RNA modification" has recently sparked interest among cancer biologists. ...
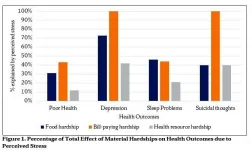
Syracuse, N.Y. - As the United States approaches the one-year anniversary of the start of COVID-19 lockdowns, a new study by researchers from Syracuse University and the University of Texas at San Antonio shows that material hardship - difficulty paying for food, bills and healthcare - is taking a toll on the mental and physical health of young adults.
In the study, " END ...
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine has become a new norm for many routine and non-emergency medical needs. But there are lessons to be learned from telemedicine's use - or lack thereof - prior to the pandemic, and a new study from a UConn School of Social Work researcher offers insight for policymakers, administrators, and public health officials when considering the implementation of new services.
A qualitative researcher, lead author and licensed clinical social worker Kelsi Carolan was brought into the study - which was conducted in 2017 and 2018 and was recently published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research - to examine the adoption of a telemedicine program in a California independent senior ...
A recent study of homeless preschoolers found a strong correlation between the bonds those children formed with teachers and the children's risk of behavioral and emotional problems.
"It's well established that children who are homeless are at higher risk of a wide variety of negative outcomes," says Mary Haskett, corresponding author of the study and a professor of psychology at North Carolina State University. "However, there's a lot of variability within this group. We wanted to learn more about what makes some of these children more resilient than others."
For ...
The systemic balance that coordinates the growth of an organism and its progress through the different stages of development occurs across the animal world and is regulated by internal and external signals. Examples of this balance are puberty in humans and metamorphosis in flies. These are transitions characterised by the production of steroid hormones and they mark the turning point that will determine the halting of growth and entry into the adult state. Certain human diseases, such as cancer and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), cause a delay in this transition.
Led by Dr. Marco Milán, scientists at IRB Barcelona ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A new study illuminates how a gene called HAND2 may have a hand in the timing of human labor.
"We don't know why humans go into labor. It's a basic aspect of human biology that we just don't know the answer to, and it's kind of embarrassing that we don't," says senior author Vincent Lynch, an evolutionary biologist at the University at Buffalo. "What happens in many other animals is that as gestation goes on, the level of progesterone keeps going up, and then a few hours before birth, progesterone levels drop to pre-pregnancy levels. Progesterone inhibits contractions, so once you lose it, the uterus starts contracting and the baby is born.
"But in ...
The reintroduction of 32 bobcats to an island off the coast of Georgia more than three decades ago created an ideal experiment to examine the accuracy of a genetic-modeling technique that predicts extinction of isolated wildlife populations.
That's the conclusion of Penn State researchers who continue to monitor the bobcat population on Cumberland Island National Seashore, and who conducted a study comparing and contrasting the Cumberland Island bobcats to a population of bobcats on Kiawah Island off the coast of South Carolina.
The research was led by Cassandra Miller-Butterworth, associate professor of biology at Penn State Beaver, and Duane Diefenbach, Penn State adjunct professor of wildlife ecology who, as a doctoral ...
Like its chemical relative carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide (N2O) is an important greenhouse gas and the dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st Century. Consequently, strategies for limiting its emissions and its catalytic decomposition with metals are being developed. A recent study indicates that nitrous oxide can bind to metals similarly to carbon dioxide, which helps to design new complexes with even stronger bonding. This could allow the use of nitrous oxide in synthetic chemistry or help to degrade it to substances harmless to the atmosphere. The results were reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition as a Very Important Paper on February 17th 2021.
A comprehensive analysis of the global N2O budget has ...