(Press-News.org) When you slip into sleep, it's easy to imagine that your brain shuts down, but University of Michigan research suggests that groups of neurons activated during prior learning keep humming, tattooing memories into your brain.
U-M researchers have been studying how memories associated with a specific sensory event are formed and stored in mice. In a study conducted prior to the coronavirus pandemic and recently published in Nature Communications, the researchers examined how a fearful memory formed in relation to a specific visual stimulus.
They found that not only did the neurons activated by the visual stimulus keep more active during subsequent sleep, sleep is vital to their ability to connect the fear memory to the sensory event.
Previous research has shown that regions of the brain that are highly active during intensive learning tend to show more activity during subsequent sleep. But what was unclear was whether this "reactivation" of memories during sleep needs to occur in order to fully store the memory of newly learned material.
"Part of what we wanted to understand was whether there is communication between parts of the brain that are mediating the fear memory and the specific neurons mediating the sensory memory that the fear is being tied to. How do they talk together, and must they do so during sleep? We would really like to know what's facilitating that process of making a new association, like a particular set of neurons, or a particular stage of sleep," said Sara Aton, senior author of the study and a professor in the U-M Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology. "But for the longest time, there was really no way to test this experimentally."
Now, researchers have the tools to genetically tag cells that are activated by an experience during a specific window of time. Focusing on a specific set of neurons in the primary visual cortex, Aton and the study's lead author, graduate student Brittany Clawson, created a visual memory test. They showed a group of mice a neutral image, and expressed genes in the visual cortex neurons activated by the image.
To verify that these neurons registered the neutral image, Aton and her team tested whether they could instigate the memory of the image stimulus by selectively activating the neurons without showing them the image. When they activated the neurons and paired that activation with a mild foot shock, they found that their subjects would subsequently be afraid of visual stimuli that looked similar to the image those cells encode. They found the reverse also to be true: after pairing the visual stimulus with a foot shock, their subjects would subsequently respond with fear to reactivating the neurons.
"Basically, the precept of the visual stimulus and the precept of this completely artificial activation of the neurons generated the same response," Aton said.
The researchers found that when they disrupted sleep after they showed the subjects an image and had given them a mild foot shock, there was no fear associated with the visual stimulus. Those with unmanipulated sleep learned to fear the specific visual stimulus that had been paired with the foot shock.
"We found that these mice actually became afraid of every visual stimulus we showed them," Aton said. "From the time they go to the chamber where the visual stimuli are presented, they seem to know there's a reason to feel fear, but they don't know what specifically they're afraid of."
This likely shows that, in order for them to make an accurate fear association with a visual stimulus, they have to have sleep-associated reactivation of the neurons encoding that stimulus in the sensory cortex, according to Aton. This allows a memory specific to that visual cue to be generated.The researchers think that at the same time, that sensory cortical area must communicate with other brain structures, to marry the sensory aspect of the memory to the emotional aspect.
Aton says their findings could have implications for how anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder are understood.
"To me this is kind of a clue that says, if you're linking fear to some very specific event during sleep, sleep disruption may affect this process. In the absence of sleep, the brain seems to manage processing the fact that you are afraid, but you may be unable to link that to what specifically you should be afraid of," Aton said. "That specification process may be one that goes awry with PTSD or generalized anxiety."
INFORMATION:
Sara Aton
Study: "Causal role for sleep-dependent reactivation of learning-activated sensory ensembles for fear memory consolidation"
SAN ANTONIO -- Feb. 22, 2021 -- From aboard the Juno spacecraft, a Southwest Research Institute-led instrument observing auroras serendipitously spotted a bright flash above Jupiter's clouds last spring. The Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) team studied the data and determined that they had captured a bolide, an extremely bright meteoroid explosion in the gas giant's upper atmosphere.
"Jupiter undergoes a huge number of impacts per year, much more than the Earth, so impacts themselves are not rare," said SwRI's Dr. Rohini Giles, lead author of a paper outlining these findings in Geophysical Research Letters. "However, they are so short-lived that it is relatively unusual to see them. Only larger impacts can be seen from Earth, and you have to be lucky to be pointing ...
Astronomers have long been looking into the vast universe in hopes of discovering alien civilisations. But for a planet to have life, liquid water must be present. The chances of that finding scenario have seemed impossible to calculate because it has been the assumption that planets like Earth get their water by chance if a large, ice asteroid hits the planet.
Now, researchers from the GLOBE Institute at the University of Copenhagen have published an eye-opening study, indicating that water may be present during the very formation of a planet. According to the study's calculations, this is true for both Earth, Venus and Mars.
'All our data suggest that water was part of Earth's building blocks, right from the beginning. And because the water ...
New research by Swansea scientists in collaboration with scientists at the University of Bristol and the Francis Crick institute in London has indicated that consuming a diet high in the sugar fructose might prevent the proper functioning of peoples' immune systems in ways that has, until now, largely been unknown.
Fructose is commonly found in sugary drinks, sweets and processed foods and is used widely in food production. It is associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its intake has increased substantially throughout the developed world in recent years. However, understanding ...
Loneliness is a risk factor associated with adolescents being drawn into compulsive internet use. The risk of compulsive use has grown in the coronavirus pandemic: loneliness has become increasingly prevalent among adolescents, who spend longer and longer periods of time online.
A study investigating detrimental internet use by adolescents involved a total of 1,750 Finnish study subjects, who were studied at three points in time: at 16, 17 and 18 years of age. The results have been published in the Child Development journal.
Adolescents' net use is a two-edged sword: while the consequences of moderate use are positive, the effects of compulsive use can be detrimental. Compulsive ...
Strategies based on the use of gene therapy to mitigate the effects of mutations that cause blindness are undergoing rapid development. Novel gene vectors now achieve widespread gene delivery and reduce the risks associated with these approaches.
The incidence of genetic mutations that result in rapid deterioration of the ability to see is larger than is generally supposed. For example, on the order of five million people around the world suffer from congenital retinal dystrophies, which often lead to blindness at an early age. These diseases are caused by defects in specific genes, which direct the production of proteins that play an essential role ...
WASHINGTON (Feb. 22, 2021) --- People living with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who have a history of severe immunosuppression and at least one copy of the Alzheimer's disease-related gene variant APOE4, might see a compounded adverse effect on the circuitry that impacts memory. This could eventually lead to an increased risk for dementia after age 65, according to Georgetown University Medical Center investigators and colleagues.
The researchers used MRI scans to examine the brain, with a focus on two regions - the hippocampus, which is critical for memory and is often affected in Alzheimer's disease, and the caudate ...
Cancer cells acquire growth advantages over normal cells in myriad ways. Changes in cell programming allow these cells to grow in an uncontrolled fashion, thereby forming the cancer mass. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), being highly malignant and invasive with a high recurrence rate and drug resistant phenotype, is one of the most dreadful cancers. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms is crucial to design therapeutic interventions and to predict patient prognosis.
Cancer cells use metabolic, immunogenic, or growth-related strategies, which can be controlled by a number of alterations in the cell process. Of these, "post-transcriptional RNA modification" has recently sparked interest among cancer biologists. ...
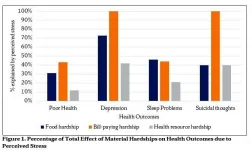
Syracuse, N.Y. - As the United States approaches the one-year anniversary of the start of COVID-19 lockdowns, a new study by researchers from Syracuse University and the University of Texas at San Antonio shows that material hardship - difficulty paying for food, bills and healthcare - is taking a toll on the mental and physical health of young adults.
In the study, " END ...
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine has become a new norm for many routine and non-emergency medical needs. But there are lessons to be learned from telemedicine's use - or lack thereof - prior to the pandemic, and a new study from a UConn School of Social Work researcher offers insight for policymakers, administrators, and public health officials when considering the implementation of new services.
A qualitative researcher, lead author and licensed clinical social worker Kelsi Carolan was brought into the study - which was conducted in 2017 and 2018 and was recently published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research - to examine the adoption of a telemedicine program in a California independent senior ...
A recent study of homeless preschoolers found a strong correlation between the bonds those children formed with teachers and the children's risk of behavioral and emotional problems.
"It's well established that children who are homeless are at higher risk of a wide variety of negative outcomes," says Mary Haskett, corresponding author of the study and a professor of psychology at North Carolina State University. "However, there's a lot of variability within this group. We wanted to learn more about what makes some of these children more resilient than others."
For ...