INFORMATION:
The research group has constructed a valuable neuroimaging database of more than 60 individuals who underwent Decoded Neurofeedback training. This database consists of structural images of the brain, functional images of the brain, machine learning decoders, and additional processed data. Anyone who wants to use the dataset must apply through the ATR institutional repository [1] or Synapse [2], an online repository of neuroscientific data. The details on how to access the dataset are specified in the original publication as well as on the ATR and Synapse websites.
[1] ATR institutional repository
[2] Synapse
Cortese A, Tanaka SC, Amano K, Koizumi A, Lau H, Sasaki Y, Shibata K, Taschereau-Dumouchel V, Watanabe T, Kawato M. " The DecNef collection, fMRI data from closed-loop decoded neurofeedback experiments " Scientific Data.
The original five studies included in the dataset are listed below:
Study 1: Shibata K, Watanabe T, Kawato M, Sasaki Y (2016) Differential activation patterns in the same brain region led to opposite emotional states: PLoS Biol. 14(9): e1002546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002546.
Study 2: Amano K, Shibata K, Kawato M, Sasaki Y, Watanabe T (2016) Learning to associate orientation with color in early visual areas by associative decoded fMRI neurofeedback. Curr Biol. 26(14):1861-1866. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.05.014.
Study 3: Koizumi A, Amano K, Cortese A, Shibata K, Yoshida W, Seymour B, Kawato M, Lau H (2016) Fear reduction without fear through reinforcement of neural activity that bypasses conscious exposure. Nat Hum Behav. 1:0006. doi: 10.1038/s41562-016-0006.
Study 4: Cortese A, Amano K, Koizumi A, Kawato M, Lau H (2016) Multivoxel neurofeedback selectively modulates confidence without changing perceptual performance. Nat Commun. 7:13669. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13669.
Study 5: Taschereau-Dumouchel V, Cortese A, Chiba T, Knotts JD, Kawato M, Lau H (2018) Towards an unconscious neural reinforcement intervention for common fears. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115(13):3470-3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721572115.
Nonconscious brain modulation to remove fears, increase confidence
Researchers release large dataset on machine learning-based brain training
2021-02-23
(Press-News.org) In recent years, researchers have discovered ways to remove specific fears from the brain, increase one's own confidence, or even change people's preferences, by using a combination of artificial intelligence and brain scanning technology. Their technique could lead to new treatments for patients with conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), phobias or anxiety disorders.
But while this technique is extremely promising, in some individuals it remains unsuccessful. Why are there such differences in outcome? Better understanding how the brain can self-regulate its own activity patterns would go a long way toward establishing the technique for clinical use. The researchers who spearheaded this technique have thus released a unique dataset (which includes five different studies) to the community, in a bid to accelerate the translation from basic science to application.
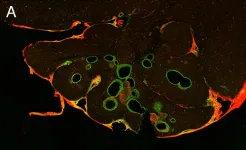
The technique is called 'Decoded Neurofeedback', and is based on a method to read and identify specific information in the brain - for example, a fear memory. Dr. Mitsuo Kawato, Director of the Computational Neuroscience Laboratories at the ATR Institute International in Japan, and senior author on the paper and who pioneered the technique a decade ago, explained: "In Decoded Neurofeedback experiments, brain scanning is used to monitor activity in the brain, and identify complex patterns of activity that resemble a specific memory or mental state. When the pattern is detected, we give our experimental participants a small reward. The simple action of repeatedly providing a reward every time the pattern is detected modifies the original memory or mental state. Importantly, participants do not need to be aware of the patterns' content for this to work."
Dr. Aurelio Cortese, senior researcher at ATR Institute International and lead author of the paper, explained the vision for releasing the data: "The Decoded Neurofeedback approach could have major benefits for clinical populations over traditional treatments. Patients could avoid the stress associated with exposure therapies, or side-effects resulting from established drugs. As such, it is crucial we accelerate the development of the Decoded Neurofeedback technique - and this will only be possible if more scientists will be able to work on the actual data."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Beta blockers can repair malformed blood vessels in the brain
2021-02-23
Peer review/Experimental study/Animals
Propranolol, a drug that is efficacious against infantile haemangiomas ("strawberry naevi", resembling birthmarks), can also be used to treat cerebral cavernous malformations, a condition characterised by misshapen blood vessels in the brain and elsewhere. This has been shown by researchers at Uppsala University in a new study published in the scientific journal Stroke.
"Up to now, there's been no drug treatment for these patients, so our results may become hugely important for them," says Peetra Magnusson of the University's Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, who headed the study.
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs, also called cavernous angiomas or cavernomas) are vascular lesions ...
Pregnancy, stress, sleep issues, physiology among women's unique cardiovascular concerns
2021-02-23
DALLAS, Feb. 23, 2021 — Women face many female-specific risks for heart disease and stroke, including pregnancy, physical and emotional stress, sleep patterns and many physiological factors, according to multiple studies highlighted in this year’s Go Red for Women® special issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association, published online today.
“Although cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in men and women, women are less likely to be diagnosed and receive preventive care and aggressive treatment compared to men,” said Journal of the American Heart Association Editor-in-Chief Barry London, M.D., Ph.D., Ph.D., the Potter Lambert Chair in Internal Medicine, director of the division ...
Basic cell health systems wear down in Huntington's disease, novel analysis shows
2021-02-23
Using an innovative computational approach to analyze vast brain cell gene expression datasets, researchers at MIT and Sorbonne Université have found that Huntington's disease may progress to advanced stages more because of a degradation of the cells' health maintenance systems than because of increased damage from the disease pathology itself.
The analysis yielded a trove of specific gene networks governing molecular pathways that disease researchers may now be able to target to better sustain brain cell health amid the devastating neurodegenerative ...
Climate-friendly foam building insulation may do more harm than good
2021-02-23
The use of the polymeric flame retardant PolyFR in "eco-friendly" foam plastic building insulation may be harmful to human health and the environment, according to a new commentary in Environmental Science & Technology. The authors' analysis identifies several points during the lifecycle of foam insulation that may expose workers, communities, and ecosystems to PolyFR and its potentially toxic breakdown products.
With the climate crisis fueling demand for energy-efficient insulation, the production of PolyFR is increasing rapidly. That's because this flame retardant is added to all foam plastic building insulation in North America to comply with flammability codes, replacing the flame retardant ...
Researchers reveal genetic predisposition to severe COVID-19
2021-02-23
HSE University researchers have become the first in the world to discover genetic predisposition to severe COVID-19. The results of the study were published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
T-cell immunity is one of the key mechanisms used by the human body to fight virus infections. The staging ground for cell immunity development is the presentation of virus peptides on the surface of infected cells. This is followed by activation of T lymphocytes, which start to kill the infected cells.
The ability to successfully present virus peptides is largely determined by genetics. In human cells, human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) molecules are responsible for this presentation. The set of six such molecules is unique in every ...
Novice drivers talking on hand-held smartphones are more likely to run red-lights
2021-02-23
Young novice drivers who speak into hand-held smartphones while driving are also likely to drive while under the influence of drink or drugs, according to researchers at Lero, the Science Foundation Ireland Research Centre for Software.
The study "Smartphone Use While Driving: An Investigation of Young Novice Driver (YND) Behaviour," also found that speaking on a hand-held phone is strongly correlated with high-risk driving behaviours such as overtaking on the inside of the car ahead, speeding, driving without a valid licence and driving while intoxicated.
Lero researchers, surveyed 700 German Young Novice Drivers ...
COVID-19 infection in pregnancy not linked with still birth or baby death
2021-02-23
COVID-19 infection in pregnancy is not associated with stillbirth or early neonatal death, according to a new study.
However the research, from over 4000 pregnant women with suspected or confirmed COVID-19, also found women who had a positive test were more likely to have a premature birth.
The research, led by scientists from Imperial College London and published in the journal Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, used data from the UK and the USA.
The study team looked at data from 4004 pregnant women who had suspected or confirmed COVID-19. Of these women, ...
Environmental policies not always bad for business, study finds
2021-02-23
ITHACA, N.Y. - Critics claim environmental regulations hurt productivity and profits, but the reality is more nuanced, according to an analysis of environmental policies in China by a pair of Cornell economists.
The analysis found that, contrary to conventional wisdom, market-based or incentive-based policies may actually benefit regulated firms in the traditional and "green" energy sectors, by spurring innovation and improvements in production processes. Policies that mandate environmental standards and technologies, on the other hand, may broadly harm output and profits.
"The conventional wisdom is not entirely ...
Polymer film protects from electromagnetic radiation, signal interference
2021-02-22
As electronic devices saturate all corners of public and personal life, engineers are scrambling to find lightweight, mechanically stable, flexible, and easily manufactured materials that can shield humans from excessive electromagnetic radiation as well as prevent electronic devices from interfering with each other.
In a breakthrough report published in Advanced Materials--the top journal in the field-- engineers at the University of California, Riverside describe a flexible film using a quasi-one-dimensional nanomaterial filler that combines excellent electromagnetic shielding with ease of manufacture.
"These novel films are promising for high-frequency communication technologies, which require electromagnetic ...
Texas A&M-UTMB team identifies potential drug to treat SARS-CoV-2
2021-02-22
A federally approved heart medication shows significant effectiveness in interfering with SARS-CoV-2 entry into the human cell host, according to a new study by a research team from Texas A&M University and The University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB).
The medication bepridil, which goes by the trade name Vascor, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat angina, a heart condition.
The team's leaders are College of Science professor Wenshe Ray Liu, professor and holder of the Gradipore Chair in the Department of Chemistry at Texas A&M, and Chien-Te Kent Tseng, professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
[Press-News.org] Nonconscious brain modulation to remove fears, increase confidenceResearchers release large dataset on machine learning-based brain training