World's first video of a space-time crystal
Periodic pattern consisting of magnons is formed at room temperature
2021-02-24
(Press-News.org) A German-Polish research team has succeeded in creating a micrometer-sized space-time crystal consisting of magnons at room temperature. With the help of the scanning transmission X-ray microscope Maxymus at Bessy II at Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin, they were able to film the recurring periodic magnetization structure in a crystal. Published in the Physical Review Letters, the research project was a collaboration between scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart, Germany, the Adam Mickiewicz University and the Polish Academy of Sciences in Pozna? in Poland.
Order in space and a periodicity in time
A crystal is a solid whose atoms or molecules are regularly arranged in a particular structure. If one looks at the arrangement with a microscope, one discovers an atom or a molecule always at the same intervals. It is similar with space-time crystals: however, the recurring structure exists not only in space, but also in time. The smallest components are constantly in motion until, after a certain period, they arrange again into the original pattern.
In 2012, the Nobel Prize winner in physics Frank Wilczek discovered the symmetry of matter in time. He is considered the discoverer of these so-called time crystals, although as a theorist he predicted them only hypothetically. Since then, several scientists have searched for materials in which the phenomenon is observed. The fact that space-time crystals actually exist was first confirmed in 2017. However, the structures were only a few nanometers in size and formed only at very cold temperatures below minus 250 degrees Celsius. The fact that the German-Polish scientists have now succeeded in imaging relatively large space-time crystals of a few micrometers in a video at room temperature is therefore considered groundbreaking. But also because they were able to show that their space-time crystal, which consists of magnons, can interact with other magnons that encounter it.
An exceptional experiment succeeded
"We took the regularly recurring pattern of magnons in space and time, sent more magnons in, and they eventually scattered. Thus, we were able to show that the time crystal can interact with other quasiparticles. No one has yet been able to show this directly in an experiment, let alone in a video," says Nick Träger, a doctoral student at Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems who, together with Pawel Gruszecki, is first author of the publication.
In their experiment, Gruszecki and Träger placed a strip of magnetic material on a microscopic antenna through which they sent a radio-frequency current. This microwave field triggered an oscillating magnetic field, a source of energy that stimulated the magnons in the strip - the quasiparticle of a spin wave. Magnetic waves migrated into the strip from left and right, spontaneously condensing into a recurring pattern in space and time. Unlike trivial standing waves, this pattern was formed before the two converging waves could even meet and interfere. The pattern, which regularly disappears and reappears on its own, must therefore be a quantum effect.
Gisela Schütz, Director at Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems who heads the Modern Magnetic Systems Department, points out the uniqueness of the X-ray camera: "Not only can it make the wavefronts visible with very high resolution, which is 20 times better than the best light microscope. It can even do so at up to 40 billion frames per second and with extremely high sensitivity to magnetic phenomena as well."
"We were able to show that such space-time crystals are much more robust and widespread than first thought," says Pawel Gruszecki, a scientist at the Faculty of Physics of the Adam Mickiewicz University in Pozna?. "Our crystal condenses at room temperature and particles can interact with it - unlike in an isolated system. Moreover, it has reached a size that could be used to do something with this magnonic space-time crystal. This may result in many potential applications."
Joachim Gräfe, former research group leader in the Department of Modern Magnetic Systems and last author of the publication, concludes: "Classical crystals have a very broad field of applications. Now, if crystals can interact not only in space but also in time, we add another dimension of possible applications. The potential for communication, radar or imaging technology is huge."
INFORMATION:
Original publication
Nick Träger, Pawe? Gruszecki, Filip Lisiecki, Felix Groß, Johannes Förster, Markus Weigand, Hubert G?owi?ski, Piotr Ku?wik, Janusz Dubowik, Gisela Schütz, Maciej Krawczyk, and Joachim Gräfe
Real-Space Observation of Magnon Interaction with Driven Space-Time Crystals
Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 057201 - Published 3 February 2021
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-24
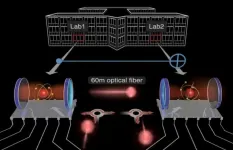
Today's quantum computers contain up to several dozen memory and processing units, the so-called qubits. Severin Daiss, Stefan Langenfeld, and colleagues from the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics in Garching have successfully interconnected two such qubits located in different labs to a distributed quantum computer by linking the qubits with a 60-meter-long optical fiber. Over such a distance they realized a quantum-logic gate - the basic building block of a quantum computer. It makes the system the worldwide first prototype of a distributed quantum computer.
The limitations of previous qubit architectures
Quantum ...
2021-02-24
A new study, published today in Nature Digital Medicine, found that 'natural language processing' (NLP) of information routinely recorded by doctors - as part of patients' electronic health records - reveal vital trends that could help clinical teams forecast and plan for surges in patients.
The researchers from King's College London, King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust (KCH), and Guy's and St Thomas' Hospital NHS Foundation Trust (GSTT), used NLP algorithms to translate the electronic notes made by doctors into a standardised, structured set of medical terms that could be analysed by a computer.
Tracking trends in patients
In the ...
2021-02-24
Social distancing - from mobility restrictions to complete lockdowns -- can take many weeks, possibly even months, a potentially devastating outcome for social and economic stability. One of the challenges is that the sick cannot be selectively isolated, since many of the spreaders remain pre-symptomatic for a period ranging from several days to as much as two weeks - invisible spreaders who continue to be socially active. Hence, it seems that without a population-wide lockdown isolating the carriers cannot be achieved effectively.
To bypass this challenge, researchers from Israel's Bar-Ilan University, led by Prof. Baruch Barzel, devised a strategy based on alternating lockdowns: first splitting the population into two groups, then ...
2021-02-24
LOGAN, UTAH -- One solution to agriculture's many challenges -- climate change-induced drought, less arable land, and decreased water quality, to name a few -- is to develop smarter fertilizers. Such fertilizers would aim not only to nourish the plant but also to maximize soil bacteria's positive effects on the plant. Tapping into a plant's microbiome may be the extra layer of defense crops need to thrive.
In their study published on Dec. 4 in Nature: Scientific Reports, researchers at Utah State University analyzed the effects of two abiotic stressors on Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 (PcO6), a health-promoting bacterium native ...
2021-02-24
URBANA, Ill. ¬- In today's global economy, production of goods depends on inputs from many trade partners around the world. Companies and governments need a deeper understanding of the global value chain to reduce costs, maintain a profitable production system, and anticipate ripple effects of disruptions in the supply chain.
Applied economists from the University of Illinois have developed a new model for in-depth analysis of global supply chain linkages across countries and industries, providing a rich tool that delivers valuable insights for businesses and policy makers around the world.
"We live in a time when production processes are very much fragmented. In order to end up with one type of ...
2021-02-24
Researchers have developed a method to estimate the value of oyster and clam aquaculture to nitrogen reduction in a coastal community. Nitrogen is a nutrient that comes from many different sources, including agriculture, fertilizers, septic systems, and treated wastewater. In excess it fuels algal growth, which can affect water quality and human health.
As a result, a growing number of communities are required to follow regulations to reduce the amount of nitrogen they release. Shellfish are an option that can be a valuable part of a community's nutrient management plan.
In a study in Environmental Science ...
2021-02-24
A UNSW Sydney-led medical research team has called for a new vaccine, improved strategies and enhanced monitoring to combat serious complications from childhood pneumonia.
The researchers examined the impact of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (13vPCV) on childhood pneumonia and empyema - complicated pneumonia - after its introduction to the Australian National Immunisation Program about a decade ago.
The new study, published in Thorax recently, found that while 13vPCV resulted in a 21 per cent decrease in childhood pneumonia hospitalisations, there was a contemporaneous 25 per cent increase in admissions for empyema.
This incidence data for childhood empyema hospitalisations is similar to that reported ...
2021-02-24
For many, 2020 was notorious for the COVID-19 pandemic, but for climate scientists, the year is also infamous for tying with 2016 as the hottest since records began. 'Nine of the warmest years on record have occurred since 2010', says JEB Editor-in-Chief, Craig Franklin. With the ice caps and glaciers melting, devastating bushfires scorching arid regions, and hurricanes and typhoons battering coastal communities, the impact on local ecosystems has been catastrophic. 'Physiologists can play a critical role in the conversation around climate change', says ...
2021-02-24
As part of the Journal of Experimental Biology's Special Issue dedicated to climate change, Anthony Pagano (San Diego Zoo Global, USA) and Terrie Williams (University of California, Santa Cruz, USA), discuss the impact of environmental change on two iconic polar species; the polar bear and narwhal. Their review article is published in Journal of Experimental Biology at https://jeb.biologists.org/content/224/Suppl_1.
Mammals in the Polar Regions face an uncertain future as unprecedented warming drives catastrophic sea ice loss, driving polar bears onto land, after losing access to sea ice and ...
2021-02-24
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder marked by joint pain, swelling and damage. Although medications, such as steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants, can help slow joint destruction and relieve pain, they have side effects and aren't completely successful. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have developed magnesium-based micromotors propelled by hydrogen bubbles, which improved rheumatoid arthritis symptoms when injected into the joints of rats.
Scientists have linked rheumatoid arthritis development to the excess production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can oxidize and degrade cartilage and bone, as well as activate the expression of inflammatory cytokines. A new type of therapy, hydrogen gas, can neutralize ROS ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] World's first video of a space-time crystal
Periodic pattern consisting of magnons is formed at room temperature