Cancer research to gain from identification of 300 proteins that regulate cell division
2021-02-24
(Press-News.org) With the hope of contributing to the fight against cancer, researchers in Sweden have published a new molecular mapping of proteins that regulate the cell division process - identifying 300 such proteins.
The release of the data, which was published today in the scientific journal, Nature, is significant because it helps bring medical research closer to the point of being able to target specific proteins to treat cancer.
Identifying and understanding what characterizes these proteins is important, says co-author Emma Lundberg, a professor at KTH Royal Institute of Technology whose research group at Science for Life Laboratory (SciLifeLab) in Stockholm contributed to the mapping of these proteins. The long-term hope is that doing so will lead to progress in development of tailor-made cancer drugs and treatments, adapted to the specific anatomical condition of the individual patient in relation to the underlying disease, Lundberg says.
In addition to the 300 newly-identified proteins, the researchers report that 20 percent of the human proteome (all protein molecules that the genome encodes for) indicates cell-to-cell variation, that is, fluctuation in gene expression within otherwise identical cells.
This information presents medical research with new insights into the cell cycle, in which a balance is moderated between those proteins which promote cell proliferation and those which inhibit it.
Lundberg says the work is now incorporated into the open-access research database, the Human Protein Atlas.
"Our hope is that this provides a valuable resource for a better understanding of, among other things: cell-to-cell variation, the human cell cycle, and the newly-identified proteins in the cell cycle and their role in the formation of tumors," she says.
In order to identify the cell cycle-specific proteins, the researchers used so-called immunofluorescent microscopy. The researchers then combined the collected data with RNA sequencing of individual cells to describe the temporal presence of RNA and proteins throughout the cell cycle.
INFORMATION:
The research work was carried out by 19 researchers from KTH, including Diana Mahdessian and Anthony Cesnik, via SciLifeLab. The Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, Uppsala University and Stanford School of Medicine also contributed. Research support was provided by the Swedish Research Council and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: National COVID-19 registry data are used in this study to describe the epidemiology, clinical characteristics, complications, and hospital and postdischarge outcomes of pediatric patients with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and to compare each in patients with severe COVID-19.
Authors: Adrienne G. Randolph, M.D., of Boston Children's Hospital, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.2091)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of ...
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: This randomized clinical trial compares the effects of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide versussplacebo for weight management as an adjunct to intensive behavioral therapy with initial low-calorie diet in adults with overweight or obesity.
Authors: Thomas A. Wadden, Ph.D., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1831)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2021-02-24
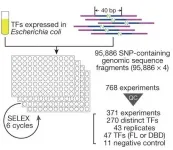
Many genetic variants have been found to have a linkage with genetic diseases, but the understanding of their functional roles in causing diseases are still limited. An international research team, including a biomedical scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU), has developed a high-throughput biological assay technique which enabled them to conduct a systematic analysis on the impact of nearly 100,000 genetic variants on the binding of transcription factors to DNA. Their findings provided valuable data for finding key biomarkers of type 2 diabetes for diagnostics and treatments. And they ...
2021-02-24
Long-term use of a medication used to treat kidney transplant patients may not be necessary in individuals with low-to-moderate risk of organ rejection, according to the results of a study led by a University of Cincinnati transplant researcher.
The randomized clinical trial of 385 patients on immunosuppressive drugs tacrolimus and mycophenolate examined whether use of these medicines called corticosteroids could be eliminated at seven days after kidney transplantation. The study shows that 15 years after transplantation no difference in kidney transplant survival or patient survival rates were found between patients who received long-term corticosteroids versus those who had corticosteroid eliminated early, explains E. Steve Woodle, MD, the William ...
2021-02-24
MEMPHIS, TN, FEBRUARY 24, 2021:- Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease has been shown to reduce cost and improve patient outcomes, but current diagnostic approaches can be invasive and costly. A recent study, published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, has found a novel way to identify a high potential for developing Alzheimer's disease before symptoms occur. Ray Romano, Ph.D., RN, completed the research as part of his Ph.D. in the Nursing Science Program at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC) College of Graduate Health Sciences. Dr. Romano conducted the research through the joint laboratory ...
2021-02-24
Plants and animals can rapidly respond to changes in their environment, such as a Venus flytrap snapping shut when a fly touches it. However, replicating similar actions in soft robots requires complex mechanics and sensors. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have printed liquid metal circuits onto a single piece of soft polymer, creating an intelligent material that curls under pressure or mechanical strain. Watch a video of the smart material here.
Ideally, soft robots could mimic intelligent and autonomous behaviors ...
2021-02-24
What The Article Says: This JAMA Insights review from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 Response team members presents data on the number of long-term care facilities and the numbers of residents and staff of those facilities who received first-dose vaccination through mid-January under the agency's public-private partnership with CVS, Walgreens and Managed Health Care Associates.
Authors: Radhika Gharpure, D.V.M., M.P.H., of the COVID-19 Response at the CDC, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
2021-02-24
Coprolites, or fossilized dog feces, are often used to understand the dietary preferences of ancient civilizations. However, the samples are often contaminated, making the analysis difficult. A new study, published in END ...
2021-02-24
PHILADELPHIA -- A second study of the injectable anti-obesity medication, semaglutide, has confirmed the large weight losses reported in a study earlier this month, establishing the reliability and robustness of this new drug. With obesity affecting more than 40 percent of American adults, the findings could have a major impact on weight management in primary care and other settings. The END ...
2021-02-24
To become climate neutral by 2050, the European Union launched two ambitious programmes: "Green Deal" and "DigitalStrategy". As a key component of their successful implementation, climate scientists and computer scientists launched the "Destination Earth" initiative, which will start in mid-?2021 and is expected to run for up to ten years. During this period, a highly accurate digital model of the Earth is to be created, a digital twin of the Earth, to map climate development and extreme events as accurately as possible in space and time.
Observational data will be continuously incorporated into the digital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cancer research to gain from identification of 300 proteins that regulate cell division