Paleontologists discover new insect group after solving 150-year-old mystery
SFU-led research team uncovers how fossil dragonfly relatives have been misclassified due to their striking similarity
2021-02-24
(Press-News.org) For more than 150 years, scientists have been incorrectly classifying a group of fossil insects as damselflies, the familiar cousins of dragonflies that flit around wetlands eating mosquitoes. While they are strikingly similar, these fossils have oddly shaped heads, which researchers have always attributed to distortion resulting from the fossilization process.
Now, however, a team of researchers led by Simon Fraser University (SFU) paleontologist Bruce Archibald has discovered they aren't damselflies at all, but represent a major new insect group closely related to them.
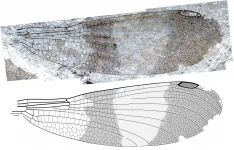
The findings, published today in Zootaxa, show that the distinctive shape of the insect's non-protruding, rounded eyes, set close to the head, are the defining features of a suborder related to damselflies and dragonflies that the researchers have named Cephalozygoptera.
"When we began finding these fossils in British Columbia and Washington State, we also thought at first they must be damselflies," says Archibald.
But on closer inspection, the team noticed they resembled a fossil that German paleontologist Hermann Hagen wrote about in 1858. Hagen set the precedent of linking the fossil to the damselfly suborder despite its different head shape, which didn't fit with damselflies at all.
Damselflies have short and wide heads with eyes distinctively protruding far to each side. Hagen's fossil, however, had an oddly rounded head and eyes. But he assumed this difference was false, caused by distortion during fossilization.
"Paleontologists since Hagen had written that these were damselflies with distorted heads," Archibald says. "A few hesitated, but still assigned them to the damselfly suborder."
The SFU-led team, including Robert Cannings of the Royal British Columbia Museum, Robert Erickson and Seth Bybee of Brigham Young University and SFU's Rolf Mathewes, sifted through 162 years of scientific papers and discovered that many similar specimens have been found since Hagen's time.
They experienced a eureka moment when they realized the odd heads of their new fossils were, in fact, their true shape.
The researchers used the fossil's defining head shape to name the new suborder Cephalozygoptera, meaning "head damselfly".
The oldest known species of Cephalozygoptera lived among dinosaurs in the Cretaceous age in China, and were last known to exist about 10 million years ago in France and Spain.
"They were important elements in food webs of wetlands in ancient British Columbia and Washington about 50 million years ago, after the extinction of the dinosaurs," says Archibald. "Why they declined and went extinct remains a mystery."
The team named 16 new species of Cephalozygoptera. Some of the fossils were found on the traditional land of the Colville Indian tribe of northern Washington, and so Archibald and his coauthors collaborated with tribal elders to name a new family of them. They called the family "Whetwhetaksidae", from the word "whetwhetaks", meaning dragonfly-like insects in the Colville people's language.
Archibald has spent 30 years combing the fossil-rich deposits of southern British Columbia and northern interior Washington. To date, in collaboration with others, he has discovered and named more than 80 new species from the area.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-24
When people hear botulinum toxin, they often think one of two things: a cosmetic that makes frown lines disappear or a deadly poison.
But the "miracle poison," as it's also known, has been approved by the F.D.A. to treat a suite of maladies like chronic migraines, uncontrolled blinking, and certain muscle spasms. And now, a team of researchers from Harvard University and the Broad Institute have, for the first time, proved they could rapidly evolve the toxin in the laboratory to target a variety of different proteins, creating a suite of bespoke, super-selective ...
2021-02-24
A Brazilian study published (http://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20217-w) in Nature Communications shows that human activities have directly or indirectly caused biodiversity and biomass losses in over 80% of the remaining Atlantic Rainforest fragments.
According to the authors, in terms of carbon storage, the biomass erosion corresponds to the destruction of 70,000 square kilometers (km²) of forest - almost 10 million soccer pitches - or USD 2.3 billion-USD 2.6 billion in carbon credits. "These figures have direct implications for mechanisms of climate change mitigation," they state in the article.
Atlantic Rainforest remnants ...
2021-02-24
DALLAS - Feb. 24, 2021 - Using machine learning tools to analyze hundreds of proteins, UT Southwestern researchers have identified a group of biomarkers in blood that could lead to an earlier diagnosis of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and, in turn, more effective therapies sooner.
The identification of nine serum proteins that strongly predict ASD were reported in a study published today by PLOS ONE.
Earlier diagnosis, followed by prompt therapeutic support and intervention, could have a significant impact on the 1 in 59 children diagnosed with autism in the United States. Being able to identify children on the autism spectrum when they are toddlers could make a big difference, says Dwight German, Ph.D., professor of psychiatry at UT Southwestern ...
2021-02-24
For decades, climate change researchers and activists have used dramatic forecasts to attempt to influence public perception of the problem and as a call to action on climate change. These forecasts have frequently been for events that might be called "apocalyptic," because they predict cataclysmic events resulting from climate change.
In a new paper published in the International Journal of Global Warming, Carnegie Mellon University's David Rode and Paul Fischbeck argue that making such forecasts can be counterproductive. "Truly apocalyptic forecasts can only ever be observed in their failure--that is the world did not end as predicted," says Rode, adjunct research faculty with the Carnegie Mellon Electricity Industry Center, "and observing ...
2021-02-24
Parenthood leads to greater reductions in short-term research productivity for mothers across three disciplines than for fathers, largely explaining the publication gender gap between women and men in academia, according to an analysis of survey data from 3,064 tenure track faculty at PhD-granting universities in the U.S. and Canada. The findings suggest that policies designed to boost workplace flexibility for parents, including easily accessible lactation rooms and affordable childcare, may help to ease the impact of parenthood on mothers in academia, giving them more time for research. While a large body of previous research across academic fields has shown that men tend to publish more papers than women, the reasons for this have remained uncertain. ...
2021-02-24
Scientists have found that comparing the ratio of two immune molecules helped predict the likelihood of transplant rejection in 339 patients who received kidney transplants, the only curative treatment for late-stage kidney failure. Their results suggest that monitoring this ratio could help distinguish high-risk patients early on, before long-term organ rejection becomes inevitable, allowing clinicians to intervene accordingly with new treatments. Kidney transplants often grant immediate benefits to patients with end-stage kidney disease, but long-term outcomes are mixed, as 35% of transplant recipients lose their new kidney within ...
2021-02-24
Cancer cells can experience stress. They have to contend with attacks by the immune system or with anti-cancer therapeutics. If they attempt to colonize other tissues, they have to break away from the extracellular matrix, enter the bloodstream and survive during the travel through the body. Then exit and start building a new colony. The ability of cells to adapt their properties to face all the challenges they encounter is called plasticity. In epithelial solid tumors, including the very common lung, breast, colon and pancreatic cancers, tumor cells plasticity hijacks a cellular development process known as epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
EMT is commonly associated to kinases - enzymes that act like a switch, turning biochemical ...
2021-02-24
Targeted radiation is often used to study and treat diverse cancer types. A multidisciplinary research team based at the University of Chicago Medicine has recently focused on a type of cell that releases a protein that enhances resistance to cancer therapies and promotes tumor progression.
The study focused on Ter cells, which are extra medullary erythroid precursers that secrete the neuropeptide artemin. In the study, published February 24, 2020, in Science Translational Medicine, the researchers showed that local tumor radiotherapy, systemic immunotherapy or the combination of both treatments were able to deplete Ter cells in the spleen, reduce artemin production and limit tumor progression both in the locally irradiated tumors as well as outside ...
2021-02-24
Researchers believe they have closed the case of what killed the dinosaurs, definitively linking their extinction with an asteroid that slammed into Earth 66 million years ago by finding a key piece of evidence: asteroid dust inside the impact crater.
Death by asteroid rather than by a series of volcanic eruptions or some other global calamity has been the leading hypothesis since the 1980s, when scientists found asteroid dust in the geologic layer that marks the extinction of the dinosaurs. This discovery painted an apocalyptic picture of dust from the vaporized asteroid and rocks from impact circling the planet, blocking ...
2021-02-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Politicization of the COVID-19 pandemic had a powerful influence over adherence to social distancing guidelines in the United States and why people did, or did not, comply during the lockdown days, a new study has found.
The analysis boiled down to whom study participants trusted most: scientists or President Donald Trump.
"People who expressed a great deal of faith in President Trump, who thought he was doing an effective job of guiding us through the pandemic, were less likely to socially distance," said Russell Fazio, senior author of the study and a professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Paleontologists discover new insect group after solving 150-year-old mystery
SFU-led research team uncovers how fossil dragonfly relatives have been misclassified due to their striking similarity