Predicts the onset of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) using deep learning-based Splice-AI
2021-02-27
(Press-News.org) Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI, President Suh Pann-ghill) announced that the research team led by Dr. Jae-Yeol Joo discovered new cryptic splice variants and SNVs in PLCg1 gene of AD-specific models for the first time using Splice-AI.
This research outcome was published in PNAS, a world-renowned academic journal.
* (Title) Prediction of Alzheimer's Disease-Specific phospholipase c gamma-1 SNV by Deep Learning-Based Approach for High-Throughput Screening
Alternative splicing variant regulates gene expression and influences diverse phenotypes. Especially, genetic variants arising due to RNA splicing are frequently found in individuals having neurodevelopmental disorders.
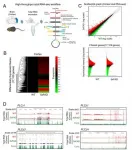
The research team revealed splicing hidden within the transcriptome to AD models via deep learning-based Splice-AI.
The novel 14 alternative splicing sites in the PLCg1 gene body, the key element of the signal transduction mechanism, were identified through deep learning.
Especially, Splice-AI analysis predicted a total of 14 splicing sites in the human PLCg1 gene, accurate delta scores, and positions were analyzed and a novel splicing site in exon 26 of human PLCg1 was identified. (exon 26 of the PLCg1 gene is 100% identical with exon 27 of the same gene in mice in terms of amino acid sequence).
* (Splicing) A form of RNA processing that regulates gene expression through the medium of genetic information
* (PLCg1, phospholipase c gamma-1) An essential protein involved in cell signal transduction and human cell growth and death
* (Exon) A part of a gene that contains protein synthesis information
Abnormal RNA processing was identified with an SNV in exon 27 of the PLCg1 gene within the brain of AD mouse models.
The research team revealed for the first time that SNV lead to changes in amino acids of proteins at exon 27. This region is very important for homeostasis because, mutated sequence is evolutionary conserved sequence through various species such as human, ape, mouse, chicken, zebrafish and so on. Moreover, AD specific nucleotide alteration sites were distributed in the histone modification region in PLCg1 gene body during the brain development.
Dr. Joo mentioned, "Emerging variants of the coronavirus have been reported in England in December 2020, and that is more transmissible than previously circulating viruses.
This variants coronavirus has mutation and altered their spike protein amino acid.
Our research will give valuable information and technique for various human diseases and through the convergence and utilization of brain research with AI technology, which is the core of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, to understand various diseases including AD, we will be able to obtain critical information for diagnosis and treatment strategy."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI) basic research program.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-26
Marine protected areas (MPAs) around O?ahu do not adequately protect populations of herbivorous reef fishes that eat algae on coral reefs. That is the primary conclusion of a study published in Coral Reefs by researchers from the University of Hawai?i at Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST).
There are over 20 species of herbivorous fishes and ten species of herbivorous urchins commonly observed on Hawaiian reefs. These species eat algae that grows on reefs, a process called herbivory, that contributes to the resilience of coral reefs by preventing algae dominance that can lead to overgrowth of corals.
The team of researchers found that of the four marine protected areas around O?ahu they assessed in the study, ...
2021-02-26
The ability to read is foundational to education, but prolonged school closures and distance learning due to the pandemic have imposed unique challenges on the teaching of many fundamental skills. When in-person classes resume, many students will likely need a period of catch-up learning, especially those who lag behind in basic reading skills.
New research published in the journal Psychological Science shows that people who were taught to read by receiving explicit instructions on the relationship between sounds and spelling experienced a dramatic improvement compared to learners who discovered this relationship naturally through the reading process. These results contribute to an ongoing debate about how best to teach children to ...
2021-02-26
New research from Baylor College of Medicine scientists shows that a combination of deep brain stimulation (DBS) and exercise has potential benefits for treating ataxia, a rare genetic neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive irreversible problems with movement.
Working with a mouse model of the human condition, researchers at Baylor and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital discovered that combining DBS targeted to the cerebellum, a major motor center in the brain, and exercise rescued limb coordination and stepping and that the benefits persisted without further stimulation. In addition, the study reports that stimulating mice with early-stage ataxia showed the most dramatic improvements. These and other ...
2021-02-26
BOSTON -- Billions of peripheral white blood cells are produced every day by the regular divisions of hematopoietic stem cells and their descendants in the bone marrow. Under normal circumstances, thousands of stem cells contribute progeny to the blood at any given time, making white blood cells a group with diverse ancestry.
Clonal hematopoiesis is a common age-related condition in which the descendants of one of these hematopoietic stem cells begin to dominate substantial portions of the blood. Genome-wide analyses have determined that clonal ...
2021-02-26
COLUMBIA, Mo. - While physical activity is important for everyone, research has shown people with developmental disabilities do not exercise as often as their typically developed peers. In an effort to close this disparity, a researcher at the University of Missouri recently created fitness picture books that help youth with autism exercise more frequently while offering low-income families a simple resource for workout motivation when outdoor fitness equipment might not be accessible.
"There is so much research geared toward helping individuals with autism improve their academic ...
2021-02-26
Treatments for beating tumours are mainly based on CD8 T lymphocytes, which specialise in detecting and eliminating intracellular infections and in killing cancer cells. A large proportion of patients, however, do not respond to these treatments. This prompted a research team from the Swiss Cancer Centre Léman (SCCL, Switzerland) to bring together the universities of Geneva (UNIGE) and Lausanne (UNIL), the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research (LICR), EPFL and CHUV to investigate CD4 T lymphocytes. While these play a supporting role with CD8 T cells, their ability to eliminate tumour cells directly has been a matter of controversy. Using innovative nanoimaging technologies designed at the EPFL laboratory, the scientists found that when the CD4 T lymphocytes ...
2021-02-26
The ocean floor is vast and varied, making up more than 70% of the Earth's surface. Scientists have long used information from sediments at the bottom of the ocean -- layers of rock and microbial muck -- to reconstruct the conditions in oceans of the past.
These reconstructions are important for understanding how and when oxygen became available in Earth's atmosphere and ultimately increased to the levels that support life as we know it today.
Yet reconstructions that rely on signals from sedimentary rocks but ignore the impact of local sedimentary processes do so at their own peril, according to geoscientists including David Fike in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis.
Their new study published Feb. ...
2021-02-26
Cells rely on membranes to protect themselves from the outside world. But these membranes can't be fully closed because nutrients and other molecules have to be able to pass through. To achieve this, cell membranes have many types of channels and pores. Also, there are receptors, antennas if you like, imbedded in the membrane that continuously monitor the outside world and signal to the cell interior. Extensive collaboration between five VIB groups resulted in a better understanding of the machinery that plants use to regulate the protein composition of their outer membrane. This discovery, published in Science Advances, enhances our basic knowledge of how the plasma membrane composition can be adapted based on external stimuli, an essential ...
2021-02-26
A team of international researchers went back to the formation of the solar system 4.6 billion years ago to gain new insights into the cosmic origin of the heaviest elements on the period-ic table.
Led by scientists who collaborate as part of the International Research Network for Nuclear Astrophysics (IReNA) (irenaweb.org) and the Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics - Center for the Evolution of the Elements (JINA-CEE) (jinaweb.org), the study is published in the lat-est issue of the journal Science (science.sciencemag.org/content/371/6532/945).
Heavy elements we encounter in our everyday life, ...
2021-02-26
HOUSTON - (Feb. 26, 2021) - Save your silver! It's better used for jewelry than as a catalyst for drugs.
Rice University scientists have developed a greatly simplified method to make fluoroketones, precursors for drug design and manufacture that typically require a silver catalyst.
Rice chemist Julian West and graduate students Yen-Chu Lu and Helen Jordan introduced a process for the rapid and scalable synthesis of fluoroketones that have until now been challenging and expensive to make.
Their open-access work graces the cover of the Feb. 21 issue of the Royal Society of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Predicts the onset of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) using deep learning-based Splice-AI