Root cause: Plant root tips are constrained to a dome shape common to arch bridges
Researchers from Osaka University, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, and Kobe University find that plant root tips are constrained to a dome shape, similar to that of an arched bridge, because of one-directional and localized tissue growth
2021-03-01
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan - Nature is full of diversity, but underneath the differences are often shared features. Researchers from Japan investigating diversity in plant features have discovered that plant root tips commonly converged to a particular shape because of physical restrictions on their growth.
In a study published in February in Development, researchers from Osaka University, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, and Kobe University have revealed that plant root tips are constrained to a dome-shaped outline because of restrictions on their tissue growth. This study is one of the papers selected as a Research Highlight published in this issue of Development that looked at how the geometric and mechanical properties of plant tissues are regulated during development, and how they contribute to growth.
In plants and animals, the outlines of organs are defined by shape and size. But despite species differences, these outlines retain a basic similarity (e.g., songbird beaks). Plant root tips are no exception, sharing a domed shape. Root tips need to be able to push through soil effectively without disintegrating, and the similarity of their shape between plant species suggests that it may be constrained by evolution.
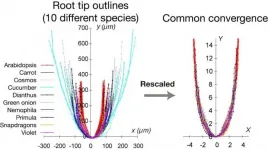
To investigate how the shape of root tips is defined, the team used morphometric (i.e., measurements of shape and form) analysis and mathematical modeling. They looked at the shape of primary and lateral root tips in Arabidopsis - small flowering plants similar to mustard and cabbage - and other flowering plant species.
"We found that the shape of the root tips in these species commonly converged to a unique curve by rescaling their size," says lead author of the study Tatsuaki Goh (Figure 1). "This curve can be described as a catenary curve - like that of arch bridges, or of a chain hanging between two points." (Figure 2)
The team also revealed with simulations that, with this shape, mechanical force is evenly spread over the surface of a root tip, and propose that this may help the tip to efficiently push through the soil. Mechanically, the formation of a curve like this in a growing structure needs a distinct boundary between a growing and non-growing region at the lateral edge of the young root, as well as spatially even, one-directional (oriented) tissue growth in the growing root tip (Figure 3).
"The very young roots of Arabidopsis show both of these characteristics, and mutant strains of these plants that disrupt either of these requirements lead to a departure from the dome shape," explains senior author Koichi Fujimoto.
Future studies could look at how localized and spatially even occurrence of one-directional tissue growth are shared constraints for the maintenance of the dome shape between different species and classes of roots and have potential applications in plant conservation and plant biotechnology.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Tissue growth constrains root organ outlines into an isometrically scalable shape," was published in Development at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.196253
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-01
Raspberry muffins are in our future.
Washington State University scientists have figured out a way to treat raspberries before they're frozen so that they maintain their structure when thawed.
The tart little berries are very delicate and freezing damages their cells. They turn to mush when baked and leak juice into the surrounding baked product, making them unattractive and diluted in flavor. As a result, frozen raspberries are rarely used in baking, whether at home or in commercial bakeries. But that's about to change.
In a recent article published in Food and Bioprocess ...
2021-03-01
Making cheese leaves a lot to chance as a batch could be ripened for months or even years before a problem is discovered, which could send a prized batch of cheddar to be sold off cheap as an ingredient for processed cheese.
It's part of why cheese is so complex and expensive to make - a factory could invest lots of time and money into what they think will be a top-graded batch, only to discover it's a flop when it's too late to fix.
But new research from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia allows quality to be checked much earlier and more precisely in the process, giving manufacturers a better chance to react to issues with the ripening process.
Dr ...
2021-03-01
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) observe underdeveloped jaw cartilage in newborn rats exposed to periods of low oxygen
Tokyo, Japan - Breathing in adequate amounts of oxygen is critical for human life. However, certain disorders can cause individuals to go through periods where they are exposed to periodical low levels of oxygen, called intermittent hypoxia (IH). This is common in people who suffer from some sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea. Although we know IH can cause neurological development issues, it is not clear how it affects cartilage. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have shown that IH can result in underdeveloped jaw cartilage in rats.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, researchers ...
2021-03-01
HIV infections are treated with antiviral drugs which effectively prevent the disease from developing. While pharmacological HIV therapy has advanced considerably, the virus cannot be entirely eliminated from the body with currently available drugs.
However, in roughly one-fifth of HIV patients the immune system does not recover as expected: the quantity of CD4 T cells, reflecting the status of the immune system, remains low even when the quantity of HI viruses in blood is suppressed to very low levels or below the measurement threshold. In such patients, indications of chronic immune activation, which erodes the immune system, can be detected.
In cooperation with the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg in Germany, researchers at the University of Helsinki have ...
2021-03-01
Wildlife tourism including white shark cage-diving is growing in popularity, but these industries remain highly contentious amongst tourists, conservationists, and scientists alike.
Many voice concerns about possible negative impacts - especially when it targets potentially dangerous animals - while proponents cite the socio-economic benefits to justify wildlife tourism activities.
In reality, wildlife tourism is complex, requiring managers to balance the benefits and drawbacks to determine what is acceptable for such industries.
To help solve this question of "is wildlife tourism good or bad?", a tool to help managers assess these industries has been created ...
2021-03-01
A painful tradeoff between a number of infected and negative economic impact must be considered before deciding on the lockdown strategy within a city. As national economies continue to crumble, citizens wonder whether their governments did a good job at regulating the lockdown measures.
Russian city of St. Petersburg is at the frontlines of this ongoing war with Covid-19. To combat this situation effectively, Russian government allocated significant funds for the research. Results followed. Scientists from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) modified the existing SIR class pandemic prediction model. Now it is better.
But why? What is the nature ...
2021-03-01
Breast cancer is the commonest fatal cancer in women. Early detection increases a woman's chances of recovery. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an accurate technique for detecting and classifying tumours in breast tissue. However, it sometimes causes "false alarms", thus requiring further investigation (biopsy) and in some cases even resulting in so-called overtreatment, that is to say unnecessary surgery. For the first time, a research team from MedUni Vienna has now confirmed a threshold value for a non-invasive imaging biomarker. This can be incorporated into short standard MRI scans ...
2021-03-01
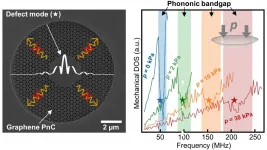
Without electronics and photonics, there would be no computers, smartphones, sensors, or information and communication technologies. In the coming years, the new field of phononics may further expand these options. That field is concerned with understanding and controlling lattice vibrations (phonons) in solids. In order to realize phononic devices, however, lattice vibrations have to be controlled as precisely as commonly realized in the case of electrons or photons.
Phononic cyrstals
The key building block for such a device is a phononic ...
2021-03-01
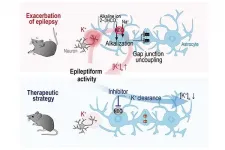
Tohoku University scientists and their colleagues in Germany have revealed that a first-time exposure to only a brief period of brain hyperactivity resulted in an acute breakdown of the inter-cellular network of glial cells. Pharmacological intervention of the glial plasticity may provide a new preventative strategy for fighting epilepsy.
The findings were detailed in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by neuronal hyper-excitation and a progression of seizures with each episode. Anti-epileptic drugs are mostly aimed at suppressing hyperactivity, ...
2021-03-01
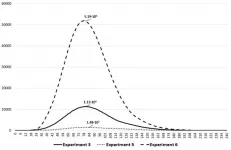
Results of a 2018 multirocket launch at Poker Flat Research Range north of Fairbanks, Alaska, will help scientists better understand the impact of more water vapor accumulating near the fringe of the Earth's atmosphere.
"This is the first time anyone has experimentally demonstrated that cloud formation in the mesosphere is directly linked to cooling by water vapor itself," said Irfan Azeem, space physicist at Astra LLC in Louisville, Colorado, and principal investigator of the Super Soaker mission.
The NASA-funded project, named Super Soaker, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Root cause: Plant root tips are constrained to a dome shape common to arch bridges
Researchers from Osaka University, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, and Kobe University find that plant root tips are constrained to a dome shape, similar to that of an arched bridge, because of one-directional and localized tissue growth