(Press-News.org) HANOVER, N.H. - March 1, 2020 - During World War II, British intelligence agents planted false documents on a corpse to fool Nazi Germany into preparing for an assault on Greece. "Operation Mincemeat" was a success, and covered the actual Allied invasion of Sicily.
The "canary trap" technique in espionage spreads multiple versions of false documents to conceal a secret. Canary traps can be used to sniff out information leaks, or as in WWII, to create distractions that hide valuable information.
WE-FORGE, a new data protection system designed at Dartmouth's Department of Computer Science, uses artificial intelligence to build on the canary trap concept. The system automatically creates false documents to protect intellectual property such as drug design and military technology.
"The system produces documents that are sufficiently similar to the original to be plausible, but sufficiently different to be incorrect," said V.S. Subrahmanian, the Distinguished Professor in Cybersecurity, Technology, and Society, and director of the Institute for Security, Technology, and Society.
Cybersecurity experts already use canary traps, "honey files," and foreign language translators to create decoys that deceive would-be attackers. WE-FORGE improves on these techniques by using natural language processing to automatically generate multiple fake files that are both believable and incorrect. The system also inserts an element of randomness to keep adversaries from easily identifying the real document.
WE-FORGE can be used to create numerous fake versions of any technical design document. When adversaries hack a system, they are faced with the daunting task of figuring out which of the many similar documents is real.
"Using this technique, we force an adversary to waste time and effort in identifying the correct document. Even if they do, they may not have confidence that they got it right," said Subrahmanian.
Creating the false technical documents is no less daunting. According to the research team, a single patent can include over 1,000 concepts with up to 20 possible replacements. WE-FORGE can end up considering millions of possibilities for all of the concepts that might need to be replaced in a single technical document.
"Malicious actors are stealing intellectual property right now and getting away with it for free," said Subrahmanian. "This system raises the cost that thieves incur when stealing government or industry secrets."
The WE-FORGE algorithm works by computing similarities between concepts in a document and then analyzing how relevant each word is to the document. The system then sorts concepts into "bins" and computes the feasible candidate for each group.
"WE-FORGE can also take input from the author of the original document," said Dongkai Chen, a graduate student at Dartmouth who worked on the project. "The combination of human and machine ingenuity can increase costs on intellectual-property thieves even more."
As part of the research, the team falsified a series of computer science and chemistry patents and asked a panel of knowledgeable subjects to decide which of the documents were real.
According to the research, published in ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems, the WE-FORGE system was able to "consistently generate highly believable fake documents for each task."
Unlike other tools, WE-FORGE specializes in falsifying technical information rather than just concealing simple information, such as passwords.
WE-FORGE improves on an earlier version of the system--known as FORGE--by removing the time-consuming need to create guides of concepts associated with specific technologies. WE-FORGE also ensures that there is greater diversity among fakes, and follows an improved technique for selecting concepts to replace and their replacements.
Almas Abdibayev, Deepti Poluru Guarini and Haipeng Chen all contributed to this research while with Dartmouth's Department of Computer Science.
INFORMATION:
Assessing a drug compound by its activity, not simply its structure, is a new approach that could speed the search for COVID-19 therapies and reveal more potential therapies for other diseases.
This action-based focus -- called biological activity-based modeling (BABM) -- forms the core of a new approach developed by National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) researchers and others. NCATS is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Researchers used BABM to look for potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents whose actions, not their structures, are similar to those of compounds already shown to be effective.
NCATS scientists ...
The hidden social, environmental and health costs of the world's energy and transport sectors is equal to more than a quarter of the globe's entire economic output, new research from the University of Sussex Business School and Hanyang University reveals.
According to analysis carried out by Professor Benjamin K. Sovacool and Professor Jinsoo Kim, the combined externalities for the energy and transport sectors worldwide is an estimated average of $24.662 trillion - the equivalent to 28.7% of global Gross Domestic Product.
The study found that the true cost of coal should be more than twice as high as current prices when factoring in the currently unaccounted ...
A study by two researchers at the UPF Department of Political and Social Sciences (DCPIS) has examined the effect of selecting party leaders by direct vote by the entire membership (a process known in southern Europe as "primaries" and in English-speaking countries as "one-member-one -vote", OMOV) on the likelihood of a woman winning a leadership competition against male rivals.
Javier Astudillo and Andreu Paneque, a tenured lecturer and PhD with the DCPIS, respectively, and members of the Institutions and Political Actors Research Group, are the authors of the article published recently in the journal ...
TROY, N.Y. -- The era of widespread remote learning brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic requires online testing methods that effectively prevent cheating, especially in the form of collusion among students. With concerns about cheating on the rise across the country, a solution that also maintains student privacy is particularly valuable.
In research published today in npj Science of Learning, engineers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute demonstrate how a testing strategy they call "distanced online testing" can effectively reduce students' ability to receive help from one another in order to score higher on a test taken at individual homes during social distancing.
"Often in remote online exams, students ...
A group of researchers including Tiago Falótico, a Brazilian primatologist at the University of São Paulo's School of Arts, Sciences and Humanities (EACH-USP), archeologists at Spain's Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES) and University College London in the UK, and an anthropologist at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Germany, have published an article in the Journal of Archeological Science: Reports describing an analysis of stone tools used by bearded capuchin monkeys (Sapajus libidinosus) that inhabit ...
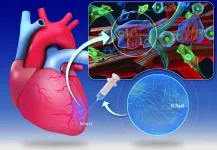
Researchers at CÚRAM, the SFI Research Centre for Medical Devices based at National University of Ireland Galway, and BIOFORGE Lab, at the University of Valladolid in Spain, have developed an injectable hydrogel that could help repair and prevent further damage to the heart muscle after a heart attack.
The results of their research have just been published in the prestigious journal Science Translational Medicine.
Myocardial infarction or heart disease is a leading cause of death due to the irreversible damage caused to the heart muscle (cardiac tissue) during a heart attack. The regeneration of cardiac tissue is minimal so that the damage caused cannot be repaired by itself. ...
Because walleyes are a cool-water fish species with a limited temperature tolerance, biologists expected them to act like the proverbial "canary in a coal mine" that would begin to suffer and signal when lakes influenced by climate change start to warm. But in a new study, a team of researchers discovered that it is not that simple.
"After analyzing walleye early-life growth rates in many lakes in the upper Midwest over the last three decades, we determined that water clarity affects how growth rates of walleyes change as lakes start to warm," said Tyler Wagner, Penn State adjunct professor of fisheries ecology. ...
The Earth's surface is subject to continual changes that dynamically shape natural landscapes. Global phenomena like climate change play a role, as do short-term, local events of natural or human origin. The 3D Geospatial Data Processing (3DGeo) research group of Heidelberg University has developed a new analysis method to help improve our understanding of processes shaping the Earth's surface like those observed in coastal or high-mountain landscapes. Unlike conventional methods that usually compare two snapshots of the topography, the Heidelberg approach can determine - fully automatically and over long periods - when and where surface alterations occur and which type of associated changes they represent.
The method, known ...
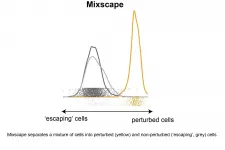
A team of researchers from New York University and the New York Genome Center has developed a new computational tool to help understand the function and regulation of human genes. The results, published today in the journal Nature Genetics, demonstrate how to interpret experiments that combine the use of CRISPR to perturb genes along with multimodal single-cell sequencing technologies.
The article describes how the new approach, called mixscape, helped to identify a new molecular mechanism for the regulation of immune checkpoint proteins that govern the immune system's ability to identify and destroy cancer cells.
"Our approach will help scientists to connect ...
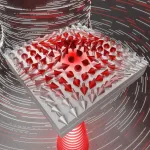
The scientists have demonstrated how to structure light such that its polarization behaves like a collective of spins in a ferromagnet forming half-skyrmion (also known as merons). To achieve this the light was trapped in a thin liquid crystal layer between two nearly perfect mirrors. Skyrmions in general are found, e.g., as elementary excitations of magnetization in a two-dimensional ferromagnet but do not naturally appear in electromagnetic (light) fields.
One of the key concepts in physics, and science overall is the notion of a "field" which can describe the spatial distribution ...