(Press-News.org) The scientists have demonstrated how to structure light such that its polarization behaves like a collective of spins in a ferromagnet forming half-skyrmion (also known as merons). To achieve this the light was trapped in a thin liquid crystal layer between two nearly perfect mirrors. Skyrmions in general are found, e.g., as elementary excitations of magnetization in a two-dimensional ferromagnet but do not naturally appear in electromagnetic (light) fields.
One of the key concepts in physics, and science overall is the notion of a "field" which can describe the spatial distribution of a physical quantity. For instance, a weather map shows the distributions of temperature and pressure (these are known as scalar fields), as well as the wind speed and direction (known as a vector field). Almost everyone wears a vector field on their head - every hair has an origin and an end, just like a vector. Over 100 years ago L.E.J. Brouwer proved the hairy ball theorem which states that you can't comb a hairy ball flat without creating whorls, whirls (vortices) or cowlicks.
In magnetism, the elementary excitations in a two-dimensional magnetization vector field have the form of such vortices and are called skyrmions. Going clockwise around the center of such a vortex, we can observe, that the vectors attached to subsequent points on our path can rotate once or many times, clockwise or anticlockwise (Fig. 2). The quantity that describes this feature is called the vorticity. Skyrmions and half-skyrmions (merons) of various vorticities can be found in such different physical systems as nuclear matter, Bose-Einstein condensates or thin magnetic layers. They are also used in the description of the quantum Hall effect, cyclones, anticyclones and tornadoes. Especially interesting are experimental setups, in which one can create various vector fields on demand and investigate the interactions of their excitations.
Scientists from University of Warsaw, Military University of Technology, University of Southampton, Skolkovo Institute in Moscow, and Institute of Physics PAS have demonstrated how to structure light such that its polarization behaves like a half-skyrmion (meron). To achieve this the light has been trapped in a thin liquid crystal layer between two nearly perfect mirrors, known as an optical cavity. By controlling the polarization of incident light and the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules they were able to observe first-order and second-order (first experimental observation) merons and anti-merons (vorticities -2, -1, 1, and 2).
A relatively simple optical cavity filled with a liquid crystal enables the scientists to create and investigate exotic states of polarization of light. The device can potentially allow to test the behavior of these excitations (annihilation, attraction or repulsion of skyrmions and merons) on an optical table when combined with more exotic optically responsive materials. Recognizing the nature of the interaction between these objects can help understand the physics of more complex systems, requiring more sophisticated experimental methods (e.g. ultra-low temperatures).
Physics and Astronomy first appeared at the University of Warsaw in 1816, under the then Faculty of Philosophy. In 1825 the Astronomical Observatory was established. Currently, the Faculty of Physics' Institutes include Experimental Physics, Theoretical Physics, Geophysics, Department of Mathematical Methods and an Astronomical Observatory. Research covers almost all areas of modern physics, on scales from the quantum to the cosmological. The Faculty's research and teaching staff includes ca. 200 university teachers, of which 87 are employees with the title of professor. The Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw, is attended by ca. 1000 students and more than 170 doctoral students.
INFORMATION:
SCIENTIFIC PAPERS:
,,Observation of second-order meron polarization textures in optical microcavities'', M. Krol et al., Optica vol. 8, 255 (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.414891
CONTACTS:
Dr. hab. Jacek Szczytko
Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw
tel. +48 225532764
email: Jacek.Szczytko@fuw.edu.pl
RELATED LINKS:
http://www.fuw.edu.pl/
The Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw website.
http://polariton.fuw.edu.pl
Webpage of the Polariton Laboratory
https://www.fuw.edu.pl/press-releases.html
Press office of the Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw.
IMAGES:
Fig. 1
FUW210222b_fot01.png
https://www.fuw.edu.pl/tl_files/press/images/2021/FUW210222b_fot01.png
Spin texture of a second-order half-skyrmion (meron) on the surface of a birefringent cavity. (Source: Physics UW, M. Krol)
Fig. 2.
FUW210222b_fot02.png
https://www.fuw.edu.pl/tl_files/press/images/2021/FUW210222b_fot02.png
Vector fields of first-order and second-order merons and anti-merons. (Source: Physics UW, M. Krol)
A joint research team co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has developed a new soft tactile sensor with skin-comparable characteristics. A robotic gripper with the sensor mounted at the fingertip could accomplish challenging tasks such as stably grasping fragile objects and threading a needle. Their research provided new insight into tactile sensor design and could contribute to various applications in the robotics field, such as smart prosthetics and human-robot interaction.
Dr Shen Yajing, Associate Professor at CityU's Department of Biomedical Engineering ...
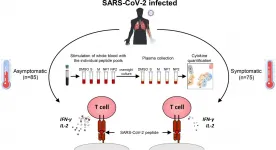
By analyzing blood samples from individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2, researchers in Singapore have begun to unpack the different responses by the body's T cells that determine whether or not an individual develops COVID-19. The study, published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that clearing the virus without developing symptoms requires T cells to mount an efficient immune response that produces a careful balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory molecules.
Many people infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus do not develop any symptoms, and the infection ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The rate of suicide among post-9/11 military veterans has been rising for nearly a decade. While there are a number of factors associated with suicide, veterans have unique experiences that may contribute to them thinking about killing themselves.
"Compared to their civilian peers, veterans are more likely to report having experienced traumatic adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) such as physical and emotional abuse," stated Keith Aronson, associate director of the Clearinghouse for Military Family Readiness at Penn State and the Social Science Research Institute ...
LAWRENCE -- A new study from University of Kansas journalism & mass communication researchers examines what influences people to be susceptible to false information about health and argues big tech companies have a responsibility to help prevent the spread of misleading and dangerous information.
Researchers shared a fake news story with more than 750 participants that claimed a deficiency of vitamin B17 could cause cancer. Researchers then measured if how the article was presented -- including author credentials, writing style and whether the article was labeled as "suspicious" or "unverified" -- affected how participants perceived its credibility and whether they would adhere to the article's recommendations or share it on social media. The findings showed that ...
AMES, Iowa - Inspired by nature's work to build spiky structures in caves, engineers at Iowa State University have developed technology capable of recovering pure and precious metals from the alloys in our old phones and other electrical waste.
Using controlled applications of oxygen and relatively low temperatures, the engineers say they can dealloy a metal by slowly moving the most reactive components to the surface where they form stalagmite-like spikes of metal oxides.
That leaves the least-reactive components in a purified, liquid core surrounded by brittle metal-oxide spikes "to create a so-called 'ship-in-a-bottle structure,'" said Martin Thuo, the leader of the research project and an associate professor of materials science and ...
A type of ultrasound scan can detect cancer tissue left behind after a brain tumour is removed more sensitively than surgeons, and could improve the outcome from operations, a new study suggests.
The new ultrasound technique, called shear wave elastography, could be used during brain surgery to detect residual cancerous tissue, allowing surgeons to remove as much as possible.
Researchers believe that the new type of scan, which is much faster to carry out and more affordable than 'gold standard' MRI scans, has the potential to reduce a patient's risk of relapse by cutting the chances that a tumour will grow ...
The amount of green space surrounding children's homes could be important for their risk of developing ADHD. This is shown by new research results from iPSYCH.
A team of researchers from Aarhus University has studied how green space around the residence affects the risk of children and adolescents being diagnosed with ADHD. And the researchers find an association.
"Our findings show that children who have been exposed to less green surroundings in their residential area in early childhood, which we define as lasting up until age five, have an increased risk of receiving an ADHD diagnosis when compared to children who have been surrounded by the highest level of green space," says ...
Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder are the three main eating disorders that 4 out of in 10 individuals living in Western Europe will experience at some point in their lives. In recent years, studies on the genetic basis of anorexia nervosa have highlighted the existence of predisposing genetic markers, which are shared with other psychiatric disorders. By analysing the genome of tens of thousands of British people, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), King's College London, the University College London, the University of North Carolina (UNC) and The Icahn ...
Research from the University of Kent has led to the development of the MeshCODE theory, a revolutionary new theory for understanding brain and memory function. This discovery may be the beginning of a new understanding of brain function and in treating brain diseases such as Alzheimer's.
In a paper published by Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, Dr Ben Goult from Kent's School of Biosciences describes how his new theory views the brain as an organic supercomputer running a complex binary code with neuronal cells working as a mechanical computer. He explains ...
Gene editing technology will play a vital role in climate-proofing future crops to protect global food supplies, according to scientists at The University of Queensland.
Biotechnologist Dr Karen Massel from UQ's Centre for Crop Science has published a review of gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 to safeguard food security in farming systems under stress from extreme and variable climate conditions.
"Farmers have been manipulating the DNA of plants using conventional breeding technologies for millennia, and now with new gene-editing technologies, we can do this with unprecedented safety, precision and speed," Dr Massel said.
"This type of gene editing mimics the way cells repair in nature."
Her review recommended ...