INFORMATION:
This research is funded by an Australian Research Council Discovery grant with support from the Queensland Department of Agriculture and Fisheries and The University of Queensland.
This research is published in Theoretical and Applied Genetics (DOI: 10.1007/s00122-020-03764-0).
Hotter, drier, CRISPR: editing for climate change
2021-03-01
(Press-News.org) Gene editing technology will play a vital role in climate-proofing future crops to protect global food supplies, according to scientists at The University of Queensland.
Biotechnologist Dr Karen Massel from UQ's Centre for Crop Science has published a review of gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 to safeguard food security in farming systems under stress from extreme and variable climate conditions.
"Farmers have been manipulating the DNA of plants using conventional breeding technologies for millennia, and now with new gene-editing technologies, we can do this with unprecedented safety, precision and speed," Dr Massel said.
"This type of gene editing mimics the way cells repair in nature."
Her review recommended integrating CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing into modern breeding programs for crop improvement in cereals.
Energy-rich cereal crops such as wheat, rice, maize and sorghum provide two-thirds of the world's food energy intake.
"Just 15 plant crops provide 90 per cent of the world's food calories," Dr Massel said.
"It's a race between a changing climate and plant breeders' ability to produce crops with genetic resilience that grow well in adverse conditions and have enriched nutritional qualities.
"The problem is that it takes too long for breeders to detect and make that genetic diversity available to farmers, with a breeding cycle averaging about 15 years for cereal crops.
"Plus CRISPR allows us to do things we can't do through conventional breeding in terms of generating novel diversity and improving breeding for desirable traits."
In proof-of-concept studies, Dr Massel and colleagues at the Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation (QAAFI) applied gene editing technology to sorghum and barley pre-breeding programs.
"In sorghum, we edited the plant's genes to unlock the digestibility level of the available protein and to boost its nutritional value for humans and livestock," she said.
"We've also used gene-editing to modify the canopy architecture and root architecture of both sorghum and barley, to improve water use efficiency."
Dr Massel's research also compared the different genome sequences of cereals - including wild variants and ancestors of modern cereals - to differences in crop performance in different climates and under different kinds of stresses.
"Wild varieties of production crops serve as a reservoir of genetic diversity, which is especially valuable when it comes to climate resilience," she said.
"We are looking for genes or gene networks that will improve resilience in adverse growing climates.
"Once a viable gene variant is identified, the trick is to re-create it directly in high-performing cultivated crops without disrupting the delicate balance of genetics related to production traits.
"These kinds of changes can be so subtle that they are indistinguishable from the naturally occurring variants that inspired them."
In 2019, Australia's Office of the Gene Technology Regulator deregulated gene-editing, differentiating it from genetically modified organism (GMO) technology.
Gene edited crops are not yet grown in Australia, but biosecurity and safety risk assessments of the technology are currently being undertaken.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Childhood exposure to diversity is best chance for community cohesion in immigration
2021-03-01
New research from the University of Kent reveals social cohesion with immigration is best ensured through childhood exposure to diversity in local neighbourhoods, leading to acceptance of other groups.
The research, which is published in Oxford Economic Papers, builds on the Nobel Laureate economist Thomas Schelling's Model of Segregation, which showed that a slight preference by individuals and families towards their own groups can eventually result in complete segregation of communities.
Shedding new light on this issue, researchers from Kent's School of Economics have introduced the theory ...
Will we enjoy work more once routine tasks are automated? - Not necessarily, a study shows
2021-03-01
Will we enjoy our work more once routine tasks are automated? - Not necessarily, suggests a recent study
Research conducted at Åbo Akademi University suggests that when routine work tasks are being replaced with intelligent technologies, the result may be that employees no longer experience their work as meaningful.
Advances in new technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics and digital applications have recently resurrected discussions and speculations about the future of working life. Researchers predict that new technologies will affect, in particular, routine and structured work tasks. According to estimations, 7-35 percent ...
Walking away from the beat - why police officers are voluntarily leaving in large numbers
2021-03-01
Home Office data shows the number of police officers voluntarily resigning from the force in England and Wales has more than doubled in the last eight years.
Scant attention has been paid to the reason for this mass exodus. Until now. Researchers from the University of Portsmouth studied government statistics, and discovered the numbers of officers voluntarily resigning from the police service is rising - from 1,158 in the year ending March 2012 to 2,363 in the year ending March 2020. The figure amounts to 1.83 per cent of the total police officer population in England and Wales up from 0.86 per cent eight years ago.
Dr Sarah Charman, from the Institute of Criminal Justice Studies at the University of Portsmouth, led the study. ...
New research will enhance corona safety during cruises
2021-03-01
New research will enhance corona safety during cruises and help cruise lines to again attract passengers onboard
Researchers within Cell Biology and Industrial Management at Åbo Akademi University have developed models aimed at ensuring corona safety during cruises.
The coronavirus pandemic stopped the cruise industry more or less completely. Major international cruise lines, such as Royal Caribbean Group and Carnival Corporation, largely suspended their cruises during 2020, which resulted in practically zero turnover and losses amounting to billions.
Upon assignment by Business Finland, an interdisciplinary research team has been working to find solutions for managing the current crisis ...
Watch: Recycled cotton becomes new fabric
2021-03-01
A lot of us recycle our old textiles, but few of us know that they are very difficult to re-use, and often end up in landfills anyway. Now, researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed a method that converts cotton into sugar, that in turn can be turned into spandex, nylon or ethanol.
WATCH: New method transforms old cotton into glucose
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B1V--prLs08
Every year, an estimated 25 million tonnes of cotton textiles are discarded around the world. In total, 100 million tonnes of textiles are thrown out. In Sweden, most of the material goes straight into an incinerator and becomes district heating. In other places, it is even worse, as clothes usually end up in landfills.
"Considering that cotton is a renewable ...
Lung cancer cells have differential signaling responses to KRAS inhibitor treatment
2021-03-01
TAMPA, Fla. - Genetic alterations of the KRAS gene are some of the most common mutations in lung cancer patients, but unfortunately these patients have few effective treatment options. Drugs that target the G12C mutation in KRAS have shown some activity in lung cancer; however, alternative signaling pathways are often activated that bypass the KRAS inhibitor, resulting in drug resistance. In a new article published in Clinical Cancer Research, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers show that various subtypes of lung cancer cells activate different signaling pathways in response to KRASG12C inhibitor treatment. These results may help identify potential combination therapy approaches and guide ...
Hot electrons send CO2 back to the future
2021-03-01
Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major driver of global warming, but this gas could also serve as a valuable resource. Researchers at KAUST have developed an efficient catalyst that uses light energy to convert CO2 and hydrogen into methane (CH4). This counteracts the release of CO2 when methane is burned as a fuel.
Many researchers worldwide are exploring ways to convert CO2 into useful carbon-based chemicals, but their efforts have been limited by low efficiencies that restrict the potential for large-scale application.
"Our approach is based on the synergistic combination of light and heat, known as the photothermal effect," says postdoc Diego Mateo. He explains that the heat is generated by the interaction of light with the catalyst, ...
Identified: A mechanism that protects plant fertility from stress
2021-03-01
Spikes in temperature can affect a plant's fertility, resulting in a reduction of yield and economic loss
How plants can protect themselves from stress has been studied by a consortium led by the University of Warwick
Two argonaute-like proteins protect the plant's fertility, understanding these proteins is critical to safeguarding crop production
As Temperatures rise due to global warming the need to protect plants from stressful conditions has increased, as stress can cause a loss in yield and cause further impact economically. A consortium led by the University of Warwick have successfully identified ...
Could our immune system be why COVID-19 is so deadly?
2021-03-01
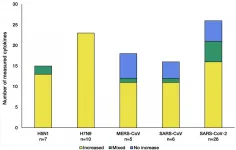
Respiratory viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 (causing COVID-19) can often catalyse an overactive immune response that leads to a life-threatening cycle, known as a cytokine storm. Analysing cytokine responses from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and similar common respiratory viruses has unearthed glaringly important differences in how SARS-CoV-2 affects cytokines compared to other common respiratory viruses.
The comprehensive data resource aims to help specialists identify better treatments and diagnosis of underlying causes that can cause the deadly cytokine storm.
Scientists at the ...
Assessing hemp-containing foodstuff
2021-03-01
In order to avoid the occurrence of such effects, the Federal Institute for Health Protection of Consumers and Veterinary Medicine (BgVV) recommended guidance values for maximum THC levels in various food groups in 2000. The guidance value for beverages was given as 0.005 mg/kg, for edible oils with 5 mg/kg and for all other foods with 0.150 mg/kg. In 2018, the BfR came to the conclusion that these values no longer correspond to current scientific knowledge.
Instead, the BfR recommends that the toxicological assessment of hemp-containing foods be carried out on the basis of the acute reference dose (ARfD) of 1 microgram Δ-THC/kg body-weight derived by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in 2015. The ARfD specifies the estimated maximum quantity ...