Identified: A mechanism that protects plant fertility from stress
2021-03-01
(Press-News.org) Spikes in temperature can affect a plant's fertility, resulting in a reduction of yield and economic loss
How plants can protect themselves from stress has been studied by a consortium led by the University of Warwick
Two argonaute-like proteins protect the plant's fertility, understanding these proteins is critical to safeguarding crop production
As Temperatures rise due to global warming the need to protect plants from stressful conditions has increased, as stress can cause a loss in yield and cause further impact economically. A consortium led by the University of Warwick have successfully identified two proteins that protect crops from stress, which is key in safeguarding food production.
Plant fertility is dramatically affected by spikes in temperature, directly resulting in yield reduction and economic loss. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that underpin plant fertility under environmental constraints is critical to safeguarding food production.
In the paper, 'A transposon surveillance mechanism that safeguards plant male fertility during stress', published in the journal Nature Plants, led by researchers from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick have studied the molecular mechanisms that maize plants utilise to safeguard fertility under high temperatures, and identified two Argonaute-like (AGO) proteins that protect the male sex cells.
By subjecting maize plants with non-functional AGO proteins to different growth conditions, researchers discovered that a 5?C increase in ambient temperature dramatically decreased male fertility.
Using a multidisciplinary approach, the team found that higher temperatures activated small pieces of ribonucleic acid (or small RNAs) in wild-type plants, which bind to these AGO proteins to control the activity of stress-activated jumping genes - pieces of DNA that can copy themselves into different parts of the genome. Therefore, these AGO proteins control the activity of jumping-genes, thereby protect plant fertility.
Professor Jose Gutierrez-Marcos, from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick explains:
"We have essentially found that when plants are stressed by high temperatures they activate an RNA-guided surveillance mechanism in the form of small RNAs and Argonaute proteins, in reproductive cells which are critical to sustain male fertility and ultimately plant survival.
"Understanding the molecular mechanism implicated in safeguarding plant fertility is critical to safeguard future crop production under unpredictable and stressful climatic conditions."
Dr Charo del Genio, from the School of Computing, Electronics and Mathematics at Coventry University adds:
"Modelling the structure of the Argonaute proteins and simulating them at the level of the single atoms revealed how they change their electric charge when subject to thermal stress, initiating the process that brings the jumping genes back under control."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-01
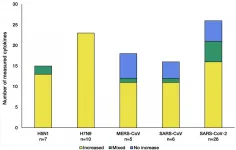
Respiratory viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 (causing COVID-19) can often catalyse an overactive immune response that leads to a life-threatening cycle, known as a cytokine storm. Analysing cytokine responses from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and similar common respiratory viruses has unearthed glaringly important differences in how SARS-CoV-2 affects cytokines compared to other common respiratory viruses.
The comprehensive data resource aims to help specialists identify better treatments and diagnosis of underlying causes that can cause the deadly cytokine storm.
Scientists at the ...
2021-03-01
In order to avoid the occurrence of such effects, the Federal Institute for Health Protection of Consumers and Veterinary Medicine (BgVV) recommended guidance values for maximum THC levels in various food groups in 2000. The guidance value for beverages was given as 0.005 mg/kg, for edible oils with 5 mg/kg and for all other foods with 0.150 mg/kg. In 2018, the BfR came to the conclusion that these values no longer correspond to current scientific knowledge.
Instead, the BfR recommends that the toxicological assessment of hemp-containing foods be carried out on the basis of the acute reference dose (ARfD) of 1 microgram Δ-THC/kg body-weight derived by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in 2015. The ARfD specifies the estimated maximum quantity ...
2021-03-01
DNA nanotechnology - the research field using DNA molecules as building material - has developed rapidly during recent years and enabled the construction of increasingly complex nanostructures. DNA nanostructures, such as DNA origami, serve as an excellent foundation for nanocarrier-based drug delivery applications, and examples of their use in medical treatments have already been demonstrated. Although the stability of such DNA nanostructures under physiological conditions can be improved, little is known about their digestion by endonucleases, which, found everywhere in our blood and tissues, are responsible for destroying foreign DNA in our bodies.
To tackle this emerging question, a ...
2021-03-01
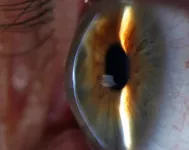
Scientists have taken a significant step forward in their search for the origin of a progressive eye condition which causes sight loss and can lead to corneal transplant.
A new study into keratoconus by an international team of researchers, including a University of Leeds group led by Chris Inglehearn, Professor of Molecular Ophthalmology in the School of Medicine, has for the first time detected DNA variations which could provide clues as to how the disease develops.
Keratoconus causes the cornea, which is?the clear outer layer?at the front of the eye, to thin and bulge outwards into a cone shape over time, resulting in blurred vision and sometimes blindness. It usually emerges in young adulthood, often with lifelong ...
2021-03-01
Researchers are in the search for generalisable rules and patterns in nature. Biogeographer Julia Kemppinen together with her colleagues tested if plant functional traits show similar patterns along microclimatic gradients across far-apart regions from the high-Arctic Svalbard to the sub-Antarctic Marion Island. Kemppinen and her colleagues found surprisingly identical patterns.
It is widely known that global vegetation patterns and plant properties follow major differences in climate. Yet, it has remained a mystery how well the same rules can be applied at very local scales. Are responses to the environment similar in plant communities ...
2021-03-01
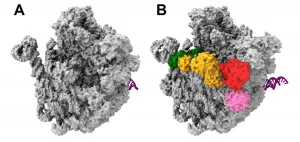
Ribosome formation is viewed as a promising potential target for new antibacterial agents. Researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin have gained new insights into this multifaceted process. The formation of ribosomal components involves multiple helper proteins which, much like instruments in an orchestra, interact in a coordinated way. One of these helper proteins - protein ObgE - acts as the conductor, guiding the entire process. The research, which produced the first-ever image-based reconstruction of this process, has been published in Molecular Cell*.
Ribosomes are an essential component of all living cells. Frequently referred to as 'molecular protein factories', they translate genetic information into chains of linked-up ...
2021-03-01
What can you see on this picture (next to thearticle)? Say what comes to your mind immediately!
If you said „star", you focus rather on the details, if you said „sun", then rather on the global pattern.
People can be different in whether they typically see the forest or the trees, but the dominant attentional mode is focusing first on the whole, and then on the details. This is the same with children. Or so it has been until now! Children of the Alpha Generation (who has been born after 2010) typically grow up with mobile devices in their hands which seems to change how they perceive the world, as Hungarian researchers showed.
The Alpha Generation Lab of Diagnostics and Therapy Excellence Programme at Eötvös Loránd University (Budapest) studies ...
2021-03-01
Materials - Quantum building blocks
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists demonstrated that an electron microscope can be used to selectively remove carbon atoms from graphene's atomically thin lattice and stitch transition-metal dopant atoms in their place.
This method could open the door to making quantum building blocks that can interact to produce exotic electronic, magnetic and topological properties.
This is the first precision positioning of transition-metal dopants in graphene. The produced graphene-dopant complexes can exhibit atomic-like behavior, inducing desired properties in the graphene.
"What could ...
2021-03-01
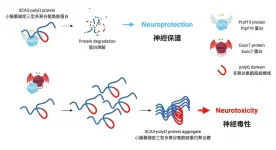
Collaborating with the University of Oxford, Professor Ho Yin Edwin Chan's research team from the School of Life Sciences of The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) recently unveiled the counteracting relationship between pre-mRNA-processing factor 19 (Prpf19) and exocyst complex component 7 (Exoc7) in controlling the degradation of disease protein and neurodegeneration of the rare hereditary ataxia. The research findings have been published in the prestigious scientific journal, Cell Death & Disease.
Protein misfolding contributes to the pathogenesis of SCA3
Proteins play a significant role in every single cell development in the human body, including neurons. Numerous studies have proved that misfolds and aggregation of ...
2021-03-01
A new paper by Dr. Miki Ben-Dor and Prof. Ran Barkai from the Jacob M. Alkow Department of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University proposes an original unifying explanation for the physiological, behavioral and cultural evolution of the human species, from its first appearance about two million years ago, to the agricultural revolution (around 10,000 BCE). According to the paper, humans developed as hunters of large animals, causing their ultimate extinction. As they adapted to hunting small, swift prey animals, humans developed higher cognitive abilities, evidenced by the most obvious evolutionary change - the growth of brain volume from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Identified: A mechanism that protects plant fertility from stress