(Press-News.org) What can you see on this picture (next to thearticle)? Say what comes to your mind immediately!
If you said „star", you focus rather on the details, if you said „sun", then rather on the global pattern.
People can be different in whether they typically see the forest or the trees, but the dominant attentional mode is focusing first on the whole, and then on the details. This is the same with children. Or so it has been until now! Children of the Alpha Generation (who has been born after 2010) typically grow up with mobile devices in their hands which seems to change how they perceive the world, as Hungarian researchers showed.
The Alpha Generation Lab of Diagnostics and Therapy Excellence Programme at Eötvös Loránd University (Budapest) studies how the use of digital devices affects children's cognitive and socio-emotional development. Now, a study they conducted have been published in the prestigious journal Computers in Human Behavior.
„Focusing on the global picture helps us in perceiving the world in meaningful, coherent patterns, and not just as a bunch of unrelated spots"- said Veronika Konok, first author of the study. „We automatically process the global pattern even if we intend to pay attention only to the details. For example, if we have to focus solely on the small details of a picture like above to decide if they are sun-shaped or not, we cannot ignore the big picture (which can be different from the small shapes) and this slows down our reaction. However, if we have to focus on the big picture, the little details do not confuse us, because we do not process them automatically."
Children using mobile devices differ in this skill! When they have to press a button upon seeing a sun either at the global or at the local level, their performance shows that they process the details first: they respond faster when the target (sun) is at the local level, in contrast with pre-schoolers who do not use mobile devices, or with typical adults.
To verify if these attentional changes are caused by the use of mobile devices, the researchers recruited pre-schoolers regardless they use mobile devices or not and investigated if a short game on tablet causes detail-focused attention in short term.
"Interestingly, 6 minutes of playing with a balloon-shooting game was enough to induce a detail-focused attentional style in a consecutive task. In contrast, children who played with a non-digital game (a whack-a-mole game) showed the typical global focus"- said Ádám Miklósi, leader of the group.
So, the use of digital devices changes how children perceive the world. The results show that the type of experiences children meet matters much, because at this age the brain is very plastic, so such massive early exposure may have a significant long-term effect.
"The atypical attentional style in mobile user children is not necessarily bad, but different for sure, and we cannot ignore this - for example in pedagogy"- said Krisztina Liszkai-Peres, a co-worker of the group, second author of the publication.
These children probably need a new way of presenting educational material. As the researchers point out, people who pay attention to details are more skilful at analytic thinking, but less creative and have weaker social skills. Therefore, it is possible that - if there will be no change in this trend - among children of the new generation there will be more scientific thinker and less artistic or social ones, and this will probably change the world we live in.
INFORMATION:
Our studies were funded by the National Research, Development and Innovation Office (ELTE Thematic Excellence Programme 2020; TKP2020-IKA-05; OTKA K124458; OTKA KH129603), by the Ministry for Innovation and Technology (ÚNKP-20-5 New National Excellence Program) and the Hungarian Academy of Science (MTA 01 031; Bolyai János Research Fellowship; MTA Lendület Programme, #LP 2018-3/2018).
Materials - Quantum building blocks
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists demonstrated that an electron microscope can be used to selectively remove carbon atoms from graphene's atomically thin lattice and stitch transition-metal dopant atoms in their place.
This method could open the door to making quantum building blocks that can interact to produce exotic electronic, magnetic and topological properties.
This is the first precision positioning of transition-metal dopants in graphene. The produced graphene-dopant complexes can exhibit atomic-like behavior, inducing desired properties in the graphene.
"What could ...
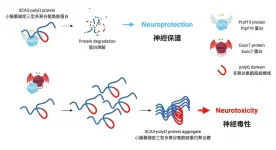
Collaborating with the University of Oxford, Professor Ho Yin Edwin Chan's research team from the School of Life Sciences of The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) recently unveiled the counteracting relationship between pre-mRNA-processing factor 19 (Prpf19) and exocyst complex component 7 (Exoc7) in controlling the degradation of disease protein and neurodegeneration of the rare hereditary ataxia. The research findings have been published in the prestigious scientific journal, Cell Death & Disease.
Protein misfolding contributes to the pathogenesis of SCA3
Proteins play a significant role in every single cell development in the human body, including neurons. Numerous studies have proved that misfolds and aggregation of ...
A new paper by Dr. Miki Ben-Dor and Prof. Ran Barkai from the Jacob M. Alkow Department of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University proposes an original unifying explanation for the physiological, behavioral and cultural evolution of the human species, from its first appearance about two million years ago, to the agricultural revolution (around 10,000 BCE). According to the paper, humans developed as hunters of large animals, causing their ultimate extinction. As they adapted to hunting small, swift prey animals, humans developed higher cognitive abilities, evidenced by the most obvious evolutionary change - the growth of brain volume from ...
A study carried out by researchers from the Institute of Genomics, University of Tartu revealed that human gut microbiome can be used to predict changes in Type 2 diabetes related glucose regulation up to four years ahead.
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disease characterized by elevated blood glucose levels that contributes to millions of deaths worldwide each year and its prevalence is rapidly increasing. Type 2 diabetes is preceded by "prediabetes" - a condition when the glucose levels have started to rise, but the progression of the disease ...
Takeaway coffees - they're a convenient start for millions of people each day, but while the caffeine perks us up, the disposable cups drag us down, with nearly 300 billion ending up in landfill each year.
While most coffee drinkers are happy to make a switch to sustainable practices, new research from the University of South Australia shows that an absence of infrastructure and a general 'throwaway' culture is severely delaying sustainable change.
It's a timely finding, particularly given the new bans on single-use plastics coming into effect in South Australia today, and the likelihood of takeaway coffee cups taking ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Single-celled algae and animal sperm cells are widely separated in evolution but both swim in the same way, by waving their protruding hairs, called cilia or flagella. Motion is driven by molecular motors, complex assemblies of proteins that exert a force when changing shape. The motor proteins are connected to the cell's internal skeleton of microtubules; the moving force from the motor causes microtubules to slide, moving the flagella and propelling the cell.
Now a team led by Professor Kazuo Inaba of the University of Tsukuba in collaboration with scientists from Osaka University, Tokyo Institute of Technology and Paul Scherrer Institute has described a new protein that is closely ...
While many people believe misinformation on Facebook and Twitter from time to time, people with lower education or health literacy levels, a tendency to use alternative medicine or a distrust of the health care system are more likely to believe inaccurate medical postings than others, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Inaccurate information is a barrier to good health care because it can discourage people from taking preventive measures to head off illness and make them hesitant to seek care when they get sick," said lead author Laura D. Scherer, PhD, with the University of Colorado School of Medicine. "Identifying who is most susceptible to misinformation ...
Electric scooters or "e-scooters" are taking over cities worldwide and have broad appeal with tourists. Although e-scooter use declined during the COVID-19 pandemic, its popularity could rebound rapidly, especially if travelers start to substitute scooters for transit on some shorter trips. Shared e-scooters in particular, are a rapidly emerging mode of transportation, but present a host of regulatory challenges from equitable distribution to parking infrastructure to pedestrian safety, among others.
Understanding travel demand patterns of shared ...
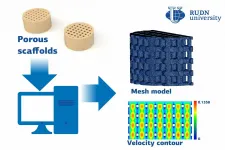
An associate professor from RUDN University found out the effect of the number and size of pores on the permeability of bone implants by biological fluids. The results of the study could help choose the optimal physical parameters of implants. The results of the study were published in the International Journal of Engineering.
For an implant to survive in the body and to take the place of bone tissue, it should be made of a non-toxic, biologically inert, and wearproof material. However, at the same time, it should be light, porous, and permeable by biological liquids. If an implant does not interfere with the transfer of oxygen, minerals, and nutrients, new bone tissue and blood vessels start to grow around it, and a patient's ...
Osaka, Japan - Osaka University researchers employed machine learning to design new polymers for use in photovoltaic devices. After virtually screening over 200,000 candidate materials, they synthesized one of the most promising and found its properties were consistent with their predictions. This work may lead to a revolution in the way functional materials are discovered.
Machine learning is a powerful tool that allows computers to make predictions about even complex situations, as long as the algorithms are supplied with sufficient example data. This is especially useful for complicated ...