(Press-News.org) While many people believe misinformation on Facebook and Twitter from time to time, people with lower education or health literacy levels, a tendency to use alternative medicine or a distrust of the health care system are more likely to believe inaccurate medical postings than others, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Inaccurate information is a barrier to good health care because it can discourage people from taking preventive measures to head off illness and make them hesitant to seek care when they get sick," said lead author Laura D. Scherer, PhD, with the University of Colorado School of Medicine. "Identifying who is most susceptible to misinformation might lend considerable insight into how such information spreads and provide us with new avenues for intervention."
In the study, published in the journal Health Psychology, researchers surveyed 1,020 people in the U.S. between the ages of 40 and 80 about the accuracy of 24 recent Facebook and Twitter postings on HPV vaccines, statin medications and cancer treatment. Researchers shared with participants an equal number of true and false postings for all three medical issues. False claims included asserting that red yeast rice is more effective at lowering cholesterol than statins, that marijuana, ginger and dandelion roots can cure cancer and that HPV vaccines are dangerous.
Participants were asked to evaluate whether the postings were completely false, mostly false, mostly true or completely true. Researchers asked follow-up questions, including participants' education level, interest in alternative treatments, understanding of health care issues, income and age.
Participants with lower education and health literacy levels were more likely to believe the misinformation, the researchers found. Those with a distrust for the health care system or who had positive attitudes toward alternative medicine also tended to believe the misinformation on the three health topics more often than others in the study. Also, participants who fell for misinformation on one health issue tended to be more susceptible to misinformation on the other two health topics.
The findings could help public health officials develop more targeted messaging and outreach for a range of health care issues, according to the researchers.
"People who were susceptible to misinformation tended to be susceptible to all three types we showed them, about a vaccine, statin medications and cancer treatment," Scherer said. "One possible implication is that these individuals are susceptible to many different types of health misinformation, making these findings potentially relevant to other health care issues beyond the ones we studied here. This information could have implications for other public information efforts, such as those currently underway to address COVID-19."
Still, more research needs to be done to fully understand how to interrupt misinformation cycles, Scherer said.
"We hope that researchers can build on these findings and develop novel and evidence-based interventions to reduce the influence and spread of health misinformation online. Such steps could save countless lives," she said.
INFORMATION:
Article: "Who is Susceptible to Online Health Misinformation? A Test of Four Psychosocial Hypotheses," by Laura D. Scherer, PhD, University of Colorado School of Medicine; Allison Kempe, MD, Larry A. Allen, MD, Christopher E. Knoepke, PhD, Channing E. Tate, MPH, and Daniel D. Matlock, MD, University of Colorado School of Medicine; Gordon Pennycook, PhD, University of Regina and Massachusetts Institute of Technology; and Jon McPhetres, PhD, University of Regina. Health Psychology, published online Feb. 25, 2021.
Contact: Laura D. Scherer, PhD, can be reached at laura.scherer@cuanschutz.edu.
Full text of the article is available online at https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/releases/hea-hea0000978.pdf
The American Psychological Association, in Washington, D.C., is the largest scientific and professional organization representing psychology in the United States. APA's membership includes nearly 122,000 researchers, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. Through its divisions in 54 subfields of psychology and affiliations with 60 state, territorial and Canadian provincial associations, APA works to advance the creation, communication and application of psychological knowledge to benefit society and improve people's lives.
Electric scooters or "e-scooters" are taking over cities worldwide and have broad appeal with tourists. Although e-scooter use declined during the COVID-19 pandemic, its popularity could rebound rapidly, especially if travelers start to substitute scooters for transit on some shorter trips. Shared e-scooters in particular, are a rapidly emerging mode of transportation, but present a host of regulatory challenges from equitable distribution to parking infrastructure to pedestrian safety, among others.
Understanding travel demand patterns of shared ...
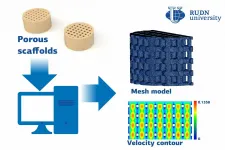
An associate professor from RUDN University found out the effect of the number and size of pores on the permeability of bone implants by biological fluids. The results of the study could help choose the optimal physical parameters of implants. The results of the study were published in the International Journal of Engineering.
For an implant to survive in the body and to take the place of bone tissue, it should be made of a non-toxic, biologically inert, and wearproof material. However, at the same time, it should be light, porous, and permeable by biological liquids. If an implant does not interfere with the transfer of oxygen, minerals, and nutrients, new bone tissue and blood vessels start to grow around it, and a patient's ...
Osaka, Japan - Osaka University researchers employed machine learning to design new polymers for use in photovoltaic devices. After virtually screening over 200,000 candidate materials, they synthesized one of the most promising and found its properties were consistent with their predictions. This work may lead to a revolution in the way functional materials are discovered.
Machine learning is a powerful tool that allows computers to make predictions about even complex situations, as long as the algorithms are supplied with sufficient example data. This is especially useful for complicated ...
With their exuberant colours, fiery personalities and captivating courtship displays, the fairy wrasses are one of the most beloved coral reef fish. Despite this, the evolutionary history of its genus was not well understood - until now.
Fairy wrasses diverged in form and colour after repeated sea level rises and falls during the last ice age, finds a new study. Published in top journal Systematic Biology, it employed a novel genome-wide dataset to make this discovery.
Lead author, ichthyologist and PhD candidate at the University of Sydney, Mr Yi-Kai (Kai) Tea, says ...
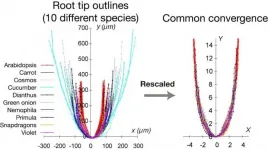
Osaka, Japan - Nature is full of diversity, but underneath the differences are often shared features. Researchers from Japan investigating diversity in plant features have discovered that plant root tips commonly converged to a particular shape because of physical restrictions on their growth.
In a study published in February in Development, researchers from Osaka University, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, and Kobe University have revealed that plant root tips are constrained to a dome-shaped outline because of restrictions on their tissue growth. This study is one of the papers selected as a Research Highlight published in this issue of Development ...
Raspberry muffins are in our future.
Washington State University scientists have figured out a way to treat raspberries before they're frozen so that they maintain their structure when thawed.
The tart little berries are very delicate and freezing damages their cells. They turn to mush when baked and leak juice into the surrounding baked product, making them unattractive and diluted in flavor. As a result, frozen raspberries are rarely used in baking, whether at home or in commercial bakeries. But that's about to change.
In a recent article published in Food and Bioprocess ...
Making cheese leaves a lot to chance as a batch could be ripened for months or even years before a problem is discovered, which could send a prized batch of cheddar to be sold off cheap as an ingredient for processed cheese.
It's part of why cheese is so complex and expensive to make - a factory could invest lots of time and money into what they think will be a top-graded batch, only to discover it's a flop when it's too late to fix.
But new research from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia allows quality to be checked much earlier and more precisely in the process, giving manufacturers a better chance to react to issues with the ripening process.
Dr ...
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) observe underdeveloped jaw cartilage in newborn rats exposed to periods of low oxygen
Tokyo, Japan - Breathing in adequate amounts of oxygen is critical for human life. However, certain disorders can cause individuals to go through periods where they are exposed to periodical low levels of oxygen, called intermittent hypoxia (IH). This is common in people who suffer from some sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea. Although we know IH can cause neurological development issues, it is not clear how it affects cartilage. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have shown that IH can result in underdeveloped jaw cartilage in rats.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, researchers ...
HIV infections are treated with antiviral drugs which effectively prevent the disease from developing. While pharmacological HIV therapy has advanced considerably, the virus cannot be entirely eliminated from the body with currently available drugs.
However, in roughly one-fifth of HIV patients the immune system does not recover as expected: the quantity of CD4 T cells, reflecting the status of the immune system, remains low even when the quantity of HI viruses in blood is suppressed to very low levels or below the measurement threshold. In such patients, indications of chronic immune activation, which erodes the immune system, can be detected.
In cooperation with the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg in Germany, researchers at the University of Helsinki have ...
Wildlife tourism including white shark cage-diving is growing in popularity, but these industries remain highly contentious amongst tourists, conservationists, and scientists alike.
Many voice concerns about possible negative impacts - especially when it targets potentially dangerous animals - while proponents cite the socio-economic benefits to justify wildlife tourism activities.
In reality, wildlife tourism is complex, requiring managers to balance the benefits and drawbacks to determine what is acceptable for such industries.
To help solve this question of "is wildlife tourism good or bad?", a tool to help managers assess these industries has been created ...