(Press-News.org) With their exuberant colours, fiery personalities and captivating courtship displays, the fairy wrasses are one of the most beloved coral reef fish. Despite this, the evolutionary history of its genus was not well understood - until now.
Fairy wrasses diverged in form and colour after repeated sea level rises and falls during the last ice age, finds a new study. Published in top journal Systematic Biology, it employed a novel genome-wide dataset to make this discovery.
Lead author, ichthyologist and PhD candidate at the University of Sydney, Mr Yi-Kai (Kai) Tea, says that the fish's divergence occurred rapidly and over a short amount of time.
"Although the fairy wrasses split from their most common ancestor some 12 million years ago, it was only within the last 2-5 million years ago that much of their divergences took place, in the Pliocene/Pleistocene epoch," said Mr Tea, a researcher in the School of Life and Environmental Sciences.
"They developed distinct colours and forms in a sort of evolutionary arms race, putting on dazzling displays in an effort to court females and chase off rival males. Also, sea level changes caused groups to become isolated, and therefore evolve separately. The repeated rise and fall of sea levels acted like a 'species pump', propelling fish into the Indian Ocean and even as far as the Red Sea. Most of this movement, however, occurred in the Pacific Ocean, in particular, around the Indo-Australian Archipelago."
Mr Tea completed the work under the supervision of Professors of Molecular Evolution, Simon Ho and Nathan Lo.
Decoding fish DNA
Despite the vast variation in colour and form, many species of fairy wrasses have highly conserved, or similar, regions of their genome. This poses a challenge in trying to reconstruct their evolutionary history.
The current study used an approach that had not been previously attempted on fairy wrasses: by combining genome-wide ultra-conserved elements with mitochondrial DNA, the researchers reconstructed a robust evolutionary tree. Using that, they began to tease apart the reason behind the fish's diversification.
Do a little dance, make a little love
In addition to sea level fluctuations, male fairy wrasses (as with many animals, the more colourful sex) developed their bright colours and individual forms to court females.
"They do a little dance, and they are capable of changing colours, sometimes temporarily flashing bright, iridescent colours. They also do this to ward off rival males," said Mr Tea. "In a reef where multiple species often occur, there is increased pressure for males to attract not only a female's attention, but also the female of the correct species."
"We have only just begun scratching the surface of this exciting group, and more work still needs to be done in order to fully understand the drivers of species diversification," he continued.
That work, and the present study, might be germane to reef conservation and management, too. For example, the finless 'mutant wrasse', an Australian endemic species restricted to a narrow distribution of reefs in far northwest Western Australia, is listed as vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of threatened species. The species has been placed in its own genus, with a single species. However, Mr Tea's study finds strong evidence that this species is simply a derived fairy wrasse, and that its loss of fins likely resulted from it being 'bottlenecked' in a narrow area.
INFORMATION:
Fairy wrasse facts
Today, there are 61 fairy wrasse species, with new species continually being discovered.
Fairy wrasses are petite - they grow no larger than 15cm in length.
They live in large groups in rubble reefs (dead coral and rocks), next to coral cover, at depths of 10 to 250 metres.
Males are more colourful, larger, and often sport more ornamented fins than females (this is known as 'sexual dimorphism').
Fairy wrasses are sequential hermaphrodites, meaning that females are capable of changing into fully functional males.
Fairy wrasses were discovered in the mid 1800s, yet scientists only began to investigate their origins and evolutionary relationships in the last few decades.
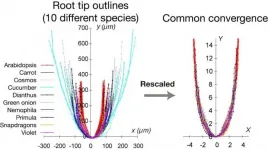
Osaka, Japan - Nature is full of diversity, but underneath the differences are often shared features. Researchers from Japan investigating diversity in plant features have discovered that plant root tips commonly converged to a particular shape because of physical restrictions on their growth.
In a study published in February in Development, researchers from Osaka University, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, and Kobe University have revealed that plant root tips are constrained to a dome-shaped outline because of restrictions on their tissue growth. This study is one of the papers selected as a Research Highlight published in this issue of Development ...
Raspberry muffins are in our future.
Washington State University scientists have figured out a way to treat raspberries before they're frozen so that they maintain their structure when thawed.
The tart little berries are very delicate and freezing damages their cells. They turn to mush when baked and leak juice into the surrounding baked product, making them unattractive and diluted in flavor. As a result, frozen raspberries are rarely used in baking, whether at home or in commercial bakeries. But that's about to change.
In a recent article published in Food and Bioprocess ...
Making cheese leaves a lot to chance as a batch could be ripened for months or even years before a problem is discovered, which could send a prized batch of cheddar to be sold off cheap as an ingredient for processed cheese.
It's part of why cheese is so complex and expensive to make - a factory could invest lots of time and money into what they think will be a top-graded batch, only to discover it's a flop when it's too late to fix.
But new research from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia allows quality to be checked much earlier and more precisely in the process, giving manufacturers a better chance to react to issues with the ripening process.
Dr ...
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) observe underdeveloped jaw cartilage in newborn rats exposed to periods of low oxygen
Tokyo, Japan - Breathing in adequate amounts of oxygen is critical for human life. However, certain disorders can cause individuals to go through periods where they are exposed to periodical low levels of oxygen, called intermittent hypoxia (IH). This is common in people who suffer from some sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea. Although we know IH can cause neurological development issues, it is not clear how it affects cartilage. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have shown that IH can result in underdeveloped jaw cartilage in rats.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, researchers ...
HIV infections are treated with antiviral drugs which effectively prevent the disease from developing. While pharmacological HIV therapy has advanced considerably, the virus cannot be entirely eliminated from the body with currently available drugs.
However, in roughly one-fifth of HIV patients the immune system does not recover as expected: the quantity of CD4 T cells, reflecting the status of the immune system, remains low even when the quantity of HI viruses in blood is suppressed to very low levels or below the measurement threshold. In such patients, indications of chronic immune activation, which erodes the immune system, can be detected.
In cooperation with the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg in Germany, researchers at the University of Helsinki have ...
Wildlife tourism including white shark cage-diving is growing in popularity, but these industries remain highly contentious amongst tourists, conservationists, and scientists alike.
Many voice concerns about possible negative impacts - especially when it targets potentially dangerous animals - while proponents cite the socio-economic benefits to justify wildlife tourism activities.
In reality, wildlife tourism is complex, requiring managers to balance the benefits and drawbacks to determine what is acceptable for such industries.
To help solve this question of "is wildlife tourism good or bad?", a tool to help managers assess these industries has been created ...
A painful tradeoff between a number of infected and negative economic impact must be considered before deciding on the lockdown strategy within a city. As national economies continue to crumble, citizens wonder whether their governments did a good job at regulating the lockdown measures.
Russian city of St. Petersburg is at the frontlines of this ongoing war with Covid-19. To combat this situation effectively, Russian government allocated significant funds for the research. Results followed. Scientists from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) modified the existing SIR class pandemic prediction model. Now it is better.
But why? What is the nature ...
Breast cancer is the commonest fatal cancer in women. Early detection increases a woman's chances of recovery. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an accurate technique for detecting and classifying tumours in breast tissue. However, it sometimes causes "false alarms", thus requiring further investigation (biopsy) and in some cases even resulting in so-called overtreatment, that is to say unnecessary surgery. For the first time, a research team from MedUni Vienna has now confirmed a threshold value for a non-invasive imaging biomarker. This can be incorporated into short standard MRI scans ...
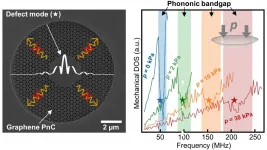
Without electronics and photonics, there would be no computers, smartphones, sensors, or information and communication technologies. In the coming years, the new field of phononics may further expand these options. That field is concerned with understanding and controlling lattice vibrations (phonons) in solids. In order to realize phononic devices, however, lattice vibrations have to be controlled as precisely as commonly realized in the case of electrons or photons.
Phononic cyrstals
The key building block for such a device is a phononic ...
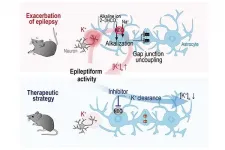
Tohoku University scientists and their colleagues in Germany have revealed that a first-time exposure to only a brief period of brain hyperactivity resulted in an acute breakdown of the inter-cellular network of glial cells. Pharmacological intervention of the glial plasticity may provide a new preventative strategy for fighting epilepsy.
The findings were detailed in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by neuronal hyper-excitation and a progression of seizures with each episode. Anti-epileptic drugs are mostly aimed at suppressing hyperactivity, ...