(Press-News.org) A lot of us recycle our old textiles, but few of us know that they are very difficult to re-use, and often end up in landfills anyway. Now, researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed a method that converts cotton into sugar, that in turn can be turned into spandex, nylon or ethanol.
WATCH: New method transforms old cotton into glucose
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B1V--prLs08
Every year, an estimated 25 million tonnes of cotton textiles are discarded around the world. In total, 100 million tonnes of textiles are thrown out. In Sweden, most of the material goes straight into an incinerator and becomes district heating. In other places, it is even worse, as clothes usually end up in landfills.
"Considering that cotton is a renewable resource, this is not particularly energy-efficient", says Edvin Ruuth, researcher in chemical engineering at Lund University.
"Some fabrics still have such strong fibres that they can be re-used. This is done today and could be done even more in future. But a lot of the fabric that is discarded has fibres that are too short for re-use, and sooner or later all cotton fibres become too short for the process known as fibre regeneration."
At the Department of Chemical Engineering in Lund where Edvin Ruuth works, there is a great deal of accumulated knowledge about using micro-organisms and enzymes, among other things, to transform the "tougher" carbohydrates in biomass into simpler molecules. This means that everything from biological waste and black liquor to straw and wood chips can become bioethanol, biogas and chemicals.
Now the researchers have also succeeded in breaking down the plant fibre in cotton - the cellulose - into smaller components. However, no micro-organisms or enzymes are involved this time; instead, the process involves soaking the fabrics in sulphuric acid. The result is a clear, dark, amber-coloured sugar solution.
"The secret is to find the right combination of temperature and sulphuric acid concentration", explains Ruuth, who fine-tuned the 'recipe' together with doctoral student Miguel Sanchis-Sebastiá and professor Ola Wallberg.
Glucose is a very flexible molecule and has many potential uses, according to Ruuth.
"Our plan is to produce chemicals which in turn can become various types of textiles, including spandex and nylon. An alternative use could be to produce ethanol."
From a normal sheet, they extract five litres of sugar solution, with each litre containing the equivalent of 33 sugar cubes. However, you couldn't turn the liquid into a soft drink as it also contains corrosive sulphuric acid.
One of the challenges is to overcome the complex structure of cotton cellulose.
"What makes cotton unique is that its cellulose has a high crystallinity. This makes it difficult to break down the chemicals and reuse their components. In addition, there are a lot of surface treatment substances, dyes and other pollutants which must be removed. And structurally, a terrycloth towel and an old pair of jeans are very different", says Ruuth.
"Thus it is a very delicate process to find the right concentration of acid, the right number of treatment stages and temperature."
The concept of hydrolizing pure cotton is nothing new per se, explains Ruuth; it was discovered in the 1800s. The difficulty has been to make the process effective, economically viable and attractive.
"Many people who tried ended up not utilising much of the cotton, while others did better but at an unsustainable cost and environmental impact", says Ruuth.
When he started making glucose out of fabrics a year ago, the return was a paltry three to four per cent. Now he and his colleagues have reached as much as 90 per cent.
Once the recipe formulation is complete, it will be both relatively simple and cheap to use.
However, for the process to become a reality, the logistics must work. There is currently no established way of managing and sorting various textiles that are not sent to ordinary clothing donation points.
Fortunately, a recycling centre unlike any other in the world is currently under construction in Malmö, where clothing is sorted automatically using a sensor. Some clothing will be donated, rags can be used in industry and textiles with sufficiently coarse fibres can become new fabrics. The rest will go to district heating.
Hopefully, the proportion of fabrics going to district heating will be significantly smaller once the technology from Lund is in place.
INFORMATION:
TAMPA, Fla. - Genetic alterations of the KRAS gene are some of the most common mutations in lung cancer patients, but unfortunately these patients have few effective treatment options. Drugs that target the G12C mutation in KRAS have shown some activity in lung cancer; however, alternative signaling pathways are often activated that bypass the KRAS inhibitor, resulting in drug resistance. In a new article published in Clinical Cancer Research, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers show that various subtypes of lung cancer cells activate different signaling pathways in response to KRASG12C inhibitor treatment. These results may help identify potential combination therapy approaches and guide ...
Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major driver of global warming, but this gas could also serve as a valuable resource. Researchers at KAUST have developed an efficient catalyst that uses light energy to convert CO2 and hydrogen into methane (CH4). This counteracts the release of CO2 when methane is burned as a fuel.
Many researchers worldwide are exploring ways to convert CO2 into useful carbon-based chemicals, but their efforts have been limited by low efficiencies that restrict the potential for large-scale application.
"Our approach is based on the synergistic combination of light and heat, known as the photothermal effect," says postdoc Diego Mateo. He explains that the heat is generated by the interaction of light with the catalyst, ...
Spikes in temperature can affect a plant's fertility, resulting in a reduction of yield and economic loss
How plants can protect themselves from stress has been studied by a consortium led by the University of Warwick
Two argonaute-like proteins protect the plant's fertility, understanding these proteins is critical to safeguarding crop production
As Temperatures rise due to global warming the need to protect plants from stressful conditions has increased, as stress can cause a loss in yield and cause further impact economically. A consortium led by the University of Warwick have successfully identified ...
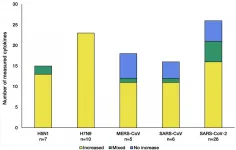
Respiratory viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 (causing COVID-19) can often catalyse an overactive immune response that leads to a life-threatening cycle, known as a cytokine storm. Analysing cytokine responses from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and similar common respiratory viruses has unearthed glaringly important differences in how SARS-CoV-2 affects cytokines compared to other common respiratory viruses.
The comprehensive data resource aims to help specialists identify better treatments and diagnosis of underlying causes that can cause the deadly cytokine storm.
Scientists at the ...
In order to avoid the occurrence of such effects, the Federal Institute for Health Protection of Consumers and Veterinary Medicine (BgVV) recommended guidance values for maximum THC levels in various food groups in 2000. The guidance value for beverages was given as 0.005 mg/kg, for edible oils with 5 mg/kg and for all other foods with 0.150 mg/kg. In 2018, the BfR came to the conclusion that these values no longer correspond to current scientific knowledge.
Instead, the BfR recommends that the toxicological assessment of hemp-containing foods be carried out on the basis of the acute reference dose (ARfD) of 1 microgram Δ-THC/kg body-weight derived by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in 2015. The ARfD specifies the estimated maximum quantity ...
DNA nanotechnology - the research field using DNA molecules as building material - has developed rapidly during recent years and enabled the construction of increasingly complex nanostructures. DNA nanostructures, such as DNA origami, serve as an excellent foundation for nanocarrier-based drug delivery applications, and examples of their use in medical treatments have already been demonstrated. Although the stability of such DNA nanostructures under physiological conditions can be improved, little is known about their digestion by endonucleases, which, found everywhere in our blood and tissues, are responsible for destroying foreign DNA in our bodies.
To tackle this emerging question, a ...
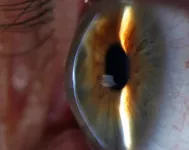
Scientists have taken a significant step forward in their search for the origin of a progressive eye condition which causes sight loss and can lead to corneal transplant.
A new study into keratoconus by an international team of researchers, including a University of Leeds group led by Chris Inglehearn, Professor of Molecular Ophthalmology in the School of Medicine, has for the first time detected DNA variations which could provide clues as to how the disease develops.
Keratoconus causes the cornea, which is?the clear outer layer?at the front of the eye, to thin and bulge outwards into a cone shape over time, resulting in blurred vision and sometimes blindness. It usually emerges in young adulthood, often with lifelong ...
Researchers are in the search for generalisable rules and patterns in nature. Biogeographer Julia Kemppinen together with her colleagues tested if plant functional traits show similar patterns along microclimatic gradients across far-apart regions from the high-Arctic Svalbard to the sub-Antarctic Marion Island. Kemppinen and her colleagues found surprisingly identical patterns.
It is widely known that global vegetation patterns and plant properties follow major differences in climate. Yet, it has remained a mystery how well the same rules can be applied at very local scales. Are responses to the environment similar in plant communities ...
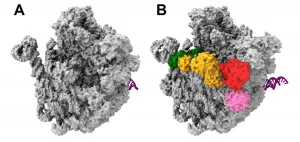
Ribosome formation is viewed as a promising potential target for new antibacterial agents. Researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin have gained new insights into this multifaceted process. The formation of ribosomal components involves multiple helper proteins which, much like instruments in an orchestra, interact in a coordinated way. One of these helper proteins - protein ObgE - acts as the conductor, guiding the entire process. The research, which produced the first-ever image-based reconstruction of this process, has been published in Molecular Cell*.
Ribosomes are an essential component of all living cells. Frequently referred to as 'molecular protein factories', they translate genetic information into chains of linked-up ...
What can you see on this picture (next to thearticle)? Say what comes to your mind immediately!
If you said „star", you focus rather on the details, if you said „sun", then rather on the global pattern.
People can be different in whether they typically see the forest or the trees, but the dominant attentional mode is focusing first on the whole, and then on the details. This is the same with children. Or so it has been until now! Children of the Alpha Generation (who has been born after 2010) typically grow up with mobile devices in their hands which seems to change how they perceive the world, as Hungarian researchers showed.
The Alpha Generation Lab of Diagnostics and Therapy Excellence Programme at Eötvös Loránd University (Budapest) studies ...