Lack of diversity in science
Women and the Global South are strikingly underrepresented
2021-03-02
(Press-News.org) The study examined the gender and affiliations of 1051 top-authors, those scientists with the most publications in 13 leading ecology and conservation journals. The results show that women and the Global South are barely represented on this list. "The overall list of top authors included only 11% women, while 75% of the articles were related to just five countries in the Global North," says Bea Maas, lead author from the University of Vienna. "This massive imbalance in scientific authorship is extremely concerning, especially in the field of ecology and conservation, where diverse perspectives are needed to address global climate and environmental challenges," Maas emphasizes.
Analysed trends over different time periods showed that the proportion of top female authors increased from 3% to 18% between 1945 and 2019, while the Global South recently represented 25% of top publishing authors. "The current proportions of women and scientists from the Global South in the top authorship are still far from societal or academic distributions, and show a clear need to catch up in the promotion of scientific diversity" says Maas. "Hardly any authors from India, China and other densely populated regions of major importance for global conservation and sustainability appear in the list, while many other countries are not represented at all," Maas notes.
The lack of representation of women and the Global South affects not only top authorship in ecology, but also scientific leadership, according to the authors of the study. "In many areas of science, publication output and especially top authorship determine career development and the allocation of leadership positions," Maas explains.
The study highlights links between top authorship and scientific leadership and derives four specific recommendations to promote scientific diversity:
First, scientific journals and societies should make special efforts to promote diversity and inclusion in leadership recruitment. Second, the authors recommend evaluating the trajectory of a scientific career based on diverse competencies beyond publication outputs. Third and fourth, the authors of the study advocate for structural changes to promote parenting time and diversity among staff, collaborators and co-authors to promote and protect the integrity of scientific communities. Other recommendations directed specifically at scientific author and community level, serve, according to Maas "to improve scientific best practice, especially with respect to actively promoting diverse and global perspectives in ecology and conservation."
INFORMATION:
Publication in Conservation Letters:
Bea Maas, Robin J Pakeman, Laurent Godet, Linnea Smith, Vincent Devictor and Richard Primack (2021). Women and Global South strikingly under-represented among top-publishing ecologists. Conservation Letters, in press DOI: 10.1111/conl.12797
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-02
The formation of double bonds between two carbon atoms (C=C) is of central significance in natural organisms. The vast majority of natural substances therefore contain one or more of these double bonds. Compounds with C=C double bonds, the alkenes or olefins, also play a prominent role in the organic chemical industry. A great many chemical processes have therefore been developed over the years to control the formation of C=C bonds.
One such process, olefin metathesis, has received particular attention over the last few decades and the 2005 Nobel Prize for Chemistry was awarded in recognition of its significance.
Despite the many ...
2021-03-02
A technological and biological development that is unprecedented in Israel and the world has been achieved at Tel Aviv University. For the first time, the ear of a dead locust has been connected to a robot that receives the ear's electrical signals and responds accordingly. The result is extraordinary: When the researchers clap once, the locust's ear hears the sound and the robot moves forward; when the researchers clap twice, the robot moves backwards.
The interdisciplinary study was led by Idan Fishel, a joint master student under the joint supervision of Dr. Ben M. Maoz of the Iby and Aladar Fleischman ...
2021-03-02
Removal of pollutants from the air, or atmospheric deposition, is a natural cleaning mechanism. However, the removed toxic matters don't just disappear on the Earth. China's Soil Pollution Survey released in 2014 shows that 19.4% of the Chinese farmland soil was polluted and 82% of pollutant was toxic heavy metals such as cadmium, which can cause chronic health problems.
Atmospheric deposition is an important source of these heavy metals in the soil but it tends to be neglected. Unlike sources from irrigation water, sewage sludge, fertilizers and livestock manures, atmospheric deposition can't easily be perceived. And the paucity of measurements also makes it difficult to track what ...
2021-03-02
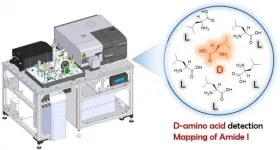
Currently, the roles of free D-amino acids and D-amino acid residues in proteins are garnering extensive attention in biological fields such as molecular biology, physiology, microbiology, and pathophysiology. Because it is crucial to analyze these materials rapidly and accurately, many methods have been employed. However, samples for measurement are currently limited to solutions containing target molecules in the pure form. Hence, there is need for an analytical method for the in situ measurement of biological samples placed on a solid support.
We report the construction of a multidimensional ...
2021-03-02
Earth's surface environments are highly oxygenated - from the atmosphere to the deepest reaches of the oceans, representing a hallmark of active photosynthetic biosphere. However, the fundamental timescale of the oxygen-rich atmosphere on Earth remains uncertain, particularly for the distant future. Solving this question has great ramifications not only for the future of Earth's biosphere but for the search for life on Earth-like planets beyond the solar system.
A new study published in Nature Geoscience this week tackles this problem using a numerical model of biogeochemistry and climate and reveals that the future lifespan ...
2021-03-02
In the group of Prof. Karl Leo, physicists, material scientists and engineers are working jointly on the development of novel organic materials and devices for high performance, flexible and possibly even biocompatible electronics and optoelectronics of the future. Increasing the performance of organic devices is one of the key challenges in their research. It was only last year, when the team headed by Dr. Hans Kleemann announced an important breakthrough with the development of efficient, printable vertical organic transistors.
Now Dr. Zhongbin Wu, Dr. Yuan Liu, and PhD student Erjuan Guo present the first electronic device that combines a vertical organic permeable base transistor (OPBT) and an OLED. With this novel device concept of an organic permeable base light-emitting ...
2021-03-02
Active or voluntary learning is a major topic in education, psychology, and neuroscience. Over the years, numerous studies have shown that when learning occurs through voluntary action, there is a modulation of attention, motivation and cognitive control that makes the process much more effective. Consequently, memory is benefited. However, although the physiological processes underlying this reality had been identified in the brain of mice, their existence in our species had not been corroborated.
Now, an international group of researchers led by ICREA Research Professor Paul Verschure from the SPECS laboratory at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) and Professor Nikolai Axmacher from the Department of Neuropsychology at Ruhr-Universität ...
2021-03-02
The first observations of a space hurricane have been revealed in Earth's upper atmosphere, confirming their existence and shedding new light on the relationship between planets and space.
Hurricanes in the Earth's low atmosphere are known, but they had never before been detected in the upper atmosphere.
An international team of scientists led by Shandong University in China analysed observations made by satellites in 2014 to reveal a long-lasting hurricane, resembling those in the lower atmosphere, in the polar ionosphere and magnetosphere with surprisingly large energy and momentum deposition despite otherwise extremely quiet geomagnetic conditions.
The analysis ...
2021-03-02
The Acheulean was estimated to have died out around 200,000 years ago but the new findings suggest it may have persisted for much longer, creating over 100,000 years of overlap with more advanced technologies produced by Neanderthals and early modern humans.
The research team, led by Dr Alastair Key (Kent) alongside Dr David Roberts (Kent) and Dr Ivan Jaric (Biology Centre of the Czech Academy of Sciences), made the discovery whilst studying stone tool records from different regions across the world. Using statistical techniques new to archaeological science, the archaeologists and conservation experts were able to reconstruct the end of the Acheulean period and re-map the archaeological record.
Previously, ...
2021-03-02
An impressive body of evidence published this week reveals the answer to a mystery that has puzzled plant scientists for more than 30 years: the role of the molecule suberin in the leaves of some of our most productive crops. This discovery could be the key to engineering better crops and ensuring future food security.
Highly productive crops such as sugarcane, sorghum and maize belong to the type of plants that use the more efficient C4 photosynthetic pathway to transform water, sunlight and carbon dioxide (CO2) into sugars.
Scientists have known for a long time that one of key factors that makes C4 photosynthesis more efficient is that they have the capacity to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Lack of diversity in science
Women and the Global South are strikingly underrepresented