INFORMATION:
Second part of the study
Led by the psychologist and researcher Rubén Nieto, the following people have also taken part in this study: Beatriz Sora, also a researcher for the eHealth Lab research group and professor at the Universitat Rovira i Virgili's (URV) Psychology Department; the clinical psychologist Rebeca Pardo, professor of Psychology at the European University of Madrid's and adjunct professor at the Autonomous University of Madrid; and Juan Vicente Luciano Devis and Albert Feliu Soler, who are researchers at the Sant Joan de Déu Research Institute and professionals at the Sant Joan de Déu Health Park.
In order to improve understanding of the situation of people with chronic pain within the context of the pandemic, the researchers have planned a second part of the study in which in-depth interviews will be performed with people suffering from chronic pain in order to gain first-hand knowledge of their situation. Rubén Nieto's team is looking for people who would like to take part. If you are interested, you can contact him by email at rnietol@uoc.edu.
This research supports sustainable development goal (SDG) 3, Good health and well-being.
UOC R&I
The UOC's research and innovation (R&I) is helping overcome pressing challenges faced by global societies in the 21st century, by studying interactions between technology and human & social sciences with a specific focus on the network society, e-learning and e-health.
Over 500 researchers and 51 research groups work among the University's seven faculties and two research centres: the Internet Interdisciplinary Institute (IN3) and the eHealth Center (eHC).
The United Nations' 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and open knowledge serve as strategic pillars for the UOC's teaching, research and innovation.
More information: research.uoc.edu. #UOC25years
The conditions of 70% of people with chronic pain have worsened during the pandemic
The typical profile of participants in this study was that of a woman aged between 30 and 59 who had been suffering pain for the last seven years
2021-03-02
(Press-News.org) The pandemic has impacted significantly on people who suffer chronic pain. A study performed by the eHealth Lab, a research group affiliated with the Faculty of Health Sciences and the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya's eHealth Center, has shown that 70% of the people with chronic pain have seen their condition worsen in terms of severity, frequency of episodes and interference in their daily activities.
A total of 502 patients took part in the study; 88% were women aged between 30 and 59, with long-duration chronic pain (mean duration, 7 years). Most participants (87.6%) had pain in more than one point; the most frequent locations were the abdomen, lower back and neck. The participants answered online surveys, designed in accordance with the IMMPACT (Initiative on Methods, Measurement, and Pain Assessment in Clinical Trials) methodology, and the CPGQ (Chronic Pain Grade Questionnaire) was used to compare changes in the pain perceived by the patients since lockdown began.
The pandemic worsens pain
The results showed that job insecurity, worries about the future, the number of people living in the same dwelling, having someone close who has died of COVID-19, or fear of becoming infected with the virus may be related with a worsening of the pain.
The study also shows that the pandemic has favoured the emergence of new pain triggers. While stress and weather changes were the most frequently mentioned triggers before the pandemic, during lockdown a large number of participants have mentioned worrying about the future, sleep problems, insecurity, negative thoughts, sadness, loneliness, insufficient physical activity and fear of contagion as triggers.
New ways of coping with pain
The pandemic has also changed how a significant proportion of patients manage their pain. More than half (54.5%) have changed how they cope with it: "The study has shown that since the state of emergency began, more than half of the patients have used rest to manage their pain, and a similar percentage have increased the consumption of medication. Both could have counterproductive effects," explained Rubén Nieto, professor and researcher at the UOC's eHealth Lab. However, with the pandemic, people have also started turning to a new positive way to combat pain. Indeed, 48.2% have included stretching exercises as a new tool for dispelling pain.
ICTs, an opportunity for the future
"When there is a chronic pain problem, it is important that people be able to learn to live with it, focusing on achieving their life goals, with or without pain. It is difficult to eliminate the pain altogether, but it is possible to learn to cope with it and live with it. Biopsychosocial interventions may be useful, in which holistic approaches to pain management are used", explained Rubén Nieto, who is a specialist in understanding, assessing and treating pain problems from a multidimensional viewpoint.
Unfortunately, most people do not have access to these interventions, as few centres offer this type of treatment, and health professionals receive little specific training in pain management, according to Nieto. However, ICTs are emerging as a useful tool for taking this type of treatment to chronic pain patients: "ICTs provide an opportunity for combating pain and improving well-being, since they can facilitate access to evidence-based interventions at an affordable cost. And they can increase personal autonomy and empowerment", explained Nieto, who focuses part of his research on applying new technologies to health problems. "We need to learn from the experience gained from the pandemic in the use of ICTs in health," he continued. "The possibilities are limitless, from the classic teleconsultation to solutions based on artificial intelligence. But first we must plan and test their use."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In equilibrium
2021-03-02
Organometallic reagents are essential tools in synthetic chemistry. They work even better and more effectively in combination with alkali alkoxides. The exact nature of this effect has never been well understood. A team based in Switzerland has now performed a detailed study of the mechanism of reaction of aryl bromides with organo-magnesium reagents and lithium alkoxides. As reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie, a complex equilibrium of bimetallic intermediates plays a key role.
Substituted aromatic ring systems are an important class of building block for the synthesis of many products, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and ...
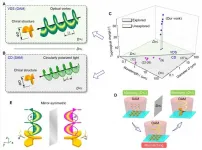
Researchers detects chiral structures using vortex light
2021-03-02
Recently, the Laboratory of Micro and Nano Engineering, School of Engineering Science, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has made important progress in the field of structural chirality detection research using vortex light and found that photon orbital angular momentum can efficiently detect the optical chiral signal of structures.
The achievement was published in an international well-known journal PNAS.
Chiral structures are widely found in nature, such as DNA double helix structures, plant tendrils and shells. In addition to observing the geometry of objects, their chirality can also be distinguished by the interaction of light with matter. For example, the detection of circular ...
Polymerization process of hydrogel microspheres on video
2021-03-02
Aqueous free-radical precipitation polymerization is one of the most useful methods to prepare the uniformly sized hydrogel microspheres (microgels), and an understanding of the polymerization mechanism is crucial to control the structure or physicochemical properties of microgels. However, the details of the mechanism of precipitation polymerization remain unclear.
Thus, first author Yuichiro Nishizawa, Prof. Daisuke Suzuki of the Graduate School of Textile Science & Technology, Shinshu University and Prof. Takayuki Uchihashi of Nagoya University set out to clarify the formation mechanism of microgels during precipitation polymerization by evaluating structural evolution and thermoresponsiveness of developing microgels during ...
Lack of diversity in science
2021-03-02
The study examined the gender and affiliations of 1051 top-authors, those scientists with the most publications in 13 leading ecology and conservation journals. The results show that women and the Global South are barely represented on this list. "The overall list of top authors included only 11% women, while 75% of the articles were related to just five countries in the Global North," says Bea Maas, lead author from the University of Vienna. "This massive imbalance in scientific authorship is extremely concerning, especially in the field of ecology and conservation, ...
Saarbruecken chemists develop variety of industrially important synthetic process
2021-03-02
The formation of double bonds between two carbon atoms (C=C) is of central significance in natural organisms. The vast majority of natural substances therefore contain one or more of these double bonds. Compounds with C=C double bonds, the alkenes or olefins, also play a prominent role in the organic chemical industry. A great many chemical processes have therefore been developed over the years to control the formation of C=C bonds.
One such process, olefin metathesis, has received particular attention over the last few decades and the 2005 Nobel Prize for Chemistry was awarded in recognition of its significance.
Despite the many ...
A world first: A robot able to "hear" through the ear of a locust
2021-03-02
A technological and biological development that is unprecedented in Israel and the world has been achieved at Tel Aviv University. For the first time, the ear of a dead locust has been connected to a robot that receives the ear's electrical signals and responds accordingly. The result is extraordinary: When the researchers clap once, the locust's ear hears the sound and the robot moves forward; when the researchers clap twice, the robot moves backwards.
The interdisciplinary study was led by Idan Fishel, a joint master student under the joint supervision of Dr. Ben M. Maoz of the Iby and Aladar Fleischman ...
Cleaner air, less soil pollution: Unintended but beneficial side effect of Clean Air Act
2021-03-02
Removal of pollutants from the air, or atmospheric deposition, is a natural cleaning mechanism. However, the removed toxic matters don't just disappear on the Earth. China's Soil Pollution Survey released in 2014 shows that 19.4% of the Chinese farmland soil was polluted and 82% of pollutant was toxic heavy metals such as cadmium, which can cause chronic health problems.
Atmospheric deposition is an important source of these heavy metals in the soil but it tends to be neglected. Unlike sources from irrigation water, sewage sludge, fertilizers and livestock manures, atmospheric deposition can't easily be perceived. And the paucity of measurements also makes it difficult to track what ...
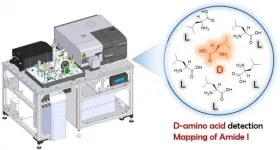
Development of a multidimensional vibrational circular dichroism system with a quantum cascade laser
2021-03-02
Currently, the roles of free D-amino acids and D-amino acid residues in proteins are garnering extensive attention in biological fields such as molecular biology, physiology, microbiology, and pathophysiology. Because it is crucial to analyze these materials rapidly and accurately, many methods have been employed. However, samples for measurement are currently limited to solutions containing target molecules in the pure form. Hence, there is need for an analytical method for the in situ measurement of biological samples placed on a solid support.
We report the construction of a multidimensional ...
How much longer will the oxygen-rich atmosphere be sustained on Earth?
2021-03-02
Earth's surface environments are highly oxygenated - from the atmosphere to the deepest reaches of the oceans, representing a hallmark of active photosynthetic biosphere. However, the fundamental timescale of the oxygen-rich atmosphere on Earth remains uncertain, particularly for the distant future. Solving this question has great ramifications not only for the future of Earth's biosphere but for the search for life on Earth-like planets beyond the solar system.
A new study published in Nature Geoscience this week tackles this problem using a numerical model of biogeochemistry and climate and reveals that the future lifespan ...
Dresden researchers develop new strategy for efficient OLED active matrix displays
2021-03-02
In the group of Prof. Karl Leo, physicists, material scientists and engineers are working jointly on the development of novel organic materials and devices for high performance, flexible and possibly even biocompatible electronics and optoelectronics of the future. Increasing the performance of organic devices is one of the key challenges in their research. It was only last year, when the team headed by Dr. Hans Kleemann announced an important breakthrough with the development of efficient, printable vertical organic transistors.
Now Dr. Zhongbin Wu, Dr. Yuan Liu, and PhD student Erjuan Guo present the first electronic device that combines a vertical organic permeable base transistor (OPBT) and an OLED. With this novel device concept of an organic permeable base light-emitting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] The conditions of 70% of people with chronic pain have worsened during the pandemicThe typical profile of participants in this study was that of a woman aged between 30 and 59 who had been suffering pain for the last seven years