Study reveals impact of lockdown on violence in a UK capital city
Emergency department data shows 'large reduction' in violent injury during lockdown -- but no change in violence in the home
2021-03-02
(Press-News.org) The first UK COVID-19 lockdown saw a "rapid and sustained" fall in violence outside the home in the Welsh capital city, a new study led by Cardiff University has shown.
Researchers from Cardiff University's Crime and Security Research Institute (CSRI) and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention studied data from Cardiff's sole emergency department (ED) from March to June 2020 and compared it to weekly data from January 2019 onwards.
They found there were almost 60% fewer attendances per week for violent injury outside the home in the first lockdown during which time going outside was allowed only for limited reasons like medical need, exercise or food shopping.
The researchers also found a significant reduction in the use of weapons and in violence-related ED visits by males of all ages.
Contrary to expectation, the analysis found no significant increase in visits resulting from violence inside the home.
The findings - the first analysis of violence from this perspective during the COVID-19 pandemic - are published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Lead author Professor Jonathan Shepherd, from the CSRI, said: "This sudden fall in violent injury is the largest any of us has ever seen. It's likely to reflect closure of city centre pubs and clubs in and around which most violence takes place, and widespread compliance with lockdown restrictions."
The researchers investigated the association between COVID-19 lockdown and ED visits for violence-related injuries using detailed violence screening first implemented in Cardiff two decades ago. They studied violence time, whether it took place inside or outside the home, weapon use, perpetrator type and the age and sex of the injured.
They examined visits at Cardiff's only emergency department - at the University Hospital of Wales - for violence-related injury from 1 January 2019 to 9 June 2020. The pre-lockdown period studied was 63 weeks and the lockdown period, 12 weeks.
They used a "difference-in-difference" regression model to identify statistically significant changes during lockdown. This model accounted for seasonal changes in the number of attendances.
For violence outside the home, they found significant decreases in ED visits during the lockdown of 92% among females under the age of 18 and 65% in males of all ages, and a significant decrease (92%) in those injured with a weapon. While people injured by strangers decreased significantly (65%), numbers of those injured by family members did not change significantly.
Regarding violence in the home, no significant change was found in any category.
"The lack of evidence of increase in violence in the home during the first UK lockdown is reassuring," said Professor Shepherd.
"The massive decrease outside the home but no increase in the home reflects the nature of the two environments. The night-time economy (pubs and clubs and the streets where they are situated) is an environment which facilitates violence and violent injury.
"On the other hand, in our study, the home environment is much less conducive to violence and violent injury. People who would have been injured in violence in the night-time economy are not injured in violence when they stay at home."
The researchers found that during these first months of the COVID-19 epidemic ED visits for all reasons dropped by 43% relative to the previous year. They said that while fears about catching COVID-19 may have affected the number of violence related ED visits, it is unlikely this affected the overall findings.
Cardiff University is due to release an England and Wales analysis of violence during the COVID-19 pandemic next month.
INFORMATION:
The study, Association between COVID-19 lockdown measures and emergency department visits for violence-related injuries in Cardiff, Wales, March-June 2020, is attached as a PDF and can be found here after the embargo
A graph of the key findings can be found here
Professor Jonathan Shepherd is available for interview
For further information and interview requests contact:
Gerry Holt, comms & marketing, Cardiff University - 029 2087 5596 or HoltG2@cardiff.ac.uk
Cardiff University is recognised in independent government assessments as one of Britain's leading teaching and research universities and is a member of the Russell Group of the UK's most research intensive universities. The 2014 Research Excellence Framework ranked the University 5th in the UK for research excellence. Among its academic staff are two Nobel Laureates, including the winner of the 2007 Nobel Prize for Medicine, Professor Sir Martin Evans. Founded by Royal Charter in 1883, today the University combines impressive modern facilities and a dynamic approach to teaching and research. The University's breadth of expertise encompasses: the College of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences; the College of Biomedical and Life Sciences; and the College of Physical Sciences and Engineering, along with a longstanding commitment to lifelong learning. Cardiff's flagship Research Institutes are offering radical new approaches to pressing global problems. More at http://www.cardiff.ac.uk
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- When a vehicle travels over a wet or flooded road, water builds up in front of the tire and generates a lift force. In a phenomenon known as hydroplaning, this force can become large enough to lift the vehicle off the ground.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, scientists from the CNRS, the University of Lyon, and The Michelin Group use a laser imaging technique to study water flow in front of and through tire grooves.
To counteract hydroplaning, tread designs are chosen to drain water from the front of the tire without decreasing its ability to adhere to the road. Very few quantitative experimental studies of the movement of water through tire grooves have been done, so little is known about the exact flow patterns in ...
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: This study suggests that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, a hotel- based isolation and quarantine strategy that delivers integrated medical and behavioral health support to people experiencing homelessness can be done safely outside the hospital setting.
Authors: Jonathan D. Fuchs, M.D., M.P.H., of the San Francisco Department of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0490)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: Wearing surgical face masks for 30 minutes was not associated with changes in respiratory parameters or clinical signs of respiratory distress in this study of 47 infants and young children in Italy.
Authors: Silvia Bloise, M.D., of Sapienza University of Rome in Italy, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0414)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
2021-03-02
The Medicare Part D program would have saved $977 million in a single year if all branded prescription drugs requested by prescribing clinicians had been substituted by a generic option, according to a new study by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. And if Medicare patients had requested generic drugs instead of brand name drugs, the Medicare Part D program would have saved an additional $673 million in one year, for a total savings of $1.7 billion.
Medicare Part D offers supplemental outpatient drug coverage plans for seniors ...
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- Cardiovascular disease remains the number one cause of death globally. Unfortunately, the heart cannot regenerate new tissue, because the cardiomyocytes, or heart muscle cells, do not divide after birth.
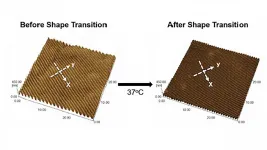
In their paper, published in APL Bioengineering by AIP Publishing, Syracuse researchers developed a shape memory polymer to grow cardiomyocytes. Raising the material's temperature from 30 degrees Celsius to 37 degrees Celsius turned the polymer's flat surface into nanowrinkles, which promoted cardiomyocyte alignment.
The research is part of the growing field of mechanobiology, which investigates how physical forces between cells and changes ...
2021-03-02
A 'Fish DJ' at The University of Queensland has used her knowledge of cool beats to understand brain networks and hearing in baby fish.
The DJ-turned-researcher used her acoustic experience to design a speaker system for zebrafish larvae and discovered that their hearing is considerably better than originally thought.
PhD candidate Rebecca Poulsen from the Queensland Brain Institute said that combining this new speaker system with whole-brain imaging showed how larvae can hear a range of different sounds they would encounter in the wild.
"For many years ...
2021-03-02
[LAKEWOOD, CO; BRIDGEWATER, NJ; March 2, 2021] Two of the world's leading veterinary organizations are proud to announce updated recommendations in the 2021 AAHA/AAFP Feline Life Stage Guidelines. The American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) and the American Association of Feline Practitioners (AAFP) convened a Task Force of experts in feline medicine to define distinct feline life stages and provide a framework for individualized healthcare plans.
Understanding a cat's life stage and lifestyle greatly impacts healthcare strategies. Veterinary professionals have a responsibility to stress ...
2021-03-02
New energy tariffs could leave people on bad deals even worse off despite the potential benefits for everyone, research has found.
The study, led by the University of Leeds, found new types of energy contracts designed for a low carbon future could benefit all types of customer, with opportunities to sell excess energy from solar panels or incentives for using energy at off-peak times.
However, many people were unlikely to choose them because they were disengaged from the energy market, didn't trust energy companies, or already feel satisfied with their current tariffs. ...
2021-03-02
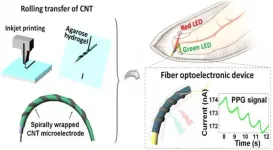
Advances in wearable devices have enabled e-textiles, which fuse lightweight and comfortable textiles with smart electronics, and are garnering attention as the next-generation wearable technology. In particular, fiber electronic devices endowed with electrical properties, while retaining the specific characteristics of textiles, are key elements in manufacturing e-textiles.
Optoelectronic devices are generally constructed using layers of semiconductors, electrodes, and insulators; their performance is greatly affected by the size and structure of the electrodes. Fiber electronic components for e-textiles need to be fabricated on thin, pliable threads; since these ...
2021-03-02
The agricultural cultivation of the staple food of rice harbours the risk of possible contamination with arsenic that can reach the grains following uptake by the roots. In their investigation of over 4,000 variants of rice, a Chinese-German research team under the direction of Prof. Dr Rüdiger Hell from the Centre for Organismal Studies (COS) of Heidelberg University and Prof. Dr Fang-Jie Zhao of Nanjing Agricultural University (China) discovered a plant variant that resists the toxin. Although the plants thrive in arsenic-contaminated fields, the grains contain far less arsenic than other ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reveals impact of lockdown on violence in a UK capital city
Emergency department data shows 'large reduction' in violent injury during lockdown -- but no change in violence in the home