A fluid solution to dendrite growth in lithium metal batteries
2021-03-02
(Press-News.org) A new paper from associate professor Jiandi Wan's group in the UC Davis Department of Chemical Engineering, published in Science Advances, proposes a potential solution to dendrite growth in rechargeable lithium metal batteries. In the paper, Wan's team prove that flowing ions near the cathode can potentially expand the safety and lifespans of these next-generation rechargeable batteries.
Lithium metal batteries use lithium metal as the anode. These batteries have a high charge density and potentially double the energy of conventional lithium ion batteries, but safety is a big concern. When they charge, some ions are reduced to lithium metal at the cathode surface and form irregular, tree-like microstructures known as dendrites, which can eventually cause a short circuit or even an explosion.
The theory is that dendrite growth is caused by the competition of mass transfer and reduction rate of lithium ions near the cathode surface. When the reduction rate of ions is much faster than the mass transfer, it creates an electroneutral gap called the space-charged layer near the cathode that contains no ions. The instability of this layer is thought to cause dendrite growth, so reducing or eliminating it might reduce dendrite growth and therefore extend the life of a battery.
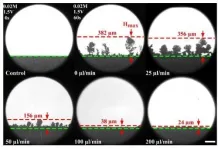
Dendrite growth reduced 99 percent
Wan's idea was to flow ions through the cathode in a microfluidic channel to restore a charge and offset this gap. In the paper, the team outlined their proof-of concept tests, finding that this flow of ions could reduce dendrite growth by up to 99 percent.
For Wan, the study is exciting because it shows the effectiveness of applying microfluidics to battery-related problems and paves the way for future research in this area.
"With this fundamental study and microfluidic approaches, we were able to quantitatively understand the effect of flow on dendrite growth," he said. "Not many groups have studied this yet."
Though it is likely not possible to directly incorporate microfluidics in real batteries, Wan's group is looking at alternative ways to apply the fundamental principles from this study and introduce local flows near the cathode surface to compensate cations and eliminate the space charge layer.
"We are quite excited to explore the new applications of our study," he said. "We are already working on design of the cathode surface to introduce convective flows."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-02
In a new study from Shiley Eye Institute at UC San Diego Health, researchers have identified a potential new marker that shows cardiovascular disease may be present in a patient using an optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan -- a non-invasive diagnostic tool commonly used in ophthalmology and optometry clinics to create images of the retina. The finding suggests it may be possible to detect heart disease during an eye examination.
In the paper published March 2, 2021 in EClinical Medicine by The Lancet, the research team examined lesions of the retina, the inner-most, light-sensitive layer of the eye, to determine if a cardiovascular disorder may be present.
"The eyes are a window into our health, and many diseases can manifest in the eye; cardiovascular ...
2021-03-02
NEW YORK, NY--March 2, 2021--In March and April 2020, mental health claim lines for individuals aged 13-18, as a percentage of all medical claim lines, approximately doubled over the same months in the previous year. At the height of the spring wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, this rise in mental health claim lines amounted to 97.0 percent in March and 103.5 percent in April. These are among the many findings in FAIR Health's new white paper, the seventh in its COVID-19 studies, The Impact of COVID-19 on Pediatric Mental Health: A Study of Private Healthcare Claims.
In those same months of March and April 2020, all medical claim lines (including mental health claim lines) decreased by approximately ...
2021-03-02
When it comes to the evolution of the mammal spine -- think of animals whose backbone allows them to gallop, hop, swim, run, or walk upright -- a key part of the tale is quite simple.
Because nonmammalian synapsids, the extinct forerunners to mammals, had similar traits to living reptiles (like having their limbs splayed out to the side instead of tucked into their body like today's mammals), the strongheld belief was that they must have also moved in similar ways. Primarily, their backbones must have moved side-to-side, bending like those of modern lizards, instead of the up-and-down bending motion mammal spines are known for. It's believed over time, and in response to selective pressures, the mammal spine evolved from that lizard like side-to-side bending ...
2021-03-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- By modeling wolves in Yellowstone National Park, researchers have discovered that how a population is organized into social groups affects the spread of infectious diseases within the population. The findings may be applicable to any social species and could be useful in the protection of endangered species that suffer from disease invasion.
Like other social carnivores, wolves tend to form territorial social groups that are often aggressive toward each other and may lead to fatalities. During these encounters, infectious diseases -- like mange and canine distemper -- can spread between groups, which can further reduce the number of individuals in a group.
"Previous social group-disease models have assumed that groups do not change ...
2021-03-02
WESTMINSTER, Colorado - March 02, 2021 - Herbicide-resistant weeds have fueled a growing demand for effective, nonchemical weed controls. Among the techniques used are chaff carts, impact mills and other harvest-time practices that remove or destroy weed seeds instead of leaving them on the field to sprout.
A recent article in the journal Weed Science explores whether such harvest-time controls would be effective against downy brome, Italian ryegrass, feral rye and rattail fescue - weeds that compete with winter wheat in the Pacific Northwest. Researchers set out to determine whether ...
2021-03-02
New research has found that shrimp like creatures on the South Coast of England have 70 per cent less sperm than less polluted locations elsewhere in the world. The research also discovered that individuals living in the survey area are six times less numerous per square metre than those living in cleaner waters.
This discovery, published today in Aquatic Toxicology, mirrors similar findings in other creatures, including humans. The scientist leading research at the University of Portsmouth believes pollutants might be to blame, further highlighted by this ...
2021-03-02
Resveratrol is a plant compound found primarily in red grapes and Japanese knotweed. Its synthetic variant has been approved as a food ingredient in the EU since 2016. At least in cell-based test systems, the substance has anti-inflammatory properties. A recent collaborative study by the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich and the Institute of Physiological Chemistry at the University of Vienna has now shown that the bitter receptor TAS2R50 is involved in this effect. The team of scientists led by Veronika Somoza ...
2021-03-02
CHICAGO, March 2, 2021 -- More than 70 percent of dentists surveyed by the American Dental Association (ADA) Health Policy Institute are seeing an increase of patients experiencing teeth grinding and clenching, conditions often associated with stress. This is an increase from ADA data released in the fall that showed just under 60 percent of dentists had seen an increase among their patients.
"Our polling has served as a barometer for pandemic stress affecting patients and communities seen through the eyes of dentists," said Marko Vujicic, Ph.D., chief economist and vice president of the ADA Health Policy Institute. "The increase over time suggests stress-related conditions have become substantially more prevalent since the onset of COVID-19."
The ...
2021-03-02
BOSTON - Lymph nodes in the armpit area can become swollen after a COVID-19 vaccination, and this is a normal reaction that typically goes away with time. Radiologists at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) who recently published an approach to managing this situation in women who receive mammograms for breast cancer screening in the American Journal of Roentgenology have now expanded their recommendations to include care for patients who undergo other imaging tests for diverse medical reasons. Their guidance is published in the Journal of the American College of Radiology.
"Our ...
2021-03-02
A new study published today in the journal Geophysical Research Letters used NASA's ice-measuring laser satellite to identify atmospheric river storms as a key driver of increased snowfall in West Antarctica during the 2019 austral winter.
These findings from scientists at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California San Diego and colleagues will help improve overall understanding of the processes driving change in Antarctica, and lead to better predictions of sea-level rise. The study was funded by NASA, with additional support from the Rhodium Group's Climate Impact Lab, a consortium ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A fluid solution to dendrite growth in lithium metal batteries






