Zinc oxide: key component for the methanol synthesis reaction over copper catalysts
A team of researchers around the Fritz Haber Institute have found out that the important industrial process of methanol production can be positively influenced if the copper catalyst used in the reaction comes into contact with zinc oxide.
2021-03-04
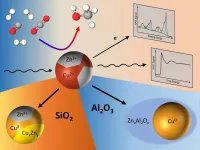
(Press-News.org) The current commercial production of methanol through the hydrogenation of the green-house gas CO2 relies on a catalyst consisting of copper, zinc oxide and aluminum oxide. Even though this catalyst has been used for many decades in the chemical industry, unknowns still remain. A team of researchers from the Interface Science Department of the Fritz-Haber-Institute of the Max Planck Society, the Ruhr-University Bochum, Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), FZ Juelich and Brookhaven National Laboratory have now elucidated the origin of intriguing catalytic activity and selectivity trends of complex nanocatalysts while at work. In particular, they shed light on the role of the oxide support and unveiled how the methanol production can be influenced by minute amounts of zinc oxide in intimate contact with copper.
Methanol can serve as an energy source or as a raw material for the production of other chemicals, with over 60 million metric tons produced yearly. The traditional copper, zinc oxide and aluminum oxide catalyst converts synthesis gas, which is composed of H2, CO and CO2, into methanol. Though reliable, this specific catalyst's efficiency changes over time, thus affecting its longevity, as is the case with many catalysts. "We therefore studied copper and mixed copper-zinc nanoparticles on various oxide supports to understand how they interact and evolve and unravel the role of each catalyst constituent. This knowledge will serve to improve future catalysts." says Núria Jiménez Divins, one of the lead authors of the study.
The team investigated the catalytic process under realistic reaction conditions reproducing those applied in the industrial process, meaning high pressures (20-60 bar) and mild temperatures. This required synchrotron-generated X-ray radiation. Simon R. Bare from the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, who contributed to the experiments, explains: "Reactions at such temperature and high pressures need to take place in a closed container which should also be transparent for the X-rays, which makes the measurements challenging. The special reactor design in combination with synchrotron radiation allowed us to undertake so-called operando-measurements, where we watched live what happens to the catalytic components at the industrially relevant reaction conditions." This allowed the researchers to follow not just the birth and death of the catalyst, but also its development and transformations leading to changes in its activity and selectivity.
By combining results from microscopy, spectroscopy and catalytic measurements, the team found that some supports had a more positive influence on the performance of the catalyst than others because of how they interacted with zinc oxide, which was available in a highly dilute manner as part of Cu-Zn nanoparticles. On silicon oxide supports, zinc oxide was partially reduced to metallic zinc or gave rise to a brass alloy during the catalytic process, which over time proved to be detrimental for the methanol production. When using aluminum oxide as a support, zinc interacts strongly with the support and gets incorporated in its lattice, giving rise to a change in reaction selectivity towards dimethyl ether. "This is an interesting finding", says David Kordus, the other lead author of the study and PhD student at the Interface Science Department at FHI. "We know now that the choice of support material has an influence on how the active components of the catalyst behaves and dynamically adapts to the reaction conditions. Especially the oxidation state of zinc is critically influenced by this, which should be considered for future catalyst design."
This work published in Nature Communications demonstrates that zinc oxide does not need to be available as part of the support, but that it still has a beneficial function even when available in highly dilute form as part of the nanoparticle catalyst itself. This will help elucidate the methanol synthesis catalysts better and potentially lead to an improvement of the catalyst for this important industrial process.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-04
In 2015, hackers infiltrated the corporate network of Ukraine's power grid and injected malicious software, which caused a massive power outage. Such cyberattacks, along with the dangers to society that they represent, could become more common as the number of cyber-physical systems (CPS) increases.
A CPS is any system controlled by a network involving physical elements that tangibly interact with the material world. CPSs are incredibly common in industries, especially those integrating robotics or similar automated machinery to the production line. However, as CPSs make their way into societal infrastructures such as public transport and energy management, it becomes even more important to ...
2021-03-04
A research review led by Oxford Brookes University has found a large proportion of COVID-19 survivors will be affected by neuropsychiatric and cognitive complications.
Psychologists at Oxford Brookes University and a psychiatrist from Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust, evaluated published research papers in order to understand more about the possible effects of the SARS-COV-2 infection on the brain, and the extent people can expect to experience short and long-term mental health issues.
Patients experienced a range of psychiatric problems
The study found that in the short term, a wide range of neuropsychiatric problems were reported. In one examined study, 95% of clinically ...
2021-03-04
As millions of Fantasy Premier League players mull over a decision whether to start Bruno Fernandes or Mohamed Salah in their teams this weekend, new research by the University of Limerick in Ireland has unlocked the secrets of the popular online game.
A new study by a team of researchers at UL has identified the underlying tactics used by the top-ranked competitors among the seven million players of Fantasy Premier League (FPL), the official - and world's largest - fantasy football game of the English Premier League.
Joseph O'Brien, Professor James Gleeson, and Dr David O'Sullivan, based within the ...
2021-03-04
With three out of four newly emerging infectious human diseases originating in animals*, there is an urgent need to monitor the legal trade in wildlife, according to new research by Vincent Nijman, Professor in Anthropology at Oxford Brookes University.
Professor Nijman, who has been involved in monitoring and regulating the legal wildlife trade for over two decades, said: "Covid-19 more than anything else has put a spotlight on emerging infectious diseases and how this is linked to the trade in wild animals. Few people are aware of its scale. With literally hundreds of millions ...
2021-03-04
New research reveals an essential step in scientists' quest to create targeted, more eco-friendly fungicides that protect food crops.
Scientists have known for decades that biological cells manufacture tiny, round structures called extracellular vesicles. However, their pivotal roles in communication between invading microorganisms and their hosts were recognized only recently.
UC Riverside geneticist Hailing Jin and her team found plants use these vesicles to launch RNA molecules at fungal invaders, suppressing the genes that make the fungi dangerous.
"These vesicles shuttle small RNAs between cells, like tiny Trojan horses with weapons hidden inside," said Jin, a professor of genetics and the Cy Mouradick Chair in the Department of Plant Pathology and Microbiology. ...
2021-03-04
In a close collaboration between experimental and theoretical physicists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), the research groups of Professor Mathias Kläui and Dr. Peter Virnau investigated the behavior of magnetic whirls within nanoscale geometric structures. In their work published in Advanced Functional Materials, the researchers confined small magnetic whirls, so-called skyrmions, in geometric structures. Skyrmions can be created in thin metal films and have particle-like properties: They exhibit high stability and are repelled from each other and from specially prepared walls. Experiments and accompanying computer simulations showed that the mobility of skyrmions within these geometric structures depends massively on their arrangement. In triangles, ...
2021-03-04
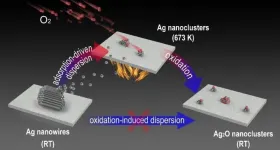
Oxidative dispersion has been widely used in the regeneration of sintered metal catalysts as well as the fabrication of single-atom catalysts.
The consensus on the oxidative dispersion process includes the formation of mobile metal oxide species from large metal particles and the capture of these species on a support surface. Nevertheless, the mechanism of oxidation-induced dispersion has yet to be confirmed via in situ electron microscopic and/or spectroscopic characterizations.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. FU Qiang and Prof. BAO Xinhe from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. YANG Bing from DICP and Prof. GAO Yi ...
2021-03-04
Administering zinc supplements to covid-19 patients with low levels of this element may be a strategy to reduce mortality and recovery time. At the same time, it could help to prevent risk groups, like the elderly, from suffering the worst effects of the disease. These are the findings of a study by physicians and researchers from the Hospital del Mar, Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) and Pompeu Fabra University (UPF), led by Dr. Robert Güerri, a physician at the Infectious Diseases Service of Hospital del Mar, which has just been published in the journal Nutrients.
The study analysed the zinc levels of 249 adult patients treated at the centre between 9 March and 1 April 2020, with an average age of 65 years. The most common symptoms presented at the time of ...
2021-03-04
Researchers discover how to control zinc content in plants: Could help the world's malnourished
Over 2 billion people worldwide are malnourished due to zinc deficiency. Led by the University of Copenhagen, an international team of researchers has discovered how plants sense zinc and use this knowledge to enhance plant zinc uptake, leading to an increase in seed zinc content by 50 percent. The new knowledge might one day be applied towards the cultivation of more nutritious crops.
A deficiency of zinc and other essential dietary nutrients is one of the greatest causes of malnutrition worldwide. More than two billion people are estimated to suffer from zinc deficiency, a problem that can lead to impaired immune systems, mental disorders and stunting. Among other things, ...
2021-03-04
Glycine can stimulate or inhibit neurons in the brain, thereby controlling complex functions. Unraveling the three-dimensional structure of the glycine transporter, researchers have now come a big step closer to understanding the regulation of glycine in the brain. These results, which have been published in Nature, open up opportunities to find effective drugs that inhibit GlyT1 function, with major implications for the treatment of schizophrenia and other mental disorders.
Glycine is the smallest amino acid and a building block of proteins, and also a critical neurotransmitter that can both stimulate or inhibit ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Zinc oxide: key component for the methanol synthesis reaction over copper catalysts
A team of researchers around the Fritz Haber Institute have found out that the important industrial process of methanol production can be positively influenced if the copper catalyst used in the reaction comes into contact with zinc oxide.