Administering zinc to covid-19 patients could help towards their recovery
Mortality in this patient group was 21% compared to 5% of those with higher levels of zinc in the blood
2021-03-04
(Press-News.org) Administering zinc supplements to covid-19 patients with low levels of this element may be a strategy to reduce mortality and recovery time. At the same time, it could help to prevent risk groups, like the elderly, from suffering the worst effects of the disease. These are the findings of a study by physicians and researchers from the Hospital del Mar, Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) and Pompeu Fabra University (UPF), led by Dr. Robert Güerri, a physician at the Infectious Diseases Service of Hospital del Mar, which has just been published in the journal Nutrients.
The study analysed the zinc levels of 249 adult patients treated at the centre between 9 March and 1 April 2020, with an average age of 65 years. The most common symptoms presented at the time of admission were fever, cough and dyspnea. In all cases, they analysed their blood zinc levels, considering those under 50 μ/dl as being low. As explained by Dr. Güerri, first author of the clinical study, they analysed this parameter because "zinc is an essential element for maintaining a variety of biological processes, and altering its levels causes increased susceptibility to infections and increased inflammatory response". For this reason, "given the comorbidities associated with zinc deficiency and its immunomodulatory and antiviral actions, zinc levels and zinc supplementation may prove useful tools to tackle the covid-19 crisis".
Higher mortality in patients with lower zinc levels
1 in 4 patients had low levels of zinc. This group had more severe symptoms and higher levels of inflammation as measured by two markers, C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), which mediate the inflammatory response. On average, their length of hospital stay was three times longer than patients with higher levels of zinc (25 days compared to 8).
Regarding mortality, zinc levels were significantly higher in patients who survived the infection, 62 μ/dl, versus 49 μ/dl for those who died. Moreover, 1 in 5 patients with low zinc levels died. Conversely, the mortality rate of those presenting higher levels upon admission was 5%. The study reveals that a one-unit increase of zinc in blood plasma is directly linked to a 7% reduction of the risk of dying from covid-19. Dr. Güerri highlights that "we have shown the importance of zinc levels in patients' blood as an additional predictor of outcome in covid-19, as well as its potential as a therapeutic tool for treatment. We therefore propose this variable as a new parameter to predict the evolution of patients and we propose initiating clinical trials concerning zinc supplementation in patients with low levels admitted for covid-19 and implementing programmes to administer supplements to groups at risk of having low zinc levels to reduce the effects of the pandemic".
Effect of zinc on the replication of the coronavirus
The study involved the collaboration of the groups of Dr. Rubén Vicente and Dr. Juana Díez at UPF. Their efforts, using in vitro techniques, have focused on studying in parallel the effects of zinc levels on the virus's capacity to expand. The results confirm that the poor prognosis in patients with low concentrations of zinc is due both to the effect that a lack of zinc has on immune imbalance and the increase in viral load, as they found that low levels of zinc enhance the expansion of the virus in infected cells.
At the same time, the results indicate that an element must be sought to enable enhancing the activity of zinc in the cell to block viral replication, as their studies have shown that contrary to what had been speculated at the onset of the pandemic, chloroquine cannot perform this function.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-04
Researchers discover how to control zinc content in plants: Could help the world's malnourished
Over 2 billion people worldwide are malnourished due to zinc deficiency. Led by the University of Copenhagen, an international team of researchers has discovered how plants sense zinc and use this knowledge to enhance plant zinc uptake, leading to an increase in seed zinc content by 50 percent. The new knowledge might one day be applied towards the cultivation of more nutritious crops.
A deficiency of zinc and other essential dietary nutrients is one of the greatest causes of malnutrition worldwide. More than two billion people are estimated to suffer from zinc deficiency, a problem that can lead to impaired immune systems, mental disorders and stunting. Among other things, ...
2021-03-04
Glycine can stimulate or inhibit neurons in the brain, thereby controlling complex functions. Unraveling the three-dimensional structure of the glycine transporter, researchers have now come a big step closer to understanding the regulation of glycine in the brain. These results, which have been published in Nature, open up opportunities to find effective drugs that inhibit GlyT1 function, with major implications for the treatment of schizophrenia and other mental disorders.
Glycine is the smallest amino acid and a building block of proteins, and also a critical neurotransmitter that can both stimulate or inhibit ...
2021-03-04
The oceans are becoming more acidic because of the rapid release of carbon dioxide (CO2) caused by anthropogenic (human) activities, such as burning of fossil fuels. So far, the oceans have taken up around 30% of all anthropogenic CO2 released to the atmosphere. The continuous increase of CO2 has a substantial effect on ocean chemistry because CO2 reacts with water and carbonate molecules. This process, called 'ocean acidification', lowers pH, and calcium carbonate becomes less available. This is a problem for calcifying organisms, such as corals and molluscs, that use calcium carbonate as the main building blocks of their exoskeleton.
In particular, organisms that build their shells from a type of calcium carbonate known as 'aragonite' are in trouble because aragonite is ...
2021-03-04
?Micro-Doppler radars could soon be used in clinical settings to predict injury risk and track recovery progress, according to Penn State researchers.?
Being able to view subtle differences in human movement?would allow health care workers to more accurately identify individuals who may be at risk for injury and to track progress precisely while individuals are recovering from an injury. In an effort to find an accurate, reliable and cost-effective way to measure these subtleties ?in human movement, College of Engineering and College of Medicine researchers teamed up to develop a radar in front ...
2021-03-04
Professor Christiani Jeyakumar Henry, Senior Advisor of Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (SIFBI), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and his team have developed a Glycaemic Index (GI) glossary of non-Western foods. The research paper was published in Nutrition & Diabetes on 6 Jan 2021: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-020-00145-w.
Observational studies have shown that the consumption of low glycaemic index (GI) foods is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly less insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. However, most published GI values focus on Western foods with minimal inclusion of other foods from non-Western countries, hence their application ...
2021-03-04
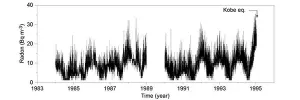
Tohoku University researchers have unearthed further details about radon concentration in the atmosphere before and after earthquakes, moving us closer to being able to anticipate when large earthquakes may hit.
The results of their research were published in the journal Science Reports on February 18, 2021.
Radon is a radioactive noble gas derived from radioactive decays of radium-226 in the ground. Radon bubbles up to the surface and is expelled into the atmosphere.
It has long been known that elevated levels of radon underneath the ground can be detected before and after earthquakes. But the relationship between the mechanisms that cause abnormal changes in radon concentration and the occurrence of earthquakes requires greater ...
2021-03-04
Interspecies interactions are the foundation of ecosystems, from soil to ocean to human gut. Among the many different types of interactions, syntrophy is a particularly important and mutually beneficial interspecies interaction where one partner provides a chemical or nutrient that is consumed by the other in exchange for a reward.
Syntrophy plays an essential role in global carbon cycles by mediating the conversion of organic matter to methane, which is about 30 times more potent than carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas and is a source of sustainable energy. And in the human gut, trillions of microbial cells also interact ...
2021-03-04
Intelligent holographic nanostructures on CMOS sensors for energy-efficient AI security schemes
Today, machine learning permeates our everyday life, with millions of users every day unlocking their phones through facial recognition or passing through AI-enabled automated security checks at airports and train stations. These tasks are possible thanks to sensors that collect optical information to feed it to a neural network in a computer. Imagine to empower the sensors in the devices you use every day to perform artificial intelligence functions without a computer - as simply as putting glasses on them.
The integrated holographic perceptrons developed by a research team at University of Shanghai for Science and Technology led ...
2021-03-04
Nairobi/Paris, 4 March 2021 - An estimated 931 million tonnes of food, or 17% of total food available to consumers in 2019, went into the waste bins of households, retailers, restaurants and other food services, according to new UN research conducted to support global efforts to halve food waste by 2030.
The weight roughly equals that of 23 million fully-loaded 40-tonne trucks -- enough bumper-to-bumper to circle the Earth 7 times.
The Food Waste Index Report 2021, from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and partner organization WRAP, looks at food waste that occurs in retail outlets, restaurants and homes - ...
2021-03-04
People with higher incomes tend to feel prouder, more confident and less afraid than people with lower incomes, but not necessarily more compassionate or loving, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
In a study of data from 162 countries, researchers found consistent evidence that higher income predicts whether people feel more positive "self-regard emotions," including confidence, pride and determination. Lower income had the opposite effect, and predicted negative self-regard emotions, such as sadness, fear and shame. The research was published online in the journal Emotion. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Administering zinc to covid-19 patients could help towards their recovery
Mortality in this patient group was 21% compared to 5% of those with higher levels of zinc in the blood