How to choose low glycaemic index (GI) foods? A GI 'glossary' of Asian foods released
Singapore research team's comprehensive study provides the glycaemic index values for a variety of foods that are consumed in non-Western countries, such as Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, India, China, Japan, South Korea, Middle East and more
2021-03-04
(Press-News.org) Professor Christiani Jeyakumar Henry, Senior Advisor of Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (SIFBI), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and his team have developed a Glycaemic Index (GI) glossary of non-Western foods. The research paper was published in Nutrition & Diabetes on 6 Jan 2021: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-020-00145-w.
Observational studies have shown that the consumption of low glycaemic index (GI) foods is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly less insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. However, most published GI values focus on Western foods with minimal inclusion of other foods from non-Western countries, hence their application is of limited global use.
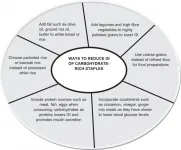
The team's comprehensive study provides the GI values for a variety of foods that are consumed in non-Western countries, such as Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, India, China, Japan, South Korea, Middle East and more. The review extends and expands on the current GI tables to widen its application globally. The GI data compiled consists of both single and mixed meals. This is a major advance to many GI tables that have focused on single foods. Mixed meals in Asia are complex in relation to ingredients used and taste. Given the complexity, the inclusion of the GI of mixed meals is a major advantage. It is hoped that this compendium will highlight ways to reduce the GI of carbohydrate-rich staples and enhance the use of GI tables for a worldwide audience.
INFORMATION:
About the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
The Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) is Singapore's lead public sector agency that spearheads economic oriented research to advance scientific discovery and develop innovative technology. Through open innovation, we collaborate with our partners in both the public and private sectors to benefit society
As a Science and Technology Organisation, A*STAR bridges the gap between academia and industry. Our research creates economic growth and jobs for Singapore, and enhances lives by contributing to societal benefits such as improving outcomes in healthcare, urban living, and sustainability.
We play a key role in nurturing and developing a diversity of talent and leaders in our Agency and research entities, the wider research community and industry. A*STAR's R&D activities span biomedical sciences and physical sciences and engineering, with research entities primarily located in Biopolis and Fusionopolis.
For ongoing news, visit http://www.a-star.edu.sg.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-04
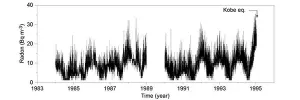
Tohoku University researchers have unearthed further details about radon concentration in the atmosphere before and after earthquakes, moving us closer to being able to anticipate when large earthquakes may hit.
The results of their research were published in the journal Science Reports on February 18, 2021.
Radon is a radioactive noble gas derived from radioactive decays of radium-226 in the ground. Radon bubbles up to the surface and is expelled into the atmosphere.
It has long been known that elevated levels of radon underneath the ground can be detected before and after earthquakes. But the relationship between the mechanisms that cause abnormal changes in radon concentration and the occurrence of earthquakes requires greater ...
2021-03-04
Interspecies interactions are the foundation of ecosystems, from soil to ocean to human gut. Among the many different types of interactions, syntrophy is a particularly important and mutually beneficial interspecies interaction where one partner provides a chemical or nutrient that is consumed by the other in exchange for a reward.
Syntrophy plays an essential role in global carbon cycles by mediating the conversion of organic matter to methane, which is about 30 times more potent than carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas and is a source of sustainable energy. And in the human gut, trillions of microbial cells also interact ...
2021-03-04
Intelligent holographic nanostructures on CMOS sensors for energy-efficient AI security schemes
Today, machine learning permeates our everyday life, with millions of users every day unlocking their phones through facial recognition or passing through AI-enabled automated security checks at airports and train stations. These tasks are possible thanks to sensors that collect optical information to feed it to a neural network in a computer. Imagine to empower the sensors in the devices you use every day to perform artificial intelligence functions without a computer - as simply as putting glasses on them.
The integrated holographic perceptrons developed by a research team at University of Shanghai for Science and Technology led ...
2021-03-04
Nairobi/Paris, 4 March 2021 - An estimated 931 million tonnes of food, or 17% of total food available to consumers in 2019, went into the waste bins of households, retailers, restaurants and other food services, according to new UN research conducted to support global efforts to halve food waste by 2030.
The weight roughly equals that of 23 million fully-loaded 40-tonne trucks -- enough bumper-to-bumper to circle the Earth 7 times.
The Food Waste Index Report 2021, from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and partner organization WRAP, looks at food waste that occurs in retail outlets, restaurants and homes - ...
2021-03-04
People with higher incomes tend to feel prouder, more confident and less afraid than people with lower incomes, but not necessarily more compassionate or loving, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
In a study of data from 162 countries, researchers found consistent evidence that higher income predicts whether people feel more positive "self-regard emotions," including confidence, pride and determination. Lower income had the opposite effect, and predicted negative self-regard emotions, such as sadness, fear and shame. The research was published online in the journal Emotion. ...
2021-03-04
A group of researchers, spanning six universities and three continents, are sounding the alarm on a topic not often discussed in the context of conservation--misinformation.
In a recent study published in FACETS, the team, including Dr. Adam Ford, Canada Research Chair in Wildlife Restoration Ecology, and Dr. Clayton Lamb, Liber Ero Fellow, both based in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Science, explain how the actions of some scientists, advocacy groups and the public are eroding efforts to conserve biodiversity.
"Outcomes, not intentions, should be the basis for how we view success in conservation," says Dr. Ford.
"Misinformation related to vaccines, climate change, and links between smoking ...
2021-03-04
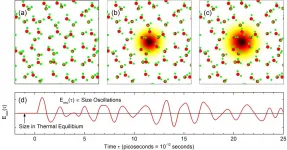
Ionization of water molecules by light generates free electrons in liquid water. After generation, the so-called solvated electron is formed, a localized electron surrounded by a shell of water molecules. In the ultrafast localization process, the electron and its water shell display strong oscillations, giving rise to terahertz emission for tens of picoseconds.
Ionization of atoms and molecules by light is a basic physical process generating a negatively charged free electron and a positively charged parent ion. If one ionizes liquid water, the free electron undergoes a sequence of ultrafast processes by which it loses energy and eventually localizes at a new site in ...
2021-03-04
CHAPEL HILL, North Carolina--UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers have successfully used an experimental safety switch, incorporated as part of a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, a type of immunotherapy, to reduce the severity of treatment side effects that sometimes occur. This advance was seen in a patient enrolled in a clinical trial using CAR-T to treat refractory acute B-cell leukemia. It demonstrates a proof-of-principle for possible expanded use of CAR-T immunotherapy paired with the safety switch.
The researchers published their findings in the journal Blood as an ahead-of-print publication.
With CAR-T therapy, T-cells from a patient's immune system ...
2021-03-04
The human genome contains roughly three million letters. On average, the genome sequences of any two people differ from each other by about one in every 1,000 letters. Yet different variants occur, from substituted letters to entire missing sections of DNA. Scientists from the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) and the Regensburg Center for Interventional Immunology (RCI) have teamed up with Icelandic researchers to develop software that reliably and quickly identifies large deletions in ten-thousands of genomes simultaneously. The researchers have now published their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
The human genome contains roughly three million letters ...
2021-03-04
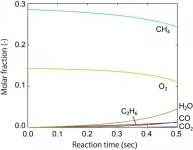
Japanese researchers have developed a simulation method to theoretically estimate the performance of heterogeneous catalyst by combining first-principles calculation (1) and kinetic calculation techniques. Up to now, simulation studies mainly focused on a single or limited number of reaction pathways, and it was difficult to estimate the efficiency of a catalytic reaction without experimental information.
Atsushi Ishikawa, Senior Researcher, Center for Green Research on Energy and Environmental Materials, National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), performed computation of reaction kinetic information from first-principles calculations based on quantum mechanics, and developed methods and programs to carry out kinetic simulations ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How to choose low glycaemic index (GI) foods? A GI 'glossary' of Asian foods released
Singapore research team's comprehensive study provides the glycaemic index values for a variety of foods that are consumed in non-Western countries, such as Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, India, China, Japan, South Korea, Middle East and more