Performance of methane conversion solid catalyst is predicted by theoretical calculation
Accelerating search for various materials to achieve a carbon-free society
2021-03-04
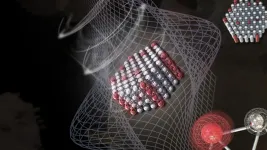
(Press-News.org) Japanese researchers have developed a simulation method to theoretically estimate the performance of heterogeneous catalyst by combining first-principles calculation (1) and kinetic calculation techniques. Up to now, simulation studies mainly focused on a single or limited number of reaction pathways, and it was difficult to estimate the efficiency of a catalytic reaction without experimental information.
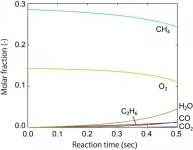
Atsushi Ishikawa, Senior Researcher, Center for Green Research on Energy and Environmental Materials, National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), performed computation of reaction kinetic information from first-principles calculations based on quantum mechanics, and developed methods and programs to carry out kinetic simulations without using experimental kinetic results. Then he applied the findings to the oxidative coupling of methane (OCM) reaction, which is an important process in the use of natural gas. He could successfully predict the yield of the products, such as ethane, without experimental information on the reaction kinetics. He also predicted changes in yield depending on the temperature and partial pressure, and the results reproduced faithfully the existing experimental results.
This research shows that the computer simulation enables the forecasting the conversion of reactant and the selectivity of products, even if experimental data are unavailable. The search for catalytic materials led by theory and calculation is expected to speed up. Furthermore, this method is highly versatile and can be applied not only to methane conversion catalysts but also to other catalyst systems such as for automobile exhaust gas purification, carbon dioxide reduction and hydrogen generation, and is expected to contribute to the realization of a carbon-free society.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by JST's Strategic Basic Research Program, Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO) Program.
(1) First-principles calculation
A theoretical calculation method for solving quantum mechanical equations without using empirical parameters, which is often applied to atomic, molecular, solid, and interface systems.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-04
The speed at which we produce facial expressions plays an important role in our ability to recognise emotions in others, according to new research at the University of Birmingham.
A team in the University's School of Psychology carried out research which showed that people tend to produce happy and angry expressions more rapidly, while sad expressions are produced more slowly.
The team found that our ability to form judgements about people's facial expressions has close links with the speeds at which those expressions are produced and is also closely related to the ways in which we would produce those expressions ourselves. The study is published in Emotion.
"Being able to recognise and interpret ...
2021-03-04
Much like the Jedis in Star Wars use 'the force' to control objects from a distance, scientists can use light or 'optical force' to move very small particles.
The inventors of this ground-breaking laser technology, known as 'optical tweezers', were awarded the 2018 Nobel Prize in physics.
Optical tweezers are used in biology, medicine and materials science to assemble and manipulate nanoparticles such as gold atoms. However, the technology relies on a difference in the refractive properties of the trapped particle and the surrounding environment.
Now scientists have discovered a new technique that allows them to manipulate particles that have the same refractive ...
2021-03-04
The vegan diet is on trend. How this type of diet affects health is the subject of scientific studies. In a new study from the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), the bone health of 36 vegans as well as 36 people following a mixed-food diet was determined with an ultrasound measurement of the heel bone. The result: on average, people following a vegan diet had lower ultrasound values compared to the other group. This indicates poorer bone health.
In the study, the scientists also determined biomarkers in blood and urine. This aims ...
2021-03-04
Managing invasive species--not eliminating them altogether--is a better use of time and conservation resources in many cases, according to a study led by a University of Alberta biologist.
Every year, hundreds of introduced species cause billions of dollars in damage to ecosystems, agriculture and infrastructure in North America alone. The research, led by Stephanie Green, makes a case for working smarter, not harder, to temper the impact of destructive and widespread invasive species using a strategy called functional eradication.
"Rather than trying to completely eliminate invasive species that have spread over large areas, which is very ...
2021-03-04
Typically, light emitted from standard lasers has a controllable degree of freedom (DoF) which may be polarisation or beam shape. By suitably manipulating a laser with the introduction of specialised optical components, an output with 2 DoFs, such as vector vortex beams with controllable polarisation and orbital angular momentum (OAM). The term 'vector' describes a structured change in the polarisation across the beam and 'vortex' describes the twisting of the phase in the beam (OAM), much like a twisting tornado. Transcending 2 DoFs from a laser was not possible. By exploiting ray-wave duality in a frequency-degenerate laser, ...
2021-03-04
Being older, overweight and having low haemoglobin levels (fewer red blood cells) could increase a patient's risk of developing debilitating nerve damage following chemotherapy, a research team led by UNSW Sydney has revealed.
The researchers aimed to identify pre-treatment clinical and blood-based risk factors in patients who developed chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) - nerve damage in peripheral body parts, like hands or feet, as a result of chemotherapy.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open recently, examined patients - mostly women - who received paclitaxel or oxaliplatin chemotherapy treatment, which are common treatments for breast, colorectal and gynaecological ...
2021-03-04
In a colourful solution to a dangerous problem, Australian scientists are adapting a component from cutting-edge solar cells to design a rapid, light-based detection system for deadly toxins.
While use of chemical warfare agents like sulfur mustard - better known as mustard gas - is banned internationally, we do rely on other strictly-controlled chemicals for agriculture, industry and throughout our daily lives, including fumigants like methyl iodide, which is used to control insects and fungi. The wrong amounts or incorrect use of these fumigants can be harmful to people and degrade the ozone layer.
Because it's invisible and doesn't smell, it's hard to tell whether there are dangerous amounts of methyl iodide present, and until ...
2021-03-04
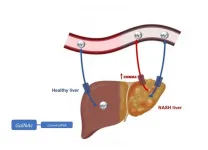
An international team of researchers has identified the CNNM4 protein as a key regulator of magnesium in the liver and potential therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, according to a study published in the Journal of Hepatology.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, a form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and liver fibrosis, is associated with obesity and has a worldwide prevalence of 1.7 billion people.
Unhealthy nutritional habits and dietary imbalances are recognized as causes of many diseases. Magnesium is widely available in both plant and animal foods; most vegetables, legumes, peas, beans, and nuts are rich in magnesium, as are some ...
2021-03-04
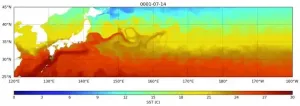
An exquisitely detailed global ocean model simulation from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) has given scientists rare insight into where baby sea turtles may go in their "lost years" after they scramble off the sandy beaches where they are born and swim into the open ocean.
This look at a critically important period in the life cycle of endangered loggerhead turtles could help inform more comprehensive conservation efforts that encompass regions of the open ocean where young turtles grow, and not just the nesting beaches. It also pinpoints regions of the ocean that are important to study to better understand how to protect sea turtles. ...
2021-03-04
DALLAS, March 4, 2021 -- The rate of cardiovascular risk factors among Hispanic/Latino people living in the U.S. is very high, and while they are often aware of their health conditions, less than half of the Hispanic/Latino adults with history of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) had healthy blood pressure and cholesterol, and about half had healthy blood sugar levels, according to new research published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
According to the American Heart Association, from 2015 to 2018, 52.3% of Hispanic men and 42.7% of Hispanic women aged 20 years and older had cardiovascular disease (CVD).
"It's a wake-up call for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Performance of methane conversion solid catalyst is predicted by theoretical calculation
Accelerating search for various materials to achieve a carbon-free society