Protein controlling magnesium identified as therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Patients with liver disease have significantly elevated expression of CNNM4 protein, which modulates magnesium in the liver
2021-03-04
(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers has identified the CNNM4 protein as a key regulator of magnesium in the liver and potential therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, according to a study published in the Journal of Hepatology.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, a form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and liver fibrosis, is associated with obesity and has a worldwide prevalence of 1.7 billion people.
Unhealthy nutritional habits and dietary imbalances are recognized as causes of many diseases. Magnesium is widely available in both plant and animal foods; most vegetables, legumes, peas, beans, and nuts are rich in magnesium, as are some seafood and spices. In recent years, there has been growing concern about inadequate magnesium intake in the general population. According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 79% of U.S. adults do not meet the recommended intake of magnesium.
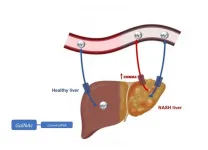
In the Journal of Hepatology study--led by Malu Martínez Chantar, principal investigator of the Liver Disease Laboratory at Spain's CIC bioGUNE and CIBER de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), and Jorge Simon, first author of the publication--the researchers found a higher expression of the CNNM4 protein in both patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and mouse models of the disease. CNNM4 facilitates transport of magnesium out of the liver and is responsible for the imbalance in the levels of magnesium that ends in the development of liver disease.
"These patients have an altered magnesium export machinery that increases the vulnerability of their liver to suffer inflammatory processes, development of fibrosis and fat deposition," explains Martínez Chantar. "This study also presents a novel therapeutic approach based on GalNac-siRNA technology that specifically targets the liver by modulating CNNM4 levels. The CNNM4 molecule developed from Silence Therapeutics' proprietary mRNAi GOLD™ (GalNAc Oligonucleotide Discovery) Platform effectively protects from liver pathology in preclinical models of steatohepatitis."
This molecule opens an unexplored therapeutic window in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
"The study underscores the importance of magnesium balance for supporting liver health. With insight into how this essential metal affects lipid metabolism at the cellular level, possible therapeutic targets for this and other liver pathologies start emerging," says Daniela Buccella, associate professor of chemistry at New York University and a study co-author.
INFORMATION:
This research was conducted by an international team of scientists from the Center for Cooperative Research in Biosciences (CIC bioGUNE), Basque Research and Technology Alliance (BRTA), CIBEREHD, University of the Basque Country, NYU, Silence Therapeutics, CABIMER, Universidad Pablo de Olavide, CIBERDEM, Fundación Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III, and University Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla/IDIVAL. The research was funded by several organizations, including the National Institutes of Health (R01-CA217817) and Silence Therapeutics.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-04
An exquisitely detailed global ocean model simulation from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) has given scientists rare insight into where baby sea turtles may go in their "lost years" after they scramble off the sandy beaches where they are born and swim into the open ocean.
This look at a critically important period in the life cycle of endangered loggerhead turtles could help inform more comprehensive conservation efforts that encompass regions of the open ocean where young turtles grow, and not just the nesting beaches. It also pinpoints regions of the ocean that are important to study to better understand how to protect sea turtles. ...
2021-03-04
DALLAS, March 4, 2021 -- The rate of cardiovascular risk factors among Hispanic/Latino people living in the U.S. is very high, and while they are often aware of their health conditions, less than half of the Hispanic/Latino adults with history of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) had healthy blood pressure and cholesterol, and about half had healthy blood sugar levels, according to new research published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
According to the American Heart Association, from 2015 to 2018, 52.3% of Hispanic men and 42.7% of Hispanic women aged 20 years and older had cardiovascular disease (CVD).
"It's a wake-up call for ...
2021-03-04
Bottom Line: Cancer survivors had a greater risk of reduced ambulatory function, which was associated with an increased risk of death.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Elizabeth Salerno, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of surgery at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, who conducted the research at the National Cancer Institute
Background: The diagnosis and treatment of cancer has been shown to be associated with poor functional health for common cancer types, such as those of the breast and prostate, but less is known about the association for other cancers, explained Salerno. "Given that cancer survivors are living longer than ever, ...
2021-03-04
A new study led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) has identified an association between slow walking pace and an increased risk of death among cancer survivors.
While the study does not establish that slow walking is a cause of death, the association persisted across at least nine tumor types. Investigators now call for more research into these relationships and whether targeted interventions such as physical activity programs could help cancer survivors improve their ability to walk and increase survival after cancer diagnosis and treatment.
The study, a collaboration between Washington University, the NCI of the ...
2021-03-04
The loss of seagrass in the waters around the UK is much higher than previously estimated. A new study published in Frontiers in Plant Science concludes that, with high certainty, at least 44% of the UK's seagrasses have been lost since 1936, of which 39% has been since the 1980s. This study is one of the first of its kind to bring together seagrass data from diverse sources and give a systematic estimate of the current and historic extent of seagrass, as well as seagrass loss in the UK.
The study was a collaboration between researchers at University College London, Kings College London, and Swansea University.
Seagrasses as climate change superheroes
Nature-based solutions are essential to mitigate the effects of the climate crisis, and seagrasses are highly ...
2021-03-04
(Boston)--Children in Zambia under age 5 die at a rate that is between nearly six to more than 10 times higher than those in the U.S; it is estimated at 40-75 per 1000, compared to 6.98 per 1000. Identifying why these children are dying is the mission of Rotem Lapidot, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM).
"Significantly, over 80 percent of all community infant deaths involved some form of delay. While it is impossible to know what would have occurred in the absence of such delays, the majority of infant deaths in Lusaka, the capital of Zambia, are from causes for which effective treatments currently exist," explained Lapidot, the corresponding author on the study ...
2021-03-04
The far-reaching mobility restrictions at the beginning of the Corona pandemic in March 2020 created a unique situation for atmospheric sciences: "During the 2020 lockdown, we were able to directly investigate the actual effects of drastic traffic restrictions on the distribution of air pollutants and on the emission of climate gases," says Innsbruck atmospheric scientist Thomas Karl. With his team, he has now published a detailed analysis of air quality during the first lockdown in the city of Innsbruck, Austria, in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. "We find significantly greater decreases of air pollutants than of carbon dioxide, for example," the researcher says, summarizing the results. In the past year, some studies showed contradicting ...
2021-03-04
Tiny photonic devices could be used to find new exoplanets, monitor our health, and make the internet more energy efficient. Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, now present a game changing microcomb that could bring advanced applications closer to reality.
A microcomb is a photonic device capable of generating a myriad of optical frequencies - colours - on a tiny cavity known as microresonator. These colours are uniformly distributed so the microcomb behaves like a 'ruler made of light'. The device can be used to measure or generate frequencies with extreme precision.
In a recent article in the journal ...
2021-03-04
Using data collected in a NASA Langley Mach 6 wind tunnel, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign replicated the hypersonic flow conditions of a compression ramp flow by means of Direct Numerical Simulation. The simulation yielded an abundance of additional data, which can be used to better understand the phenomena that occur surrounding vehicles traveling at hypersonic speeds.
"Data from experiments are somewhat limited--for example taken from pressure probes at a few locations on a test object. When we run a numerical simulation, we acquire information - such as pressure, temperature, ...
2021-03-04
A rapid microbiological point-of-care test to diagnose respiratory infections has proved popular with GPs and could reduce antibiotic prescribing in primary care, according to a National Institute for Health Research funded study by researchers at the Centre for Academic Primary Care, University of Bristol.
There are high rates of antibiotic prescribing in primary care and the UK government has called for the introduction of rapid diagnostics to curb overuse.
The RAPID-TEST study, published in the journal Family Practice today [4 March] evaluated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Protein controlling magnesium identified as therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Patients with liver disease have significantly elevated expression of CNNM4 protein, which modulates magnesium in the liver