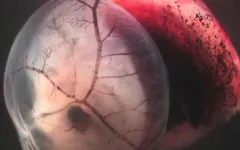
(Press-News.org) In a new study by the Yale Department of Immunobiology and Yale Cancer Center, researchers report combined liver and growth factor humanization enhances human red blood cell production and survival in circulation the immunodeficient murine host. The discovery could help in the development of treatments of life-threatening blood disorders, such as myelodysplastic syndrome, and diseases afflicting red blood cells, including sickle cell disease and malaria. The study is published online today in the journal Science.
"Red blood cell diseases, such as thalassemia and sickle cell disease involve approximately 5% of the population worldwide," said Yuanbin Song, MD, adjunct Assistant Professor of Medicine (Hematology) at Yale Cancer Center and co-lead author of the study. "Our findings highlight the unique potential of this model in studies of diseases that intricately link red blood cells and the liver, such as malaria."
"MISTRG" mice were developed in the Yale laboratory of Richard Flavell, PhD, Sterling Professor of Immunobiology at Yale University School of Medicine and Yale Cancer Center and co-senior author of the study to have human growth factors and a human-like immune system. Analysis of the fate of human red cells in MISTRG mice revealed that the mouse liver represents one of the major sites of red blood cell sequestration and destruction. Deletion of the fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (Fah) gene in MISTRG mice allowed replacement of mouse with human hepatocytes and rescue of human red blood cells in circulation.
Human red blood cells, one of the most common cell types in the body, have been under intense genetic selection throughout human evolution, the damaging consequences of which place a heavy burden on many human populations and healthcare systems.
"This is the first xenotransplantation model with circulating human red cells and it will open novel avenues for the study of disease pathophysiological mechanisms and for preclinical testing of treatments for many diseases, including myelodysplasia, bone marrow failure, sickle cell disease, and others," said Stephanie Halene, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine (Hematology), Chief of Hematology at Yale Cancer Center and Smilow Cancer Hospital and co-senior author of the study.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, The Frederick A. DeLuca Foundation, the National Institutes of Health.
Co-lead authors for the study are Rana Gbyli, MSc, from Yale, and Liang Shan, PhD, from Washington University School of Medicine. Contributing authors include Wei Liu, PhD, Till Strowig, PhD, Amisha Patel, MSc, Xiaoying Fu, MD, Xiaman Wang, MD, Mina L. Xu, MD, Yimeng Gao, PhD, Ashley Qin, Emanuela M. Bruscia, PhD, Toma Tebaldi, PhD, Giulia Biancon, PhD, Padmavathi Mamillapalli. MSc, David Urbonas, Elizabeth Eynon, PhD, David G. Gonzalez, PhD, Jie Chen, PhD, Diane S. Krause, MD, PhD and Jonathan Alderman, PhD.
About Yale Cancer Center and Smilow Cancer Hospital
Yale Cancer Center (YCC) is one of only 51 National Cancer Institute-designated comprehensive cancer centers in the nation and the only such center in Connecticut. Cancer treatment for patients is available at Smilow Cancer Hospital through 13 multidisciplinary teams and at 15 Smilow Cancer Hospital Care Centers in Connecticut and Rhode Island. Comprehensive cancer centers play a vital role in the advancement of the NCI's goal of reducing morbidity and mortality from cancer through scientific research, cancer prevention, and innovative cancer treatment.
Professor Byoungwoo Kang develops a high-density cathode material through controlling local structures of the Li-rich layered materials.
Researchers in Korea have developed a high-capacity cathode material that can be stably charged and discharged for hundreds of cycles without using the expensive cobalt (Co) metal. The day is fast approaching when electric vehicles can drive long distances with Li- ion batteries.
Professor Byoungwoo Kang and Dr. Junghwa Lee of POSTECH's Department of Materials Science and Engineering have successfully developed a high energy-density cathode material that can stably maintain charge and discharge for over 500 cycles without the expensive ...
Most people have heard of stem cells, cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the architects of blood cell development and are responsible for blood cell formation throughout the life of an organism. HSCs are also used in the treatment of cancer and immune disturbances.
Previous research into HSC transplantation has involved the use of adult and fetal mice. This has involved the removal of recipient HSCs using approaches including irradiation and the administration of DNA damaging drugs. In a first of its kind, researchers from the University of Tsukuba devised a novel approach for HSC deletion in mouse embryos. This report provides the first description of embryonic HSC depletion and transplantation of donor HSCs ...
SMU Office of Research and Tech Transfer - One of the motivations for the recently published Journal of Accounting Research paper "Politically Connected Governments" was the daily experience with the subway system in New York City.
The author of the paper, SMU Assistant Professor of Accounting Kim Jungbae, told the Office of Research & Tech Transferthe research question for the paper which examines the consequences of powerful political connections for local governments, was inspired by the New York Times article "The Most Expensive Mile of Subway Track on Earth" (January 24, 2018).
"The article suggests that the NYC subway system is ...
Since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, charts and graphs have helped communicate information about infection rates, deaths, and vaccinations. In some cases, such visualizations can encourage behaviors that reduce virus transmission, like wearing a mask. Indeed, the pandemic has been hailed as the breakthrough moment for data visualization.
But new findings suggest a more complex picture. A study from MIT shows how coronavirus skeptics have marshalled data visualizations online to argue against public health orthodoxy about the benefits of mask mandates. Such "counter-visualizations" are often quite sophisticated, using datasets from official sources and state-of-the-art visualization ...
SMU Office of Research & Tech Transfer - Even before countries began rolling out their vaccination campaigns, Pfizer, Moderna and AstraZeneca's announcements had already proved fortifying shots. Stocks rallied and healthcare workers celebrated in the wake of the vaccine news late last year. But months on, that early euphoria has somewhat evaporated, replaced by uncertainty and debate over vaccine safety, possible side effects and varying degrees of citizen reluctance.
Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers and health experts modelling COVID-19's spread ...
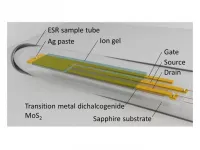
Tsukuba, Japan and Warsaw, Poland - Scientists from the University of Tsukuba and a scientist from the Institute of High Pressure Physics detected and mapped the electronic spins moving in a working transistor made of molybdenum disulfide. This research may lead to much faster computers that take advantage of the natural magnetism of electrons, as opposed to just their charge.
Spintronics is a new area of condensed matter physics that attempts to use the intrinsic magnetic moment of electrons, called "spins," to perform calculations. This would be a major advance ...
Kanazawa, Japan - Non-rigid point set registration is the process of finding a spatial transformation that aligns two shapes represented as a set of data points. It has extensive applications in areas such as autonomous driving, medical imaging, and robotic manipulation. Now, a method has been developed to speed up this procedure.
In a study published in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, a researcher from Kanazawa University has demonstrated a technique that reduces the computing time for non-rigid point set registration relative to other approaches.
Previous ...
Kanazawa, Japan - As the global population ages, the rate of dementia is increasing worldwide. Given that early detection is critical for treatment, effective ways to screen for dementia are a high research priority. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a new screening tool that can be administered in a matter of minutes.
In a study published in PLOS ONE, researchers from Kanazawa University have revealed a new computerized cognitive test, termed the computerized assessment battery for cognition (C-ABC), which they found to be effective in screening for both dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in just 5 minutes.
Computerized cognitive tests are frequently chosen over paper-and-pencil ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Heavy snowfall slows things down and makes it harder to get from point A to point B. But snow clouds have a silver lining--heavy snow may prevent serious road injuries and even save lives. How? By getting people off bicycles and switching to safer modes of transport.
Japanese researchers examined 10 years of police data on road injuries among commuting junior high school students. They found that areas with monthly snowfall of at least 100 cm had almost no bicycling-related injuries. Total injuries among cyclists and pedestrians also fell by 68%. The findings were published in the Journal of Epidemiology.
The logic is quite simple. ...
A new data-driven study from Texas A&M University casts serious doubt on the stereotype that male students perform better than female students in science -- specifically, physics.
A team of researchers in the Department of Physics and Astronomy analyzed both the midterm exam scores and final grades of more than 10,000 Texas A&M students enrolled in four introductory physics courses across more than a decade, finding no evidence that male students consistently outperform female students in these courses.
The work was led by Texas A&M physicist ...