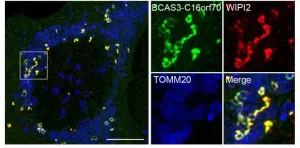
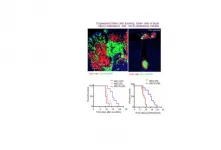
How bone marrow regenerates after chemotherapy
Researchers from Osaka University identify the molecular mechanism underlying bone marrow regeneration after chemotherapy
2021-03-05
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan - Chemotherapy has a damaging effect on hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) in bone marrow. However, once chemotherapy ends, HSPCs regenerate, a process that has remained unknown--until now. In a new study, researchers from Osaka University have identified the molecular mechanism by which HSPCs recover after injury.
HSPCs reside in the bone marrow and give rise to several types of blood cells, such as red blood cells (which carry oxygen), some white blood cells (which are important for the immune system) and platelets (which are necessary to stop bleeding). Because HSPCs constantly divide to generate new cells, they are particularly sensitive to injury induced by, for example, chemotherapy. Interestingly, HSPCs have the capability to regenerate upon injury.
"The bone marrow is a very active organ because it has to constantly produce new blood cells," says corresponding author of the study Masaru Ishii. "Once it loses its function, such as during chemotherapy, deadly conditions such as anemia, neutropenia and bleeding can occur. In this study, we wanted to understand how hematopoietic stem cells residing in the bone marrow regenerate upon chemotherapy-induced injury to recover their full function."
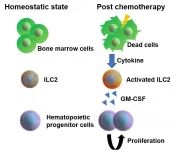
To achieve their goal, the researchers focused on a specific subset of blood cells that are produced from HSPCs, so-called group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). While ILC2s exist in a number of tissues and play an important role in the immune system and tissue repair, those residing in bone marrow are thought to have a distinct role specific to their location. However, the nature of their function was unclear. To unravel the biological role of ILC2s, the researchers treated mice with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a chemotherapeutic agent toxic to HSPCs, and transplanted fresh, undamaged HSPCs into these mice, akin to a stem cell transplantation therapy in patients with leukemia. Interestingly, the researchers found that the injured HSPC microenvironment in 5-FU-treated mice promoted the proliferation of the transplanted HSPCs. By analyzing this finding at the molecular level, the researchers found that ILC2s in the bone marrow of treated mice produced granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) to aid in the process of HSPC regeneration.
But how exactly do ILC2s know that they should produce GM-CSF after bone marrow injury? To answer this question, the researchers widened their focus to investigate if there are other cells or molecules that direct ILC2s to the production of GM-CSF. They found that progenitors of antibody-producing B cells in the bone marrow produced interleukin (IL)-33 after injury, which in turn activated ILC2s, demonstrating how multiple molecular players are required to recover the damaged bone marrow. Importantly, the researchers showed that the transfer of isolated ILC2s to 5-FU-treated mice accelerates hematopoietic recovery, while the reduction of ILC2s results in the opposite effect, suggesting that ILC2s may serve as a sensor of bone marrow damage.
"These are striking results that show the bone marrow regenerates after chemotherapy," says first author of the study Takao Sudo. "Our results may contribute to the development of a novel therapeutic approach for chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression."
INFORMATION:
The article, "Group 2 innate lymphoid cells support hematopoietic recovery under stress conditions," was published in Journal of Experimental Medicine at DOI:
https://doi.org.10.1084/jem.20200817
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-05
Semiconductor materials play an indispensable role in our modern information-oriented society. For reliable performance of semiconductor devices, these materials need to have superior mechanical properties: they must be strong as well as resistant to fracture, despite being rich in nanoscale structures.
Recently, it has become increasingly clear that the optical environment affects the structural strength of semiconductor materials. The effect can be much more significant than expected, especially in light-sensitive semiconductors, and particularly since due to technological constraints ...
2021-03-05
Background: Although caregivers of patients with eating disorders usually experience a heavy caregiving burden, the effects of social support on caregivers of patients with eating disorders are unknown. This study aimed to investigate how social support for mothers who are caregivers of patients with an eating disorder improves the mothers' mental status and, consequently, the symptoms and status of the patients.
Methods: Fifty-seven pairs of participants were recruited from four family self-help groups and one university hospital in Japan. Recruitment was conducted from July 2017 to August 2018. Mothers were ...
2021-03-05
Autophagy is an intracellular degradation process of cytosolic materials and damaged organelles. Researchers at Ubiquitin Project of TMIMS have been studying the molecular mechanism of mitophagy, the selective autophagy process to eliminate damaged mitochondria. PINK1 (a serine/threonine kinase) and Parkin (a ubiquitin ligating enzyme: E3) work together to ubiquitylate the outer membrane proteins of damaged mitochondria, then ubiquitin chains are recognized as signals for autophagy degradation. Dysfunction of mitophagy causes a decrease in mitochondrial quality with overproduction of ROS, and is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's disease.
In Autophagy machinery, cellular components targeted for degradation are engulfed by phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P)-rich ...
2021-03-05
Frequently occurring chronic skin inflammation like in atopic dermatitis (AD or neurodermatitis) and psoriasis have different causes such as genetic predisposition, stress or allergens. These frequently occurring skin diseases are mostly attributed by biomedical scientists to a disturbed immune system, although the noticeable thickening and flaking of the epidermis, which is the outermost layer of skin, also indicates a disruption of the epithelial cells. A team of researchers from the University Clinic for Dermatology and the Clinical Institute for Laboratory Medicine at MedUni Vienna has now been able to identify new molecular ...
2021-03-05
WHO: Giovanni Traverso, MB, BChir, PhD, Associate Physician, Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women's Hospital; corresponding author of a new article published in JAMA Network Open.
Peter Chai, MD, MMS, Assistant Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; first author.
WHAT: In the age of COVID-19, mobile robotic telehealth systems could help clinicians and patients interact without contact. Last spring, some health care systems deployed robotic systems within a hospital to evaluate and interact with patients. In a JAMA Network Open article, Traverso and colleagues report the results of a national survey and a cohort study in an emergency department (ED), which analyzed patients' satisfaction with an initial evaluation ...
2021-03-05
MoS2 thin films of superposed alternating layers of molybdenum and sulfur atoms form a two-dimensional semiconducting surface. However, even a surprisingly low-intensity blue light pulse is enough to alter the properties of the surface and make it metallic. This has now been demonstrated by a team at BESSY II.
The exciting thing is that the MoS2 layers in this metallic phase are also particularly active catalytically. They can then be employed, for example, as catalysts for splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen. As inexpensive catalysts, they could facilitate the production of hydrogen - an energy ...
2021-03-05
Approximately 15-to-30 percent of patients with metastatic breast cancer have brain metastasis (BM), with basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) metastasizing to the brain most frequently. The prognosis for BLBC-BM patients is poor, as the blood-brain barrier prevents most therapeutics from reaching the brain. Testing candidate therapies in clinical trials is also challenging because animal models that mimic BM are limited. In a new study, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and collaborators engineered a bimodal tumor-suppressing and killing molecule that can be delivered to the brain by stem cells. They tested ...
2021-03-05
Beijing, 26 February 2021: the journal Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications (CVIA) has just published the third issue of Volume 5. This issue brings together important research from authors in the USA and China, including several important papers concerned with the various cardiological implications of COVID-19.
Papers in the issue are as follows.
RESEARCH PAPERS
Diyu Cui, Yimeng Liao, Jianlin Du and Yunqing Chen
A Meta-analysis of Major Complications between Traditional Pacemakers and Leadless Pacemakers
(http://ow.ly/CgYO30rz3eA)
Yue Wu, Guoyue Zhang, Rong Hu and Jianlin Du
Risk of Target Organ Damage in Patients with Masked Hypertension versus
Sustained Hypertension: A Meta-analysis (http://ow.ly/x63E30rzjEp)
Jing Li, Lijie Sun, Fang Wang, Bing Liu, Hui Li, Guodong ...
2021-03-05
If you stretch an elastic band, it becomes thinner - a physical behavior that applies to most "common" materials. Since the 20th century, an opposite behavior has been known in materials research: The so-called auxetic (from ancient Greek auxetos, meaning 'stretchable') materials expand in the direction orthogonal to the strain. Likewise, they shrink when they are compressed. Scientifically, they are characterized by a negative Poisson's ratio. Probably the best known and oldest application of unusual Poisson's ratios is the bottle cork, which has a Poisson's ratio of zero. This has the effect that the cork ...
2021-03-05
Biodiversity is declining at an unprecedented rate, due primarily to human activity. Illegal and unsustainable wildlife trade is one of the major drivers of these declines, while much wildlife trade is legal, and the quantity of trade provides the opportunity to launder illegally sourced and traded species and products.
Researchers from the Conservation Forensics Lab at HKU and Research Division for Ecology and Biodiversity, analyzed trends in global legal wildlife trade from 1997 to 2016, and revealed that legal wildlife trade averaged $220 billion per year over this period, approximately double the international trade in tea, coffee and spices, and eclipsing - by order of magnitude - annual trade in trafficked wildlife, estimated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How bone marrow regenerates after chemotherapy
Researchers from Osaka University identify the molecular mechanism underlying bone marrow regeneration after chemotherapy