(Press-News.org) In recent years there has been an increased focus on the circular economy and a heightened demand for products made of recyclable materials, however many materials can only be recycled so many times before they begin to wear out.
This is the case with carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites, non-biodegradable materials which, until now, have lacked a viable recycling method.
CRFP composites are present in products such as wind turbines, aeroplane parts, vehicles such as cars and ships, and everyday technology such as laptops and mobile phones.
They are typically disposed of in landfills or by incineration, which pose significant threats to both the environment and public health.
The vast majority of existing recycling methods also cause a major reduction in the mechanical and physical properties of the recovered material, weakening its core functionality.
Researchers from the University of Sydney's School of Civil Engineering have developed an optimised method for recycling CFRP composites while maintaining 90 percent of their original strength.
"Globally and in Australia there has been a march towards better recycling processes, however there is often the belief that a material can be recycled an infinite amount of times - this simply isn't the case. Most recycling processes diminish mechanical or physical properties of materials," said the study's lead researcher Dr Ali Hadigheh.
"Until now, it has been impossible to continuously recycle products made of carbon fibres. Given that most recycling involves shredding, cutting or grinding, fibres are worn out, decreasing a future product's viability," said Dr Hadigheh.
"This presents a huge challenge and threat to our environment, as it has led to the production of virgin carbon fibre which contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
"To combat this issue and to support a true circular economy, we developed an efficient and cost-effective method for recycling carbon fibre, which is present in tablets through to BMWs."
"To do this we used a two phased, optimised process. The first step is called "pyrolysis", which breaks down a material using heat, but significantly chars the materials which prevents it from developing a good bond with a resin matrix. The second process, oxidation, uses high temperatures to remove this char.
"Pyrolysis and oxidation alone are not enough to preserve carbon fibres and these processes have existed for some time already. To ensure a high quality recovery and economic efficiency, thermal decomposition of CFRPs need to be guided by analysing the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction in the composit, and separate carbon fibres from the surrounding resin matrix.
"What makes our method so successful is that we have added specific parameters - such as temperature, heating rate, atmosphere or time spent being oxidised and heated - that preserve the functionality of carbon fibre."
"We embarked on the project with the aim of producing high grade, low cost structural materials made from recycled carbon fibre composites, for use in industries from aerospace and automotive through to sporting goods and renewable energy and construction."
In 2010, the global production of fibre reinforced polymers (FRP) was approximately 6 million tonnes with a projected growth of 300 percent in the next decade. With this projection, the consumption of FRPs will exceed 18 million tonnes by 2025, with an end-product value of AUD $80 billion.
"The 2016 Australian National Waste Report concludes that the use of composite materials is creating future challenges to recycling. Plainly put, if we do not develop efficient and cost-effective methods to recycle carbon fibre composites, we risk damaging the environment significantly," said Dr Hadigheh.
The United States, Japan and China lead the world in carbon fibre manufacturing. The researchers hope to increase the capacity of the Australian industry and work with manufacturers of wind turbines and commercial aircraft, as well as producers of sporting goods, and the construction, automotive and ship-building industries.
INFORMATION:
DECLARATION:
The research was supported by the Australian Government through the Australian Research Council's Discovery Early Career Researcher Award (DECRA) fellowship scheme (project number DE200100406), which was received by Dr Hadigheh.
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
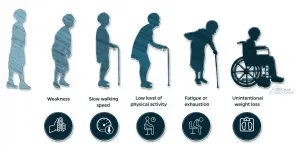
Physicians understand frailty as a dysregulation among multiple systems in the body that make it less resilient and unable to recover completely when faced with a physical challenge such as injury or illness. "Defining frailty on a scientific level, however, has been a challenging task," explains END ...
SPOKANE, Wash. - New clues as to why night shift workers are at increased risk of developing certain types of cancer are presented in a new study conducted at Washington State University Health Sciences Spokane. ...
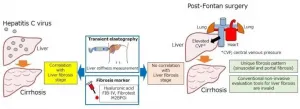
It is well-known that patients who undergo Fontan surgery slowly develop liver fibrosis for years post-operatively. In the past decade, these incidences have been steadily increasing and this is due partly to the need for an accurate diagnostic method. A research group led by Dr. Daisuke Tokuhara, Associate Professor of Pediatrics, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine and Dr. Yuki Cho have found that the conventional methods of ultrasound elastography and biomarkers via blood tests do not show the actual status of postoperative liver ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- In a study conducted shortly before COVID-19 vaccines became available in the U.S., more than two-thirds of nursing home and assisted living staff in Indiana indicated willingness to receive a vaccine immediately or in the future. The study was led by researchers from Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University and the State of Indiana. Vaccine uptake by front-line staff is important because it will help protect against serious illness and death for the high-risk people who receive care in these facilities.
"The vaccines offer the opportunity to return to a more normal life within the nursing ...
Native to the southeastern United States, a weedy grass has spread northward to Canada and also made its way to Australia and Japan. Andropogon virginicus grows densely packed and up to seven feet tall, disrupting growth patterns of other plants and competing for resources. When burned, it grows back stronger. There is no way to effectively remove the weed once it has invaded. But there might be a way to use it to human advantage.
An international team of researchers has found that A. virginicus extracts appear to be effective against several human diseases, including diabetes and cancer. The results were published on Dec. 31, 2020, in a special issue of Plants, titled ...
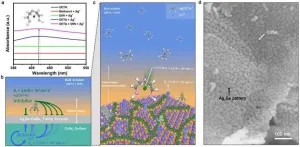
Hydrogen has been hailed as the 'fuel of the future' owing to several reasons. First, compared to the conventionally used hydrocarbons, hydrogen exhibits higher energy yield. Second, the commercial use of hydrogen fuel, which yields only water as a byproduct product, would help mitigate the imminent global warming crisis by reducing the use of exhaustible and polluting fossil fuels. Thus, ongoing research has been focusing on efficient and environment-friendly ways to produce of hydrogen fuel.
Solar hydrogen production through photoelectrochemical (PEC) water-splitting reaction is an attractive "green" method of ...
Research from the University of Kent predicts an end to deregulated competitive pubic transport in the UK as a consequence of Covid-19 social distancing measures leading to drastically reduced ridership, requiring a major rethinking of the provision of public transport.
This paper, published in Transport Policy, argues that the situation will require a fundamental approach to long-term policy for transport as a whole. This is an opportunity to reconstruct the system whilst addressing such problems as the environmental impact of transport, congestion and questions of transport justice such as accessibility ...
A new substance could improve the treatment of persistent cancers. Researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Greifswald have developed a new inhibitor that makes drug-resistant tumour cells respond again to chemotherapy. The new substance blocks a protein in the cancer cells that normally transports the cancer drugs back out of the cells. The results were published in the scientific journal Molecules.
In addition to radiation therapy, cytotoxic agents, also known as chemotherapy, are frequently used to treat cancer. They prevent cells from dividing and thus cancer cells are unable to multiply unchecked. "Cytotoxic agents remain a very important form ...
In 1952, Alan Turing, the father of computer science and artificial intelligence, proposed that certain repetitive natural patterns may be produced by the interaction of two specific substances through the "reaction-diffusion" process. In this system, activator promotes the reaction and inhibitor inhibits the reaction. When the two meet, the reaction diffuses. When the difference in diffusion coefficient between the two reaches a certain level, the high diffusion ratio between them will cause the system imbalance and induce the formation of periodic complex patterns.
"Turing structure" exists widely in nature, such as the body patterns of zebras, the phyllotaxis of sunflowers, the follicle spacing of ...
The precise choice of treatment for breast cancer depends upon the status of the hormone receptors (for oestrogen and progesterone). Their conventional determination by means of immunohistochemistry (IHC) is associated with a certain error rate, which can be reduced by adding genomic data. Even conventional statistics can bring about a notable improvement but now it is possible to use decision theory to optimally combine diagnostic findings, particularly where they are contradictory. This is the finding of a recent study conducted by MedUni Vienna under the leadership of Wolfgang Schreiner from the Center for Medical Statistics, Informatics and Intelligent Systems (CeMSIIS). The methodology has applications way beyond breast cancer and can be deployed ...