Establishing the origin of solar-mass black holes and the connection to dark matter
2021-03-08
(Press-News.org) What is the origin of black holes and how is that question connected with another mystery, the nature of dark matter? Dark matter comprises the majority of matter in the Universe, but its nature remains unknown.
Multiple gravitational wave detections of merging black holes have been identified within the last few years by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), commemorated with the 2017 physics Nobel Prize to Kip Thorne, Barry Barish, and Rainer Weiss. A definitive confirmation of the existence of black holes was celebrated with the 2020 physics Nobel Prize awarded to Andrea Ghez, Reinhard Genzel and Roger Penrose. Understanding the origin of black holes has thus emerged as a central issue in physics.
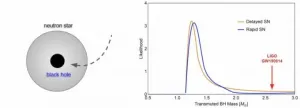
Surprisingly, LIGO has recently observed a 2.6 solar-mass black hole candidate (event GW190814, reported in Astrophysical Journal Letters 896 (2020) 2, L44). Assuming this is a black hole, and not an unusually massive neutron star, where does it come from?
Solar-mass black holes are particularly intriguing, since they are not expected from conventional stellar evolution astrophysics. Such black holes might arise in the early Universe (primordial black holes) or be "transmuted" from existing neutron stars. Some black holes could have formed in the early universe long before the stars and galaxies formed. Such primordial black holes could make up some part or all of dark matter. If a neutron star captures a primordial black hole, the black hole consumes the neutron star from the inside, turning it into a solar-mass black hole. This process can produce a population of solar mass black holes, regardless of how small the primordial black holes are. Other forms of dark matter can accumulate inside a neutron star causing its eventual collapse into a solar-mass black hole.
A new study, published in Physical Review Letters, advances a decisive test to investigate the origin of solar-mass black holes. This work was led by the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU) Fellow Volodymyr Takhistov and the international team included George M. Fuller, Distinguished Professor of Physics and Director of the Center for Astrophysics and Space Science at the University of California, San Diego, as well as Alexander Kusenko, Professor of Physics and Astronomy at the University of California, Los Angeles and a Kavli IPMU Visiting Senior Scientist.
As the study discusses (see Fig. 1), "transmuted" solar-mass black holes remaining from neutron stars being devoured by dark matter (either tiny primordial black holes or particle dark matter accumulation) should follow the mass-distribution of the original host neutron stars. Since the neutron star mass distribution is expected to peak around 1.5 solar masses, it is unlikely that heavier solar-mass black holes have originated from dark matter interacting with neutron stars. This suggests that such events as the candidate detected by LIGO, if they indeed constitute black holes, could be of primordial origin from the early Universe and thus drastically affect our understanding of astronomy. Future observations will use this test to investigate and identify the origin of black holes.
Previously (see Fuller, Kusenko, Takhistov, Physical Review Letters 119 (2017) 6, 061101), the same international team of researchers also demonstrated that disruption of neutron stars by small primordial black holes can lead to a rich variety of observational signatures and can help us understand such long-standing astronomical puzzles as the origin of heavy elements (e.g. gold and uranium) and the 511 keV gamma-ray excess observed from the center of our Galaxy.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-08
To effectively fight off SARS-CoV-2, the immune system depends on both antibodies and T cells, a type of white blood cell, which work together to eradicate the virus. However, little was known about virus-specific T cells in asymptomatic patients.
"We now know that many people are getting infected with SARS-CoV-2 without realising it, as they stay healthy and don't develop any symptoms. These asymptomatic infections may provide the key to understanding how the immune system can control the virus without triggering pathological processes," explained Dr Nina Le Bert, Senior Research Fellow ...
2021-03-08
A Korean research group has developed a technology that allows for the differentiation of stem cells into desired cell types, such as vascular mural cells or osteoblasts, without special pretreatment. This technology is expected to facilitate the production of artificial organs for preclinical studies or artificial tissues for transplants such as artificial skin and cardiac patches.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research group led by Dr. Youngmee Jung of the Center for Biomaterials has developed a new cell co-culture platform ...
2021-03-08
In recent years there has been an increased focus on the circular economy and a heightened demand for products made of recyclable materials, however many materials can only be recycled so many times before they begin to wear out.
This is the case with carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites, non-biodegradable materials which, until now, have lacked a viable recycling method.
CRFP composites are present in products such as wind turbines, aeroplane parts, vehicles such as cars and ships, and everyday technology such as laptops and mobile ...
2021-03-08
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
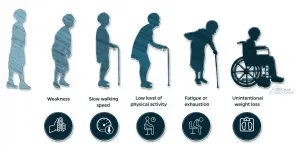
Physicians understand frailty as a dysregulation among multiple systems in the body that make it less resilient and unable to recover completely when faced with a physical challenge such as injury or illness. "Defining frailty on a scientific level, however, has been a challenging task," explains END ...
2021-03-08
SPOKANE, Wash. - New clues as to why night shift workers are at increased risk of developing certain types of cancer are presented in a new study conducted at Washington State University Health Sciences Spokane. ...
2021-03-08
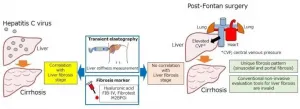
It is well-known that patients who undergo Fontan surgery slowly develop liver fibrosis for years post-operatively. In the past decade, these incidences have been steadily increasing and this is due partly to the need for an accurate diagnostic method. A research group led by Dr. Daisuke Tokuhara, Associate Professor of Pediatrics, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine and Dr. Yuki Cho have found that the conventional methods of ultrasound elastography and biomarkers via blood tests do not show the actual status of postoperative liver ...
2021-03-08
INDIANAPOLIS -- In a study conducted shortly before COVID-19 vaccines became available in the U.S., more than two-thirds of nursing home and assisted living staff in Indiana indicated willingness to receive a vaccine immediately or in the future. The study was led by researchers from Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University and the State of Indiana. Vaccine uptake by front-line staff is important because it will help protect against serious illness and death for the high-risk people who receive care in these facilities.
"The vaccines offer the opportunity to return to a more normal life within the nursing ...
2021-03-08
Native to the southeastern United States, a weedy grass has spread northward to Canada and also made its way to Australia and Japan. Andropogon virginicus grows densely packed and up to seven feet tall, disrupting growth patterns of other plants and competing for resources. When burned, it grows back stronger. There is no way to effectively remove the weed once it has invaded. But there might be a way to use it to human advantage.
An international team of researchers has found that A. virginicus extracts appear to be effective against several human diseases, including diabetes and cancer. The results were published on Dec. 31, 2020, in a special issue of Plants, titled ...
2021-03-08
Hydrogen has been hailed as the 'fuel of the future' owing to several reasons. First, compared to the conventionally used hydrocarbons, hydrogen exhibits higher energy yield. Second, the commercial use of hydrogen fuel, which yields only water as a byproduct product, would help mitigate the imminent global warming crisis by reducing the use of exhaustible and polluting fossil fuels. Thus, ongoing research has been focusing on efficient and environment-friendly ways to produce of hydrogen fuel.
Solar hydrogen production through photoelectrochemical (PEC) water-splitting reaction is an attractive "green" method of ...
2021-03-08
Research from the University of Kent predicts an end to deregulated competitive pubic transport in the UK as a consequence of Covid-19 social distancing measures leading to drastically reduced ridership, requiring a major rethinking of the provision of public transport.
This paper, published in Transport Policy, argues that the situation will require a fundamental approach to long-term policy for transport as a whole. This is an opportunity to reconstruct the system whilst addressing such problems as the environmental impact of transport, congestion and questions of transport justice such as accessibility ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Establishing the origin of solar-mass black holes and the connection to dark matter