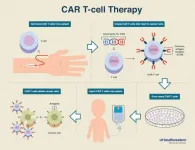
(Press-News.org) DALLAS - March 8, 2021 - A new type of CAR T-cell therapy more than triples the expected length of remission for multiple myeloma patients who have relapsed several times, according to an international clinical trial with UT Southwestern as the lead enrolling site.
Results of the trial, published recently in the New England Journal of Medicine, were significantly better than those seen with other therapies available to heavily relapsed and refractory myeloma patients who had already received the three main classes of treatment. Nearly three-quarters of the patients had at least a partial response to the therapy. About a third achieved a complete remission, with the disappearance of all traces of cancer.
Median time without the disease worsening was 8.8 months with this new treatment, but Larry D. Anderson Jr., M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of internal medicine and co-first author of the journal article, points out that patients who received the trial's maximum dose of engineered T-cells experienced longer remissions, bringing the average to more than 12 months. Previously, similar patients treated with currently available therapies following multiple relapses have only had an average of three to four months of remission before their disease returned.
"We have patients that are over two years out from their single infusion of CAR T-cells and still in remission despite having no other treatment options when they were enrolled in this trial," says Anderson, a member of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center who cares exclusively for patients with plasma cell disorders, mostly myeloma patients. "The results mark a true breakthrough with unprecedented depth and duration of remissions from what we hope will be the first cellular therapy option to become available for myeloma patients. Even though we don't yet know if some of these patients may be cured, and many relapse within one to two years, it can at least buy many patients time until other treatment options become available. Most patients also have good quality of life with relatively low risk of severe CAR T-cell-related side effects."
Multiple myeloma, the second most common blood cancer, is a cancer of plasma cells, a white blood cell important in the immune system. The disease's attack on bone marrow puts patients at risk of life-threatening infections. It is diagnosed in more than 32,000 people a year, and African Americans are twice as likely as the general population to be diagnosed with this disease.
Three main classes of treatment are available now for multiple myeloma: drugs called proteasome inhibitors, drugs to modulate the immune system, and antibody treatments. Among more than a dozen new therapies for myeloma approved by the Food and Drug Administration over the past decade, most offer only a few months of remission for patients with multiple relapses. Until now, most treatments induce responses in only a third of patients, and complete remissions are rare.
The phase 2 trial involved 128 patients, ages 18 and older, who previously had been given regimens from the three main classes of treatment. The patients received a median of six previous antimyeloma regimens; 120 formerly had undergone stem cell transplantation.
The clinical trial included nine sites in the U.S., one in Canada, and 10 sites in five European countries. Several patients traveled from as far away as Michigan and Minnesota to UT Southwestern's Dallas campus to be part of the trial.
Study participants had their T-cells engineered to target a molecule called B-cell maturation antigen, or BCMA, which is only found in plasma cells and myeloma cells. This new T-cell therapy for myeloma patients is called idecabtagene vicleucel, or ide-cel. It is also known as bb2121.
The infusions of the engineered cells started a two-week hospitalization period during which doctors watched for possible side effects such as anemia; neutropenia, a drop in a type of white blood cells; and thrombocytopenia, a drop in blood platelets. Although low blood counts were common, they were manageable, and other severe side effects were uncommon.
"One of the nice things we saw in this study was that the rates of severe CAR T-cell-related toxicities - called neurotoxicity and cytokine release syndrome - were very low in multiple myeloma compared to what we have seen with lymphoma CAR T-cell infusions," Anderson says. "The majority of people had some side effects, but most were low level and manageable, and I would say this therapy is often much better tolerated than a stem cell transplant, which most of these patients had already gone through."
Pioneered in the late 1980s, CAR T-cell therapy is a promising and still emerging treatment for blood cancers. CAR, which stands for chimeric antigen receptor, takes part of its name from the chimera, the mythical animal with the tail of a serpent and head of a lion. In modern medicine's version of the chimera, the head is an antibody, and the tail is a T-cell receptor. CAR T-cell therapy involves harvesting a patient's own T-cells by withdrawing blood, reengineering them in a lab to have this cancer-fighting chimera, and then growing hundreds of millions of them to put back into the patient by infusion.
CAR T-cell therapy is currently approved for use only in lymphoma and leukemia. Several different CAR T-cell treatments for myeloma are in clinical trials, but this CAR T-cell treatment is the first to complete and publish data from an FDA registration trial. Based on these results, the pharmaceutical companies Bristol Myers Squibb and bluebird bio are seeking FDA approval of ide-cel as a standard therapy for relapsed myeloma with a decision expected by the end of March.
The trial was funded by bluebird bio and Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb company. Anderson is a consultant who serves on an advisory board for Celgene and has other consulting activities disclosed in the manuscript.
INFORMATION:
A woman grips her purse tightly as you approach. A store manager follows you because you look "suspicious." You enter a high-end restaurant, and the staff assume you're applying for a job. You're called on in work meetings only when they're talking about diversity.
The indignities and humiliations Black men -- even those who have "made it" -- regularly endure have long been seen as part and parcel of life in the United States among the Black community, a sort of "Black tax" that takes a heavy toll on physical and mental health.
Now, a new UCLA-led study reveals these "hidden costs" of being Black in America. ...
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - Moral outrage is an attractive behavior, particularly to people seeking long-term relationships, according to a new paper by researchers including a University of Arkansas psychologist.
The work indicates that people who displayed moral outrage were considered more benevolent and trustworthy than a control person not displaying outrage, and therefore more likely to possess other prosocial behaviors that would benefit a long-term relationship. There was a catch, however: Researchers found that people had to take action to address the moral wrong in question and not just talk about ...
Aurora, Colo. (March 8, 2021) - In a new study published in JAMA Pediatrics, researchers at Children's Hospital Colorado (Children's Colorado) have found that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component of marijuana, stays in breast milk for up to six weeks, further supporting the recommendations of the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine to abstain from marijuana use during pregnancy and while a mother is breastfeeding. This is the first study examining THC in breastmilk and plasma among women with known marijuana use in pregnancy since a 1982 study in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"With the increasing utilization of marijuana in society as a ...
Research from Queen Mary University of London has concluded that there is convincing evidence that type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's disease. The same study found that there was also evidence that type 2 diabetes may contribute to faster disease progression in patients who already have Parkinson's.
Treating people with drugs already available for type 2 diabetes may reduce the risk and slow the progression of Parkinson's. Screening for and early treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with Parkinson's may be advisable.
Previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses have produced conflicting results around ...
Key Takeaways:
Machine learning offers more accurate targeting in mobile advertising.
Behavioral targeting is more effective than contextual targeting.
There is a possibility for self-regulation because too much behavioral targeting can reduce competition and hurt ad networks' revenues.
CATONSVILLE, MD, March 8, 2021 - It's a common assumption among marketers that if you can customize any form of marketing, particularly mobile advertising, you'll get better results. With this in mind, mobile marketing relies significantly on user tracking data ...
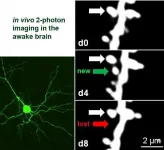
Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying brain "plasticity"(how the brain can learn, develop and reorganise itself) is crucial for explaining many illnesses and conditions. Neurocientists from the University of Göttingen and University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG) have now managed to repeatedly image synapses, the tiny contact sites between neurons, in awake adult mice. They are the first to discover that adult neurons in the primary visual cortex with an increased number of "silent synapses" (ie newly formed synapses that are inactivated), lacking a certain protein (PSD-95), display structural changes that were previously only reported in young mice. This ...
Professor Rosalind Gill, from City, University of London's Gender and Sexualities Research Centre, has today published a new report to mark International Women's Day.
The report - Changing the Perfect Picture: Smartphones, Social Media and Appearance Pressures - is based on research with 175 young women and nonbinary people in the UK.
Covering a range of issues - experiences of lockdown, feelings about 'body positivity', how to show support for Black Lives Matter - the research documents young people's persistent anger with a mass media that they deem 'too white', 'too heterosexual' and too focused on very narrow definitions ...
Mental health issues such as burnout and psychological distress are matters for concern among young adults, and are even more pertinent in today's uncertain global climate. A recent paper by Yale-NUS College alumna Ms Joanna Chue (Class of 2019) and Assistant Professor of Social Sciences (Psychology) Cheung Hoi Shan identified five components of resilience that are applicable in Singapore's cultural context, and demonstrated that college students possessing a higher degree of resilience were less susceptible to burnout and psychological distress. By identifying learnable components ...
Researchers at Paderborn and Bielefeld University are hoping to change this, and are discussing how the explainability of artificial intelligence can be improved and adapted to the needs of human users. Their work has recently been published in the respected journal IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems. The researchers describe explanation as a social practice, in which both parties co-construct the process of understanding.
Explainability research
"Artificial systems have become complex. This is a serious problem - particularly when humans are held accountable for computer-based decisions," says Professor Philipp Cimiano, a computer scientist at Bielefeld University. Particularly in the ...
In the EU alone, 78,800 men died of prostate cancer last year. While tumors discovered at an early stage can often be completely removed by surgery and radiation therapy, the prospects of successful treatment are reduced if the cancer has further metastasized. At present, physicians cannot predict drug response or therapy resistance in patients.
Three-dimensional structures
The team led by PD Dr. Marianna Kruithof-de Julio at the Urology Research Laboratory at the Department for BioMedical Research (DBMR) of the University of Bern and Inselspital Bern, has developed a new strategy for the generation of prostate cancer organoids that ...