(Press-News.org) Scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have developed a tool to monitor communications within the brain in a way never before possible, and it has already offered an explanation for why Alzheimer's drugs have limited effectiveness and why patients get much worse after going off of them.
The researchers expect their new method will have tremendous impact on our understanding of depression, sleep disorders, autism, neurological diseases and major psychiatric conditions. It will speed scientific research into the workings of the brain, they say, and facilitate the development of new treatments.
"We can now 'see' how brain cells communicate in sharp detail in both the healthy and diseased brains," said lead researcher J. Julius Zhu, PhD, of UVA's Department of Pharmacology.
Unexpected Transmissions
The new method developed by Zhu and his collaborators lets scientists examine transmissions inside the brain at both the microscopic level and the far, far smaller nanoscopic level. It combines a biological "sensor" with two different forms of cutting-edge imaging.
The approach can quantify "neuromodulatory" transmissions, which are associated with major brain disorders, including addiction, Alzheimer's, depressive disorders and schizophrenia. They're also linked to autism, epilepsy, eating disorders and sleep disorders.
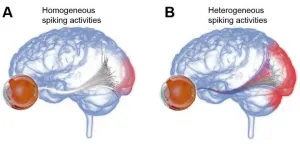
Neuromodulatory transmissions are the "slower" transmissions in the brain. They're typically thought to involve lots of neurons in large regions. That's in contrast to the much faster transmissions that happen neuron-to-neuron.
But Zhu's new tool has already shown it's not that simple.
In Alzheimer's disease, Zhu and his colleagues discovered a surprising degree of "fine control and precision" in the supposedly shotgun neuromodulatory transmissions. Widely used Alzheimer's drugs known as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors may inhibit this precise communication, the scientists report. That may explain the limited effectiveness of the drugs, they say.
The researchers went on to identify potential changes in the brain that could be brought about by long-term use of the drugs, which could explain why patients often get much worse when they stop taking them. "The new method points out Alzheimer's defects in the unprecedented spatial and temporal resolution, defining the precise targets for medicine," Zhu said.
Alzheimer's, the researchers say, is just the tip of the iceberg. The new system has "broad applicability" across the spectrum of neurological and psychiatric diseases and disorders, they report. In the years to come, the scientists predict, it will help doctors understand neurological illnesses and psychiatric problems, screen drugs for potential treatments, identify disease-causing genes and develop better, more personalized medicine tailored for specific patient needs.
"If we see problems," Zhu said, "we will be ready to treat them."
INFORMATION:
Results Published
The researchers have described new approach and their findings in the scientific journal Molecular Psychiatry. The research teams consisted of Li Lin, Smriti Gupta, W. Sharon Zheng, Ke Si and Zhu, and Paula K. Zhu, W. Sharon Zheng, Peng Zhang, Miao Jing, Philip M. Borden, Farhan Ali, Kaiming Guo, Jiesi Feng, Jonathan S. Marvin, Yali Wang, Jinxia Wan, Li Gan, Alex C. Kwan, Li Lin, Loren L. Looger, Yulong Li and Yajun Zhang.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog
(LOS ANGELES) - Recent advances in technology have opened many possibilities for using wearable and implantable sensors to monitor various indicators of patient health. Wearable pressure sensors are designed to respond to very small changes in bodily pressure, so that physical functions such as pulse rate, blood pressure, breathing rates and even subtle changes in vocal cord vibrations can be monitored in real time with a high degree of sensitivity.
Such responses occur when a substance in the sensor "gates," or allows selected pressure signals to pass to a transistor, which then conducts and amplifies these signals for detection. A recent type of transistor, organic electrochemical transistors ...
Visual sensation begins at the retina, which is the neural tissue located at the back of eyeballs. It has been known that the retina detects light using photoreceptors which are light-sensitive nerve cells.In case of retinal degenerative diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration, those light sensing neurons are gradually damaged, leading to a profound vision loss. At this moment, no cure is available for the abovementioned ailments. But, microelectronic retinal prostheses can create artificial vision by electrically stimulating remaining retinal neurons although the prosthetic vision is still far removed from normal vision.
To further improve the quality of prosthetic artificial vision, Dr. Maesoon ...
A staple for many, chickpeas are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber and offer many health benefits, such as improving digestion and reducing the risk of ailments including heart disease and cancer. However, chickpeas possess a rather narrow genetic diversity and are susceptible to Ascochyta blight, a devastating disease that can cause a yield loss of up to 100 percent. In Australia alone, this disease costs an average of $4.8 million annually.
To help curtail the impact of Ascochyta blight, plant pathologists in Western Australia have turned to wild relatives of the ...
In the spring of 2020, the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic appeared to coincide with the tree pollen season in the northern hemisphere. These observations prompted an international team of researchers to conduct an extensive investigation: The scientists wanted to know whether there is a demonstrable link between airborne pollen concentrations and SARS-CoV-2 infection rates.
Pollen is a significant environmental factor influencing infection rates
Under the leadership of first author Athanasios Damialis, the team at the Chair of Environmental Medicine at TUM collected data on airborne pollen concentrations, weather conditions and SARS-CoV-2 infections - taking into consideration the variation of infection rates from ...
Depending on the topic, people's attitudes can change from moment to moment or last a lifetime. The factors that make one opinion long-lasting and another ephemeral, however, are not always clear.
Past studies have demonstrated that opinions based on hard facts and data can remain constant over time, but new research published in the journal Psychological Science reveals that attitudes based on feelings and emotions can also stand the test of time. This research has implications for both predicting whose attitudes are fixed versus fleeting and how to nudge people to form more long-lasting opinions.
"We have ...
Washington, March 9, 2021--A comprehensive meta-analysis of prior research has found, overall, that children ages 1 to 8 were less likely to understand picture books when they read the digital, versus print, version. However, when digital picture books contain the right enhancements that reinforce the story content, they outperform their print counterparts. The results were published today in Review of Educational Research, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
Authors Natalia Kucirkova at the University of Stavanger in Norway and The Open University in the United Kingdom, and May Irene Furenes and Adriana G. Bus at the University of Stavanger, analyzed the results of 39 studies that included a total 1,812 children between the ages of 1 and 8. For their ...
PHILADELPHIA-- Head injury in the United States is common, END ...
Imagine using stem cells from your bone marrow to grow a piece of bone tissue in the lab, after which medical doctors explore which drugs have the desired effect on your bones. In this way, a tailor-made treatment plan would be made for everyone, with the best approach being clear in advance. Personalized medicine at its best.
That vision of the future is no longer science fiction now that researchers from Eindhoven University of Technology and Radboud university medical center have actually realized the first part: growing a lifelike piece of bone tissue from human stem cells. It is the first organoid of bone, a simplified version of the original, the researchers report today in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
Coherent picture
"With ...
Smart speakers, such as Amazon Echo and Google Home, have proven adept at monitoring certain health care issues at home. For example, researchers at the University of Washington have shown that these devices can detect cardiac arrests or monitor babies breathing.
But what about tracking something even smaller: the minute motion of individual heartbeats in a person sitting in front of a smart speaker?
UW researchers have developed a new skill for a smart speaker that for the first time monitors both regular and irregular heartbeats without physical contact. The system sends inaudible sounds from the speaker out into ...
Nanoengineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a "wearable microgrid" that harvests and stores energy from the human body to power small electronics. It consists of three main parts: sweat-powered biofuel cells, motion-powered devices called triboelectric generators, and energy-storing supercapacitors. All parts are flexible, washable and can be screen printed onto clothing.
The technology, reported in a paper published Mar. 9 in Nature Communications, draws inspiration from community microgrids.
"We're applying the concept of the microgrid to create wearable systems that are powered sustainably, reliably and independently," said co-first author Lu Yin, a nanoengineering Ph.D. student ...