(Press-News.org) People over 65 shouldn't take three or more medicines that act on their brain and nervous system, experts strongly warn, because the drugs can interact and raise the risk of everything from falls to overdoses to memory issues.
But a new study finds that 1 in 7 people with dementia who live outside nursing homes are taking at least three of these drugs.
Even if they received the drugs to calm some of dementia's more troubling behavioral issues, the researchers say, taking them in combination could accelerate their loss of memory and thinking ability, and raise their chance of injury and death.
The new study is published in JAMA by a team led by a University of Michigan geriatric psychiatrist who has studied the issue of medication for dementia-related behaviors for years.
It's based on data from 1.2 million people with dementia covered by Medicare and focuses on medications such as antidepressants, sedatives used as sleep medications, opioid painkillers, antipsychotics, and anti-seizure medications.
More than 831,000 of the entire study population received at least one of the medications at least once during the study period in 2018. More than 535,000 of them -- nearly half of all the people with dementia in the study -- took one or two of them for more than a month.
But the researchers focused on the 13.9% of the study population who took three or more drugs that act on the central nervous system, and took them for more than a month. They dubbed this "CNS-active polypharmacy."
That level of use goes beyond the limits recommended by the internationally accepted guidelines called the END
A trio that could spell trouble: Many with dementia take risky combinations of medicines
Despite guidelines, 14% are on three or more drugs that act on the brain and nervous system; families and providers should review prescriptions regularly
2021-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
90-day dapivirine ring for women's HIV prevention passes its first test in Phase I study
2021-03-09
PITTSBURGH, 9 March 2021 - If approved, the monthly dapivirine vaginal ring would be the first biomedical HIV prevention method designed specifically for cisgender women, as well as the first long-acting method. Looking to the future, researchers from the National Institutes of Health-funded END ...
Characterizing different cell types in the upper gastrointestinal tract
2021-03-09
Researchers from the group of Hans Clevers identified and characterized rare cell types in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Using single cell RNA sequencing, they studied the cellular composition of the esophagus, stomach and upper part of the small intestine. They provide detailed gene expression analyses for all epithelial cells in these organs. Furthermore, they identified a rare cell type that is most likely responsible for the secretion of high volumes of water in humans. This cell type provides a link to gastrointestinal defects in patients with cystic fibrosis. The paper was published in Cell Reports on the 9th ...
Social distancing policies, changes in traffic volume, accidents, injuries
2021-03-09
What The Study Did: Researchers compared traffic volume and motor vehicle crash injuries before, during and after COVID-19-related state-of-emergency and stay-at-home orders in Ohio from January to July last year with the same period in 2019.
Authors: Motao Zhu, Ph.D., of the Abigail Wexner Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.25770)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article ...
Adhesion, contractility enable metastatic cells to go against the grain
2021-03-09
Bioengineers at the University of California San Diego and San Diego State University have discovered a key feature that allows cancer cells to break from typical cell behavior and migrate away from the stiffer tissue in a tumor, shedding light on the process of metastasis and offering possible new targets for cancer therapies.
It has been well documented that cells typically migrate away from softer tissue to stiffer regions within the extracellular matrix-- a process called durotaxis. Metastatic cancer cells are the rare exception to this rule, moving away from the stiffer tumor tissue to softer tissue, and spreading ...
Injectable porous scaffolds promote better, quicker healing after spinal cord injuries
2021-03-09
WASHINGTON, March 9, 2021 -- Spinal cord injuries can be life-changing and alter many important neurological functions. Unfortunately, clinicians have relatively few tools to help patients regain lost functions.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from UCLA have developed materials that can interface with an injured spinal cord and provide a scaffolding to facilitate healing. To do this, scaffolding materials need to mimic the natural spinal cord tissue, so they can be readily populated by native cells in the spinal cord, essentially filling in gaps left by injury.
"In this study, we demonstrate that incorporating a regular network of pores throughout these materials, where pores are sized similarly to normal cells, increases infiltration of cells from spinal cord tissue ...
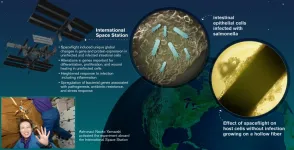
New study highlights first infection of human cells during spaceflight
2021-03-09
Astronauts face many challenges to their health, due to the exceptional conditions of spaceflight. Among these are a variety of infectious microbes that can attack their suppressed immune systems.
Now, in the first study of its kind, Cheryl Nickerson, lead author Jennifer Barrila and their colleagues describe the infection of human cells by the intestinal pathogen Salmonella Typhimurium during spaceflight. They show how the microgravity environment of spaceflight changes the molecular profile of human intestinal cells and how these expression patterns are further changed in response to infection. In another first, the researchers were also able to detect ...
Five herbal medicines potent against tick-borne disease babesiosis in lab, says new study
2021-03-09
PORTOLA VALLEY, CA, March 9, 2021 -- Bay Area Lyme Foundation, a leading sponsor of Lyme disease research in the U.S., today announced the publication of new data finding that five herbal medicines had potent activity compared to commonly-used antibiotics in test tubes against Babesia duncani, a malaria-like parasite found on the West Coast of the U.S. that causes the disease babesiosis. Published in the journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, the laboratory study was funded in part by the Bay Area Lyme Foundation. Collaborating researchers were from Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, California Center for Functional Medicine, and FOCUS Health Group, Naturopathic.
"This research is particularly important ...
Amyloid plaque mutation map opens new avenues for early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2021-03-09
A study published in the journal eLife made all the possible mutations in the amyloid beta peptide and tested how they influence its aggregation into plaques, a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease.
The comprehensive mutation map, which is the first of its kind, has the potential to help clinical geneticists predict whether the mutations found in amyloid beta can make an individual more prone to developing Alzheimer's disease later in life.
The complete atlas of mutations will also help researchers better understand the biological mechanisms that control the onset of the disease.
"The genetic sequencing of individuals is increasingly common. As a result, we are ...
Type 2 diabetes: an unknown danger for women with gestational diabetes
2021-03-09
While it's an unfair reality that women who develop gestational diabetes are ten times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life, only a third of these women realise that they're at high risk, according to new research by the University of South Australia.
Conducted in partnership with the University College Dublin, the research examined the views of 429 Australian women with a history of gestational diabetes to establish their perceived risks of developing type 2 diabetes, potential barriers to losing weight, and useful strategies for supporting a healthy weight.
Lead researcher, UniSA's Kristy ...
Plants as protein factories: Antioxidant boosts the yield of valuable biologics
2021-03-09
Tsukuba, Japan - Producing high-value pharmaceutical proteins in plants--sometimes called "molecular pharming"--offers advantages over some other manufacturing methods, notably the low cost and ease of scaling up production to meet demand. But expressing large quantities of "foreign" proteins in plants can also sometimes lead to problems, such as dehydration and premature cell death in the leaves.
Now a team led by Professor Kenji Miura of the University of Tsukuba has discovered that spraying leaves with high concentrations of the antioxidant ascorbic acid (vitamin C) can increase protein production three-fold or even more. They recently published their findings in Plant Physiology.
The team worked with a close relative of tobacco, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
[Press-News.org] A trio that could spell trouble: Many with dementia take risky combinations of medicinesDespite guidelines, 14% are on three or more drugs that act on the brain and nervous system; families and providers should review prescriptions regularly