(Press-News.org) Some of Princeton's leading cancer researchers were startled to discover that what they thought was a straightforward investigation into how cancer spreads through the body -- metastasis -- turned up evidence of liquid-liquid phase separations: the new field of biology research that investigates how liquid blobs of living materials merge into each other, similar to the movements seen in a lava lamp or in liquid mercury.
"We believe this is the first time that phase separation has been implicated in cancer metastasis," said Yibin Kang, the Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis Professor of Molecular Biology. He is the senior author on a new paper featured on the cover of the current issue of Nature Cell Biology.
Not only does their work tie phase separations to cancer research, but the merging blobs turned out to create more than the sum of their parts, self-assembling into a previously unknown organelle (essentially an organ of the cell).
Discovering a new organelle is revolutionary, Kang said. He compared it to finding a new planet within our solar system. "Some organelles we have known for 100 years or more, and then all of a sudden, we found a new one!"
This will shift some fundamental perceptions of what a cell is and does, said Mark Esposito, a 2017 Ph.D. alumnus and current postdoc in Kang's lab who is the first author on the new paper. "Everybody goes to school, and they learn 'The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell,' and a few other things about a few organelles, but now, our classic definition of what's inside a cell, of how a cell organizes itself and controls its behavior, is starting to shift," he said. "Our research marks a very concrete step forward in that."
The work grew out of collaborations between researchers in the labs of three Princeton professors: Kang; Ileana Cristea, a professor of molecular biology and leading expert in the mass spectroscopy of living tissue; and Cliff Brangwynne, the June K. Wu '92 Professor of Chemical and Biological Engineering and director of the Princeton Bioengineering Initiative, who pioneered the study of phase separation in biological processes.
"Ileana is a biochemist, Cliff is a biophysicist and engineer, and I am a cancer biologist -- a cell biologist," Kang said. "Princeton is just a wonderful place for people to connect and collaborate. We have a very small campus. All the science departments are right next to each other. Ileana's lab is actually on the same floor of Lewis Thomas as mine! These very close relationships, among very diverse research areas, allow us to bring in technologies from many different angles, and allow breakthroughs to understanding the mechanisms of metabolism in cancer -- its progression, metastasis and the immune response -- and also come up with new ways to target it."
The latest breakthrough, featuring the as-yet unnamed organelle, adds new understanding to the role of the Wnt signaling pathway, a system whose discovery led to the 1995 Nobel Prize for Eric Wieschaus, Princeton's Squibb Professor in Molecular Biology and a professor in the Lewis-Sigler Institute for Integrative Genomics. The Wnt pathway is vital to embryonic development in countless organisms, from tiny invertebrate insects to humans. Wieschaus discovered that cancer can co-opt this pathway, essentially corrupting its ability to grow as rapidly as embryos must, to grow tumors.
Subsequent research has revealed that the Wnt signaling pathway plays multiple roles in healthy bone growth as well as in cancer metastasizing to bones. Kang and his colleagues were investigating the complex interplay between Wnt, a signaling molecule called TGF-b, and a relatively unknown gene named DACT1 when they discovered this new organelle.
Think of it as panic-shopping before a storm, said Esposito. Buying up bread and milk before a blizzard -- or hoarding hand sanitizer and toilet paper when a pandemic is looming on the horizon -- aren't just human traits, it turns out. They happen on the cellular level, too.
Here's how it works: The panicked shopper is DACT1, and the blizzard (or pandemic) is TGF-ß. The bread and hand sanitizer are Casein Kinase 2 (CK2), and in the presence of a storm, DACT1 grabs up as much of them as possible, and the newly discovered organelle sequesters them away. By hoarding CK2, the shopper prevents other folks from making sandwiches and sanitizing their hands, i.e. preventing the healthy operation of the Wnt pathway.
Through a series of detailed and complex experiments, the researchers pieced together the story: bone tumors initially induce Wnt signaling, to disseminate (spread) through the bone. Then, TGF-b, which is abundant in bones, inspires the panicked shopping, suppressing Wnt signaling. The tumors then stimulate the growth of osteoclasts, which scrub away old bone tissue. (Healthy bones are constantly being replenished in a two-part process: osteoclasts scrub away a layer of bone, then osteoblasts rebuild the bone with new material.) This further increases the TGF-b concentration, prompting even more DACT1 hoarding and subsequent Wnt suppression that has been shown to be important in further metastasis.
By discovering the roles of DACT1 and this organelle, Kang and his team have found new possible targets for cancer drugs. "For example, if we have a way to disrupt the DACT1 complex, perhaps the tumor will disseminate, but it will never be able to 'grow up' to be life-threatening metastasis. That's the hope," Kang said.
Kang and Esposito recently co-founded KayoThera to pursue the development of medications for patients with late-stage or metastatic cancers, based on their work together in the Kang lab. "The kind of fundamental study that Mark is doing both presents groundbreaking science findings and can also lead to medical breakthroughs," said Kang.
The researchers have found that DACT1 plays many other roles as well, which their team is only beginning to explore. The mass spectrometry collaboration with Cristea's team revealed more than 600 different proteins in the mysterious organelle. Mass spectrometry allows scientists to find out the exact components of almost any substance imaged on a microscope slide.
"This is a more dynamic signaling node than just controlling Wnt and TGF-b." said Esposito. "This is just the tip of the iceberg on a new field of biology."
This bridge between phase separations and cancer research is still in its infancy, but it already shows great potential, said Brangwynne, who was a co-author on the paper.
"The role that biomolecular condensates play in cancer -- both its genesis but particularly its spread through metastasis -- is still poorly understood," he said. "This study provides new insights into the interplay of cancer signaling pathways and condensate biophysics, and it will open up new therapeutic avenues."
INFORMATION:
"TGF-β-induced DACT1 biomolecular condensates repress Wnt signaling to promote bone metastasis," by Mark Esposito, Cao Fang, Katelyn C. Cook, Nana Park, Yong Wei, Chiara Spadazzi, Dan Bracha, Ramesh T. Gunaratna, Gary Laevsky, Christina J. DeCost, Hannah Slabodkin, Clifford P. Brangwynne, Ileana M. Cristea, and Yibin Kang, appears in the March 9 issue of Nature Cell Biology (DOI: 10.1038/s41556-021-00641-w). This work was supported the National Institutes of Health (R01CA212410 to YK, R01GM114141 to IMC, F31CA192461 to ME, and F31AI147637 and T32GM007388 to KCC); the New Jersey Commission on Cancer Research (DCHS19PPC029 to RG); the Brewster Foundation; and the U. S. Department of Defense (BC123187 to YK).
Broad political, economic, and social factors influence disciplinary punishment. In particular, over the last half century, such considerations have shaped jurisdictions' use of the death penalty, which has declined considerably since the 1990s. A new study examined the factors associated with use of the death penalty at the county level to provide a fuller picture of what issues influence court outcomes. The study concludes that partisan politics, religious fundamentalism, and economic threat influenced local decisions about the death penalty. The study also found that the size of the African American population, which ...
CHAPEL HILL, NC -- In a viewpoint perspective published in JAMA on March 9, 2021, a University of North Carolina Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center researcher and two other experts endorsed the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services' (CMS) requirement for a patient and their doctor to engage in a shared discussion of benefits and harms before proceeding with a low-dose spiral computed tomography (LDCT) scan as a method for preventing lung cancer death. An accompanying evidence report detailed the benefits and harms from screening, suggesting that shared decision-making between a patient ...
URBANA, Ill. - If you haven't been the parent or caregiver of an infant in recent years, you'd be forgiven for missing the human milk oligosaccharide trend in infant formulas. These complex carbohydrate supplements mimic human breast milk and act like prebiotics, boosting beneficial microbes in babies' guts.
Milk oligosaccharides aren't just for humans, though; all mammals make them. And new University of Illinois research suggests milk oligosaccharides may be beneficial for cats and dogs when added to pet diets.
But before testing the compounds, scientists had to find them.
"When we first looked into this, there had only been one study on milk oligosaccharides in dogs, and none in domestic cats. The closest were really small studies on a single lion and a single ...
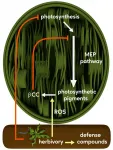
In a new study in PNAS, an international team of researchers including scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology has shown that Arabidopsis thaliana plants produce beta-cyclocitral when attacked by herbivores and that this volatile signal inhibits the methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway. The MEP pathway is instrumental in plant growth processes, such as the production of pigments for photosynthesis. In addition to down-regulating the MEP pathway, beta-cyclocitral also increases plant defenses against herbivores. Since the MEP pathway is only found in plants and microorganisms, but not animals, knowledge of a signal molecule like beta-cyclocitral opens up new possibilities for the development ...
Brazilian researchers who study a native venomous fish have confirmed a route to drug development for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis and asthma.
The venomous toadfish Thalassophryne nattereri contains a peptide (TnP) with anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic potential. Confirmation of this potential has now come via the zebrafish Danio rerio, a popular aquarium species native to South Asia that shares 70% of its genome with humans and is widely used as a model for in vivo trials in drug development.
The researchers tested TnP in D. rerio to measure its toxicity. In a little over a year, their research showed that the peptide is safe. It did not cause cardiac dysfunction or neurological problems in the toxicity tests ...
Health care systems could save lives and minimize losses by optimizing resource allocation and implementing mitigation strategies, according to two new studies. Colorado State University researchers explored how our health care systems might perform under multiple disasters and multiple waves of COVID-19, and how we can keep them functioning when we need them most.
In the first study, published in Nature Communications, Civil and Environmental Engineering Ph.D. student Emad Hassan and Associate Professor Hussam Mahmoud investigated the compound effects of pandemics and natural disasters on health care systems. They combined wildfire ...
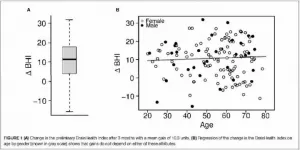
DALLAS (March 9, 2021) - Better brain health and performance for humankind is one step closer to reality with the successful trial of the groundbreaking BrainHealth Project. A cross-disciplinary team with the Center for BrainHealth® at The University of Texas at Dallas unveiled an easy-to-use online platform that delivers a novel, science-backed approach to measuring, improving and tracking one's own brain fitness.
A key innovation of the Project centers on the BrainHealth Index™ (BHI), which is based on a multidimensional definition of brain health and its upward potential. The BHI is a composite derived from a series of best-in-class assessments that explore ...
Farmers in the Midwest may be able to bypass the warming climate not by getting more water for their crops, but instead by adapting to climate change through soil management says a new study from Michigan State University.
"The Midwest supplies 30% of the world's corn and soybeans," said Bruno Basso, an ecosystems scientist and MSU Foundation Professor in the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences within the College of Natural Science. "These crops are sensitive to temperature and water changes."
Previous studies have suggested that by 2050, the Midwest will need about 35% more water to sustain its current levels of corn and soybean yields. But research done by Basso and colleagues found that the data does not support this idea. The Midwest is in a unique location that ...
If past natural disasters have taught us anything about their effects on pregnant women and developing babies, it is to pay close attention, for the added stress will surely have an impact on them. Amanda Venta, associate professor of psychology at the University of Houston, is sounding that alarm as it relates to the COVID-19 pandemic in a newly released study published in Child Psychiatry & Human Development.
"There is strong evidence to suggest that the coronavirus pandemic will affect mothers and infants through immune pathways that, in previous research, have been shown to link stress and social isolation during the pre- and post-natal periods with deficits in maternal mental health and infant well-being and development across developmental stages," reports Venta.
Research ...
The relationship between the Hawaiian bobtail squid and the bioluminescent bacteria living in its light organ has been studied for decades as a model of symbiosis. Now researchers have used a powerful chemical analysis tool to identify a small molecule produced by the bacteria that appears to play an important role in their colonization of the light organ.
The study, published March 9 in the journal mBio, adds a new wrinkle to scientists' understanding of the chemical signaling involved in this iconic symbiotic relationship. "It's exciting that there are still new things to discover, even in such a well-studied system," said corresponding author Laura Sanchez, associate professor ...