INFORMATION:
New Study Shows 24-72 Hours of Poor Oral Hygiene Impacts Oral Health
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) Poor oral hygiene produces gum-disease bacteria and accelerates oral microbiome aging faster than previously thought.
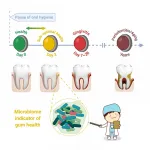
A new study shows that within 24-72 hours of the interruption of oral hygiene, there was a steep decrease in the presence of 'good oral bacteria' and the beneficial anti-inflammatory chemicals they are associated with. An increase of 'bad bacteria' typically present in the mouths of patients with periodontitis, a severe gum disease which can lead to tooth damage or loss, was also discovered.
The research team, led by scientists from Single-Cell Center, Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Procter & Gamble Company (P&G), published their findings in the journal mBio on Mar. 9, 2021.
The researchers asked 40 study participants with different levels of naturally occurring gingivitis to perform optimal oral hygiene for three weeks. This led to reduced gingivitis and a healthy baseline for the study. Gingivitis was then induced when their oral hygiene routine was interrupted over the course of four weeks. Restart of oral hygiene leads to recovery due to the reversible nature of gingivitis.
The researchers performed genetic analyses on the population of bacteria in the participants' gum as it changed. Chemical analyses of the molecules produced by the bacteria were performed and immune responses of the study participants were recorded.
Within just 24-72 hours of the cessation of oral hygiene, the researchers found there was a steep decrease in the presence of multiple Rothia species as well as the chemical betaine, which was reported to play an anti-inflammatory role in several inflammatory diseases.
In addition, there was a swift, full activation of multiple salivary cytokines - proteins and other molecules produced by immune system cells associated with inflammation. And just as the presence of the 'good bacteria' had declined, there was a sharp increase in the presence of the types of bacteria typically present in the mouths of patients with periodontitis even though there weren't any symptoms of the illness yet.
Taken together, the positive association with betaine and the negative association with gingivitis suggest that Rothia may be 'good bacteria' beneficial to gum health, contributing to the production of betaine in some way.
"We also found a sudden 'aging' of the bacteria in the mouth," said XU Jian, Director of Single-Cell Center at QIBEBT and senior author of the study. "Their oral microbiome had aged the equivalent of about a year in less than a month."
Previous studies have demonstrated that the composition of the population of oral bacteria (the oral microbiome) is a good predictor of the age of a patient. As one ages, one sees less of some species of bacteria and more of others. Older people, for example, tend to have far fewer Rothia species of bacteria.
"After only 28 days of gingivitis, we found the study participants had the 'oral microbial age' of those a year older," said HUANG Shi, one investigator leading this study.
The researchers now want to continue to study the link between Rothia, betaine and inflammation to see if they can come up with better early-stage responses to gingivitis.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Moiré than meets the eye
2021-03-10
Material behaviors depend on many things including not just the composition of the material but also the arrangement of its molecular parts. For the first time, researchers have found a way to coax carbon nanotubes into creating moiré patterns. Such structures could be useful in materials research, in particular in the field of superconducting materials.
Professor Hiroyuki Isobe from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Tokyo, and his team create nanoscopic material structures, primarily from carbon. Their aim is to explore new ways to create carbon nanostructures and to find useful applications for them. The most recent breakthrough from their lab is a new form of carbon nanotube with a very specific arrangement ...
Climate change could have direct consequences on malaria transmission in Africa
2021-03-10
The slowdown in global warming that was observed at the end of last century was reflected by a decrease in malaria transmission in the Ethiopian highlands, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by "la Caixa" Foundation, and the University of Chicago. The results, published in Nature Communications, underscore the close connection between climate and health.
For several years there has been a heated debate on the impact of global warming on malaria incidence. It is believed that the largest effect could occur in the highlands, where lower temperatures ...
Mapping functional connectivities in 3D artificial brain model by analyzing neural signals
2021-03-10
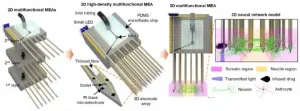
The human brain is less accessible than other organs because it is covered by a thick, hard skull. As a result, researches have been limited to low-resolution imaging or analysis of brain signals measured outside the skull. This has proved to be a major hindrance in brain research, including research on the different developmental stages, causes of diseases, and their treatments. Recently, studies have been performed using primary neurons from rats or human-derived *induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to create artificial brain models that have been applied to investigate brain developmental ...
A stronger maths foundation in first grade
2021-03-10
First grade teachers can find out who is on track with math and who is lagging, using an accurate diagnostic test that they can administer in the classroom.
After Covid-19 school reopening, or during catch-up sessions in the holidays, this is instrument can also be useful, especially in large, multilingual classrooms.
The test is supplemented by a 15-week 1-hour-a week "maths boost" invention program for first graders.
The program provides teachers good instructional material to support children in an efficient way.
Uniquely, the test measures numeracy skills along with listening comprehension and executive functions, pinpointing additional reasons why students improve ...
Avatar marketing: Moving beyond gimmicks to results
2021-03-10
Researchers from University of Texas-Arlington, University of Virginia, Sun Yat-Sen University, and University of Washington published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that seeks to advance the discipline of avatar-based marketing.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "An Emerging Theory of Avatar Marketing" and is authored by Fred Miao, Irina Kozlenkova, Haizhong Wang, Tao Xie, and Robert Palmatier.
In 2020, Samsung's Star Labs brought digital avatars to CES 2020. However, this promotion was burned by its own fanfare. The avatars looked realistic ...
Huge potential for electronic textiles made with new cellulose thread
2021-03-10
Electronic textiles offer revolutionary new opportunities in various fields, in particular healthcare. But to be sustainable, they need to be made of renewable materials. A research team led by Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, now presents a thread made of conductive cellulose, which offers fascinating and practical possibilities for electronic textiles.
"Miniature, wearable, electronic gadgets are ever more common in our daily lives. But currently, they are often dependent on rare, or in some cases toxic, materials. They are also leading to a gradual build-up of great mountains of electronic waste. There is a real need for organic, renewable materials for use in electronic textiles," says Sozan Darabi, doctoral student at the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering ...
The mystery of the missing energy - solved
2021-03-10
The efficiency of solar cells can be increased by exploiting a phenomenon known as singlet fission. However, unexplained energy losses during the reaction have until now been a major problem. A research group led by scientists at Linköping University, Sweden, has discovered what happens during singlet fission and where the lost energy goes. The results have been published in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science.
Solar energy is one of the most important fossil-free and eco-friendly sustainable sources of electricity. The silicon-based solar cells currently in use can at most use approximately 33% of the energy in sunlight and convert it to electricity. This ...
Multicellular liver-on-a-chip for modeling fatty liver disease
2021-03-10
(LOS ANGELES) - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver disease worldwide. It is found in 30% of people in developed countries and occurs in approximately 25% of people in the United States. Risk factors for the disease include obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol and poor eating habits, although this does not exclude individuals without these risk factors.
There is normally a small amount of fat found in the liver; however, if the amount of fat makes up 5% or more of the liver, this is considered to be NAFLD and it must be managed ...
Soft contact lenses eyed as new solutions to monitor ocular diseases
2021-03-10
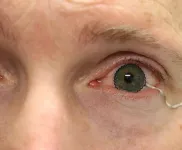
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New contact lens technology to help diagnose and monitor medical conditions may soon be ready for clinical trials.
A team of researchers from Purdue University worked with biomedical, mechanical and chemical engineers, along with clinicians, to develop the novel technology. The team enabled commercial soft contact lenses to be a bioinstrumentation tool for unobtrusive monitoring of clinically important information associated with underlying ocular health conditions.
The team's work is published in Nature Communications. The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization helped secure a patent for the technology and it is available ...
Class assignment leads to published research
2021-03-10
Armando Collazo Garcia III got more than he expected from a graduate course he took last spring. He developed a new understanding of the physics of transonic shocks produced across a laminar flow airfoil with boundary-layer suction and added a published paper to his resume.
"When I got the assignment to do a research project, I realized I already had a good data set from my master's thesis that I could use in a new way," Collazo Garcia said. "I was able to apply linear algebra techniques to manipulate the flow field data and decompose the information into modes. The modes provided a snapshot of various aspects of the flow and were ranked by their energy contribution, ...