The secret of catalysts that increase fuel cell efficiency
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) Fuel cells, which are attracting attention as an eco-friendly energy source, obtain electricity and heat simultaneously through the reverse reaction of water electrolysis. Therefore, the catalyst that enhances the reaction efficiency is directly connected to the performance of the fuel cell. To this, a POSTECH-UNIST joint research team has taken a step closer to developing high-performance catalysts by uncovering the ex-solution and phase transition phenomena at the atomic level for the first time.
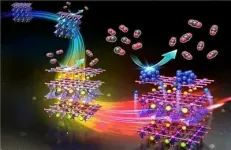
A joint research team of Professor Jeong Woo Han and Ph.D. candidate Kyeounghak Kim of POSTECH's Department of Chemical Engineering, and Professor Guntae Kim of UNIST have uncovered the mechanism by which PBMO - a catalyst used in fuel cells - is transformed from perovskite structure to layered structure with nanoparticles ex-solution1 to the surface, confirming its potential as an electrode and a chemical catalyst. These research findings were recently published as an outside back cover paper of the Energy & Environmental Science, an international journal in the field of energy.
Catalysts are substances that enhance chemical reactions. PBMO (Pr0.5Ba0.5MnO3-δ), one of the catalysts for fuel cells, is known as a material that stably operates even when directly used as a hydrocarbon, not hydrogen. In particular, it exhibits high ionic conductivity as it changes to a layered structure under a reduction environment that loses oxygen. At the same time, the ex-solution phenomenon occurs in which the elements inside the metal oxide segregate to the surface.
This phenomenon occurs voluntarily under a reduction environment without any particular process. As the elements inside the material rise to the surface, the stability and performance of the fuel cell improve immensely. However, it was difficult to design the materials because the process through which these high-performance catalysts were formed was unknown.
Focusing on these features, the research team confirmed that the process goes through a progression of phase transition, particle ex-solution, and catalyst formation. This was proved using the first-principles calculation based on quantum mechanics and the in-situ XRD2 experiment that allows the observation of real-time crystal structural changes in materials. The researchers also confirmed that the oxidation catalyst developed this way displays up to four times better performance than the conventional catalysts, verifying that this study is applicable to various chemical catalysts.
"We were able to accurately understand the materials in atomic units that were difficult to confirm in previous experiments, and successfully demonstrated it thus overcoming the limitations of existing research by accurately understanding materials in atomic units, which were difficult to confirm in existing experiments, and successfully demonstrating them," explained Professor Jeong Woo Han who led the study. "Since these support materials and nanocatalysts can be used for exhaust gas reduction, sensors, fuel cells, chemical catalysts, etc., active research in numerous fields is anticipated in the future."
INFORMATION:
This research was conducted with the support from the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center and the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-10
Italian and Russian researchers confirmed the hypothesis that the self-maintaining order in eukaryotic cells (cells with nuclei) is a result of two spontaneous mechanisms' collaboration. Similar molecules gather into 'drops' on the membrane and then leave it as tiny vesicles enriched by the collected molecules. The paper with the research results was published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
The research was carried out by an international interdisciplinary team of biologists (from Polytechnic University of Turin, Italian Institute for Genomic Medicine of the University of Turin and Candiolo Cancer Institute) and ...
2021-03-10
Variant B.1.1.7 of COVID-19 associated with a significantly higher mortality rate, research shows
The highly infectious variant of COVID-19 discovered in Kent, which swept across the UK last year before spreading worldwide, is between 30 and 100 per cent more deadly than previous strains, new analysis has shown.
A pivotal study, by epidemiologists from the Universities of Exeter and Bristol, has shown that the SARS-CoV-2 variant, B.1.1.7, is associated with a significantly higher mortality rate amongst adults diagnosed in the community compared to previously circulating strains.
The study compared death rates among people infected ...
2021-03-10
Newly published research has revealed a close link between proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease and age-related sight loss. The findings could open the way to new treatments for patients with deteriorating vision and through this study, the scientists believe they could reduce the need for using animals in future research into blinding conditions.
Amyloid beta (AB) proteins are the primary driver of Alzheimer's disease but also begin to collect in the retina as people get older. Donor eyes from patients who suffered from age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the most common cause of blindness amongst adults in the UK, have been shown to contain high levels of AB in their retinas.
This new study, published in the journal Cells, builds on previous ...
2021-03-10
The Telomeres and Telomerase Group led by Maria A. Blasco at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) continues to make progress in unravelling the role that telomeres -the ends of chromosomes that are responsible for cellular ageing as they shorten- play in cancer. The CNIO team was among the first to propose that shelterins, proteins that wrap around telomeres and act as a protective shield, might be therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. Subsequently, they found that eliminating one of these shelterins, TRF1, blocks the initiation and progression of lung cancer and glioblastoma in mouse models and prevents glioblastoma stem cells from forming secondary tumours. Now, in a study published in PLOS Genetics, ...
2021-03-10
People with aphantasia - that is, the inability to visualise mental images - are harder to spook with scary stories, a new UNSW Sydney study shows.
The study, published today in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, tested how aphantasic people reacted to reading distressing scenarios, like being chased by a shark, falling off a cliff, or being in a plane that's about to crash.
The researchers were able to physically measure each participant's fear response by monitoring changing skin conductivity levels - in other words, how much the story made a person sweat. This type of test is commonly ...
2021-03-10
WESTMINSTER, Colorado - March 10, 2021 - The paperbark tree (Melaleuca quinquenervia) was introduced to the U.S. from Australia in the 1900s. Unfortunately, it went on to become a weedy invader that has dominated natural landscapes across southern Florida, including the fragile wetlands of the Everglades.
According to an article in the journal END ...
2021-03-10
ften, humans display biases, i.e., unconscious tendencies towards a type of decision. Despite decades of study, we are yet to discover why biases are so persistent in all types of decisions. "Biases can help us make better decisions when we use them correctly in an action that has previously given us great reward. However, in other cases, biases can play against us, such as when we repeat actions in situations when it would be better not to", says Rubén Moreno Bote, coordinator of the UPF Theoretical and Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory.
In these cases, decisions are guided by tendencies, or inclinations, that do not benefit our wellbeing. For example, playing the lottery more regularly after winning ...
2021-03-10
Recent studies estimate that we use an astounding 129 billion face masks globally every month - that is 3 million a minute. Most of them are disposable face masks made from plastic microfibers.
- With increasing reports on inappropriate disposal of masks, it is urgent to recognize this potential environmental threat and prevent it from becoming the next plastic problem, researchers warn in a comment in the scientific journal Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering.
The researchers are Environmental Toxicologist Elvis Genbo Xu from University of Southern Denmark and Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering ...
2021-03-10
Global targets to improve the welfare of people across the planet will have mixed impacts on the world's forests, according to new research.
The United Nations' 17 key areas for global development - known as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) - range from tackling poverty, hunger and sanitation to promoting clean energy, economic growth and reducing inequality.
Many of these goals, such as improved peace and justice, good health and wellbeing, and quality education, will have a positive impact on the Earth's natural forests.
But others, including creating new roads, industry and infrastructure, ...
2021-03-10
Nearly 100 percent of the red snapper sampled in the Gulf of Mexico over a six-year period by University of South Florida (USF) marine scientists showed evidence of liver damage, according to a study reported in Aquatic Toxicology.
The study is the first to correlate the concentration of crude oil found in the workhorses of the digestive system -- the liver, gall bladder, and bile - with microscopic indicators of disease, such as inflammation, degenerative lesions, and the presence of parasites. The team sampled nearly 570 fish from 72 Gulf locations between 2011 to 2017 in the wake of the historic 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
"The results add to the list of other species we've analyzed indicating early warning ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The secret of catalysts that increase fuel cell efficiency