(Press-News.org) WESTMINSTER, Colorado - March 10, 2021 - The paperbark tree (Melaleuca quinquenervia) was introduced to the U.S. from Australia in the 1900s. Unfortunately, it went on to become a weedy invader that has dominated natural landscapes across southern Florida, including the fragile wetlands of the Everglades.
According to an article in the journal END
Study offers insights into management of invasive paperbark trees
2021-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In decision-making, biases are an unconscious tendency that are difficult to eradicate
2021-03-10
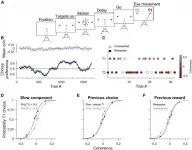
ften, humans display biases, i.e., unconscious tendencies towards a type of decision. Despite decades of study, we are yet to discover why biases are so persistent in all types of decisions. "Biases can help us make better decisions when we use them correctly in an action that has previously given us great reward. However, in other cases, biases can play against us, such as when we repeat actions in situations when it would be better not to", says Rubén Moreno Bote, coordinator of the UPF Theoretical and Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory.
In these cases, decisions are guided by tendencies, or inclinations, that do not benefit our wellbeing. For example, playing the lottery more regularly after winning ...
Face masks are a ticking plastic bomb
2021-03-10
Recent studies estimate that we use an astounding 129 billion face masks globally every month - that is 3 million a minute. Most of them are disposable face masks made from plastic microfibers.
- With increasing reports on inappropriate disposal of masks, it is urgent to recognize this potential environmental threat and prevent it from becoming the next plastic problem, researchers warn in a comment in the scientific journal Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering.
The researchers are Environmental Toxicologist Elvis Genbo Xu from University of Southern Denmark and Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering ...
How global sustainable development will affect forests
2021-03-10
Global targets to improve the welfare of people across the planet will have mixed impacts on the world's forests, according to new research.
The United Nations' 17 key areas for global development - known as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) - range from tackling poverty, hunger and sanitation to promoting clean energy, economic growth and reducing inequality.
Many of these goals, such as improved peace and justice, good health and wellbeing, and quality education, will have a positive impact on the Earth's natural forests.
But others, including creating new roads, industry and infrastructure, ...
Red Snapper in the Gulf show signs of stress
2021-03-10
Nearly 100 percent of the red snapper sampled in the Gulf of Mexico over a six-year period by University of South Florida (USF) marine scientists showed evidence of liver damage, according to a study reported in Aquatic Toxicology.
The study is the first to correlate the concentration of crude oil found in the workhorses of the digestive system -- the liver, gall bladder, and bile - with microscopic indicators of disease, such as inflammation, degenerative lesions, and the presence of parasites. The team sampled nearly 570 fish from 72 Gulf locations between 2011 to 2017 in the wake of the historic 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
"The results add to the list of other species we've analyzed indicating early warning ...
For first time, researchers send entangled qubit states through a communication channel
2021-03-10
In a breakthrough for quantum computing, University of Chicago researchers have sent entangled qubit states through a communication cable linking one quantum network node to a second node.
The researchers, based in the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) at the University of Chicago, also amplified an entangled state via the same cable first by using the cable to entangle two qubits in each of two nodes, then entangling these qubits further with other qubits in the nodes.
The results, published February 24, 2021 in Nature, could help make quantum computing more feasible and could lay the groundwork for future quantum communication networks.
"Developing methods that ...
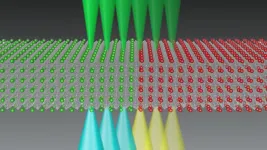
Nano-mapping phase transitions in electronic materials
2021-03-10
"Phase transitions" are a central phenomenon in physical sciences. Despite being technical-sounding, they are actually something we all experience in everyday life: ice melting into liquid water, or hot water evaporating as steam. Solid, liquid, and gas are three well known "phases" and, when one turns into another, that is a phase transition.
Rare-earth nickelate oxides, also called nickelates, have attracted a lot of interest from researchers because they display an electronic phase transition, which may be exploited in future electronic devices. This particular phase transition consists of turning from a metallic ...
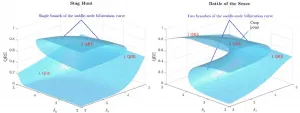
SUTD wins best paper at 35th AAAI conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021
2021-03-10
Game theory is known to be a useful tool in the study of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Multi-Agent interactions.
One basic component of these ML and AI systems is the exploration-exploitation trade-off, a fundamental dilemma between taking a risk with new actions in the quest for more information about the environment (exploration) and repeatedly selecting actions that result in the current maximum reward or (exploitation).
However, the outcome of the exploration-exploitation process is often unpredictable in practice and ...
Bacteria and viruses: a network of intestinal relationships
2021-03-10
The balance of human intestinal microbiota, consisting of hundreds of bacterial species and phages (bacteria viruses), is crucial to good health. A research team, including scientists from the CNRS* and the Institut Pasteur, has characterised the phage-bacterial interaction networks of the microbiota in ten healthy individuals, with unprecedented precision. Scientists detected several hundred bacterial and phage genomes and identified the thousands of interactions that bind them by quantifying the contacts between the DNA molecules of viruses and their hosts. This method has the advantage ...
Successful trial shows way forward on quieter drone propellers
2021-03-10
Researchers have published a study revealing their successful approach to designing much quieter propellers.
The Australian research team used machine learning to design their propellers, then 3D printed several of the most promising prototypes for experimental acoustic testing at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation's specialised 'echo-free' chamber.
Results now published in Aerospace Research Central show the prototypes made around 15dB less noise than commercially available propellers, validating the team's design methodology.
RMIT University aerospace engineer and lead researcher Dr Abdulghani Mohamed said the impressive results were enabled by two key innovations - the numerical algorithms ...
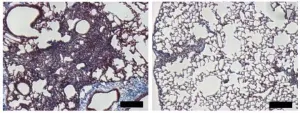
Targeting mechanosensitive protein could treat pulmonary fibrosis, study suggests
2021-03-10
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham have identified a new molecular target that could potentially treat the deadly, aging-related lung disease idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The study, which will be published March 10 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that targeting a protein called MDM4 could prevent respiratory failure by initiating a genetic program that removes scar tissue from the lungs.
IPF is characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue that stiffens the lungs and makes it difficult for patients to breathe and get sufficient oxygen into their blood. Though the causes of IPF remain unclear, age is a significant risk factor: the disease is ...