SUTD wins best paper at 35th AAAI conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021
The researchers have developed a novel connection which can help in the design of more efficient multi-agent AI systems.
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) Game theory is known to be a useful tool in the study of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Multi-Agent interactions.
One basic component of these ML and AI systems is the exploration-exploitation trade-off, a fundamental dilemma between taking a risk with new actions in the quest for more information about the environment (exploration) and repeatedly selecting actions that result in the current maximum reward or (exploitation).
However, the outcome of the exploration-exploitation process is often unpredictable in practice and the reasons behind its volatile performance have been a long-standing open question in the ML and AI communities.
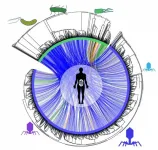
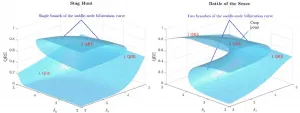
Dr Stefanos Leonardos and Assistant Professor Georgios Piliouras, researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), applied analytical tools from the theory of dynamical systems in the study of multi-agent systems and established a deep connection between exploration-exploitation and Catastrophe Theory (Figures 1 and 2). The latter is a branch of mathematics that formally explains phase transitions in all kinds of natural systems ranging from the transition from water to ice and disease outbreaks to collapses of financial markets.
This newly established connection provides a tool to predict the consequences and improve the performance of exploration-exploitation techniques in the development of multi-agent AI systems, such as robotic space missions, healthcare management or automated financial investing algorithms.
Their work, titled 'Exploration-Exploitation in Multi-Agent Learning: Catastrophe Theory Meets Game Theory', was honored with the Best Paper Award at the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021.
"In this work, we reasoned about the rich mathematical structure in multi-agent interactions and showed how this underlying geometry shapes the performance of AI systems. We believe our new findings will support the research community in achieving its ambitious goal to push beyond the current AI boundaries," explained first author Dr Stefanos Leonardos from SUTD.
"We are deeply honored by this recognition and are excited to continue our investigation of phase transitions and their implications to AI systems," added Assistant Professor Georgios Piliouras from SUTD.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-10
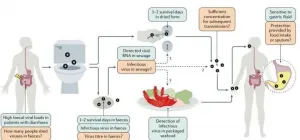
The balance of human intestinal microbiota, consisting of hundreds of bacterial species and phages (bacteria viruses), is crucial to good health. A research team, including scientists from the CNRS* and the Institut Pasteur, has characterised the phage-bacterial interaction networks of the microbiota in ten healthy individuals, with unprecedented precision. Scientists detected several hundred bacterial and phage genomes and identified the thousands of interactions that bind them by quantifying the contacts between the DNA molecules of viruses and their hosts. This method has the advantage ...
2021-03-10
Researchers have published a study revealing their successful approach to designing much quieter propellers.
The Australian research team used machine learning to design their propellers, then 3D printed several of the most promising prototypes for experimental acoustic testing at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation's specialised 'echo-free' chamber.
Results now published in Aerospace Research Central show the prototypes made around 15dB less noise than commercially available propellers, validating the team's design methodology.
RMIT University aerospace engineer and lead researcher Dr Abdulghani Mohamed said the impressive results were enabled by two key innovations - the numerical algorithms ...
2021-03-10
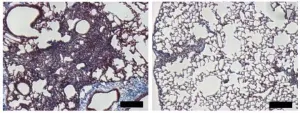
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham have identified a new molecular target that could potentially treat the deadly, aging-related lung disease idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The study, which will be published March 10 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that targeting a protein called MDM4 could prevent respiratory failure by initiating a genetic program that removes scar tissue from the lungs.
IPF is characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue that stiffens the lungs and makes it difficult for patients to breathe and get sufficient oxygen into their blood. Though the causes of IPF remain unclear, age is a significant risk factor: the disease is ...
2021-03-10
Blood pressure measurements in children and adolescents should be taken from both arms after new research showed substantial differences could be seen depending on which arm was used.
The study, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the Journal of Hypertension, found even a small difference in blood pressure measurements between arms could lead to a wrong diagnosis.
MCRI PhD candidate and study lead author Melanie Clarke said this was the first study worldwide to determine the size and frequency of inter-arm blood pressure differences in children and adolescents.
The study involved ...
2021-03-10
A researcher at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is the lead author of a study with proposals for "technosignatures" -evidence for the use of technology or industrial activity in other parts of the Universe- for future NASA missions. The article, published in the specialized journal Acta Astronautica, contains the initial conclusions of a meeting of experts in the search for intelligent extraterrestrial life, sponsored by the space agency to gather advice about this topic.
In the article, several ideas are presented to search for technosignatures that would indicate the existence of extraterrestrial civilizations, ...
2021-03-10
They say a picture is worth a thousand words. However, many women artists - and the stories their works tell - comprise less than 4 per cent of total art sold at auction and fail to attract high selling prices compared to male artists.
A world-first international study by researchers at Monash University, Maastricht University (The Netherlands) and Artnet Worldwide, based in New York City, found that a staggering 96.1 per cent (2,572,346) of all artworks sold at auctions worldwide between 2000 and 2017 are attributed to male artists.
However, work by female artists are on average 4.4 per cent more ...
2021-03-10
When the body detects a pathogen, such as bacteria or viruses, it mounts an immune system response to fight this invader. In some people, the immune system overreacts, resulting in an overactive immune response that causes the body to injure itself, which may prove fatal in some cases.
Now, scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have created a compound that could help to reduce this overactivation without impairing the body's entire immune response.
An overactive immune system leads to many autoimmune disorders - when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy ...
2021-03-10
Recently, Prof. ZHU Shu from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of CAS and Prof. Richard A. Flavell from Yale University were invited to publish a review article in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology. They systematically summarized the gastrointestinal manifestations in patients with COVID-19 and explored the possible mechanisms of intestinal symptoms caused by COVID-19 infection.
Although the clinical manifestations of COVID-19 are primarily fever, cough, and pulmonary imaging, gastrointestinal symptoms have also ...
2021-03-10
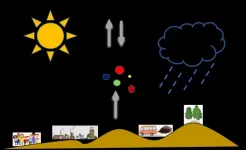
At the end of December 2019, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) quickly spread throughout Hubei Province and other parts of China. During the 2020 Spring Festival, public activities were cancelled, people tried their best to stay at home, and human and industrial activities were reduced to a basic or minimum level. However, during this period, severe fog-haze events occurred over the North China Plain. What was the leading factor that caused these severe smog incidents? And what were the individual impacts of meteorological conditions and emission reductions?
To evaluate the impacts of meteorological conditions and emission reduction measures on the near-surface PM2.5 (fine particulate matter) during the COVID-19 lockdown, ...
2021-03-10
Flexible and adaptive microelectronics is considered an innovation driver for new and more effective biomedical applications. These include, for example, the treatment of damaged nerve bundles, chronic pain, or the control of artificial limbs. For this to work, close contact between electronics and neural tissue is essential for effective electrical and mechanical coupling. In addition, potential applications arise from the production of tiny and flexible surgical tools.
An international team led by Prof. Dr. Oliver G. Schmidt, head of the Institute for Integrative Nanosciences at the Leibniz Institute ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SUTD wins best paper at 35th AAAI conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021
The researchers have developed a novel connection which can help in the design of more efficient multi-agent AI systems.