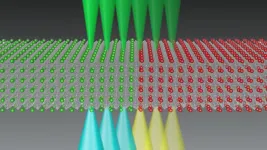
(Press-News.org) In a breakthrough for quantum computing, University of Chicago researchers have sent entangled qubit states through a communication cable linking one quantum network node to a second node.
The researchers, based in the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) at the University of Chicago, also amplified an entangled state via the same cable first by using the cable to entangle two qubits in each of two nodes, then entangling these qubits further with other qubits in the nodes.
The results, published February 24, 2021 in Nature, could help make quantum computing more feasible and could lay the groundwork for future quantum communication networks.
"Developing methods that allow us to transfer entangled states will be essential to scaling quantum computing," said Prof. Andrew Cleland, who led the research.
Sending entangled photons through a network
Qubits, or quantum bits, are the basic units of quantum information. By exploiting their quantum properties, like superposition, and their ability to be entangled together, scientists and engineers are creating next-generation quantum computers that will be able solve previously unsolvable problems.
Cleland Lab uses superconducting qubits, tiny cryogenic circuits that can be manipulated electrically.
To send the entangled states through the communication cable - a one-meter-long superconducting cable - the researchers created an experimental set-up with three superconducting qubits in each of two nodes. They connected one qubit in each node to the cable and then sent quantum states, in the form of microwave photons, through the cable with minimal loss of information. The fragile nature of quantum states makes this process quite challenging.
Cleland's former postdoctoral fellow, paper first author Youpeng Zhong, was able to develop a system in which the whole transfer process - node to cable to node - takes only a few tens of nanoseconds (a nanosecond is one billionth of a second). That allowed them to send entangled quantum states with very little information loss.
The system also allowed them to "amplify" the entanglement of qubits. The researchers used one qubit in each node and entangled them together by essentially sending a half-photon through the cable. They then extended this entanglement to the other qubits in each node. When they were finished, all six qubits in two nodes were entangled in a single globally entangled state.
Creating a scaled, networked quantum computer
In the future, quantum computers will likely be built out of modules where families of entangled qubits conduct a computation. These computers could ultimately be built from many such networked modules, similar to how supercomputers today conduct parallel computing on many central processing units connected to one another. The ability to remotely entangle qubits in different modules, or nodes, is a significant advance to enabling such modular approaches.
"These modules will need to send complex quantum states to each other, and this is a big step toward that," Cleland said. A quantum communication network could also potentially take advantage of this advance.
Cleland and his group hope to next extend their system to three nodes to build three-way entanglement.
"We want to show that superconducting qubits have a viable role going forward," he said.
INFORMATION:
Other authors on the paper include David Schuster, associate professor of physics and molecular engineering; graduate students Hung-Shen Chang, Ming-Han Chou, Christopher R. Conner, Joel Grebel, Rhys G. Povey, and Haoxiong Yan; and former postdoctoral researchers Étienne Dumur and Audrey Bienfait.
"Phase transitions" are a central phenomenon in physical sciences. Despite being technical-sounding, they are actually something we all experience in everyday life: ice melting into liquid water, or hot water evaporating as steam. Solid, liquid, and gas are three well known "phases" and, when one turns into another, that is a phase transition.
Rare-earth nickelate oxides, also called nickelates, have attracted a lot of interest from researchers because they display an electronic phase transition, which may be exploited in future electronic devices. This particular phase transition consists of turning from a metallic ...
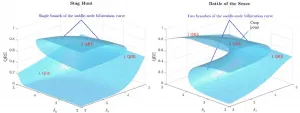
Game theory is known to be a useful tool in the study of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Multi-Agent interactions.
One basic component of these ML and AI systems is the exploration-exploitation trade-off, a fundamental dilemma between taking a risk with new actions in the quest for more information about the environment (exploration) and repeatedly selecting actions that result in the current maximum reward or (exploitation).
However, the outcome of the exploration-exploitation process is often unpredictable in practice and ...
The balance of human intestinal microbiota, consisting of hundreds of bacterial species and phages (bacteria viruses), is crucial to good health. A research team, including scientists from the CNRS* and the Institut Pasteur, has characterised the phage-bacterial interaction networks of the microbiota in ten healthy individuals, with unprecedented precision. Scientists detected several hundred bacterial and phage genomes and identified the thousands of interactions that bind them by quantifying the contacts between the DNA molecules of viruses and their hosts. This method has the advantage ...
Researchers have published a study revealing their successful approach to designing much quieter propellers.
The Australian research team used machine learning to design their propellers, then 3D printed several of the most promising prototypes for experimental acoustic testing at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation's specialised 'echo-free' chamber.
Results now published in Aerospace Research Central show the prototypes made around 15dB less noise than commercially available propellers, validating the team's design methodology.
RMIT University aerospace engineer and lead researcher Dr Abdulghani Mohamed said the impressive results were enabled by two key innovations - the numerical algorithms ...
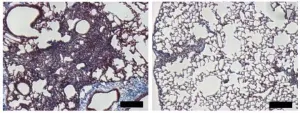
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham have identified a new molecular target that could potentially treat the deadly, aging-related lung disease idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The study, which will be published March 10 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that targeting a protein called MDM4 could prevent respiratory failure by initiating a genetic program that removes scar tissue from the lungs.
IPF is characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue that stiffens the lungs and makes it difficult for patients to breathe and get sufficient oxygen into their blood. Though the causes of IPF remain unclear, age is a significant risk factor: the disease is ...
Blood pressure measurements in children and adolescents should be taken from both arms after new research showed substantial differences could be seen depending on which arm was used.
The study, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the Journal of Hypertension, found even a small difference in blood pressure measurements between arms could lead to a wrong diagnosis.
MCRI PhD candidate and study lead author Melanie Clarke said this was the first study worldwide to determine the size and frequency of inter-arm blood pressure differences in children and adolescents.
The study involved ...
A researcher at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is the lead author of a study with proposals for "technosignatures" -evidence for the use of technology or industrial activity in other parts of the Universe- for future NASA missions. The article, published in the specialized journal Acta Astronautica, contains the initial conclusions of a meeting of experts in the search for intelligent extraterrestrial life, sponsored by the space agency to gather advice about this topic.
In the article, several ideas are presented to search for technosignatures that would indicate the existence of extraterrestrial civilizations, ...
They say a picture is worth a thousand words. However, many women artists - and the stories their works tell - comprise less than 4 per cent of total art sold at auction and fail to attract high selling prices compared to male artists.
A world-first international study by researchers at Monash University, Maastricht University (The Netherlands) and Artnet Worldwide, based in New York City, found that a staggering 96.1 per cent (2,572,346) of all artworks sold at auctions worldwide between 2000 and 2017 are attributed to male artists.
However, work by female artists are on average 4.4 per cent more ...
When the body detects a pathogen, such as bacteria or viruses, it mounts an immune system response to fight this invader. In some people, the immune system overreacts, resulting in an overactive immune response that causes the body to injure itself, which may prove fatal in some cases.
Now, scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have created a compound that could help to reduce this overactivation without impairing the body's entire immune response.
An overactive immune system leads to many autoimmune disorders - when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy ...
Recently, Prof. ZHU Shu from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of CAS and Prof. Richard A. Flavell from Yale University were invited to publish a review article in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology. They systematically summarized the gastrointestinal manifestations in patients with COVID-19 and explored the possible mechanisms of intestinal symptoms caused by COVID-19 infection.
Although the clinical manifestations of COVID-19 are primarily fever, cough, and pulmonary imaging, gastrointestinal symptoms have also ...