Firefly tourism takes flight, sparking wonder and concern
First comprehensive review on the growing global phenomenon of firefly tourism
2021-03-11
(Press-News.org) Firefly beetles rank among the world's most charismatic creatures, with luminous courtship displays that have now turned them into a popular attraction for wildlife tourists. In the first comprehensive review of firefly tourism, published in the journal Conservation Science and Practice, an international team of biologists led by a Tufts University researcher, reveal that an estimated 1 million people now travel each year to witness bioluminescent performances starring some two dozen firefly species around the world.
But the authors also point out that while this unique, insect-based tourism can bring economic, social, and psychological benefits to local communities and tourists alike, it also threatens to extinguish some local firefly populations unless adequate protections are put in place.
"With this review of the current state of firefly tourism and the declining health of their habitats, we are putting out a call to action to engage local communities and governments, as well as the tourists themselves, to act as guardians of the fireflies," said lead author Sara Lewis, professor of biology at Tufts University and co-chair of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature's (IUCN) Firefly Specialist Group, which conducted the review. The IUCN firefly group works to identify key threats and conservation issues facing fireflies in different geographic regions, and advocates for the most threatened species at national and global levels. Lewis' earlier work on fireflies with the IUCN has drawn considerable attention and fascination among the public and other researchers, with media coverage including CNN and The Washington Post.
In recent years, the number of tourists has skyrocketed at several sites in Mexico, India, Taiwan, Malaysia, Thailand, and the United States. "In Mexico, the rapid growth of firefly tourism over the past decade is thrilling but also alarming," said Tania López-Palafox, graduate student at Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México and co-author of the review. "The COVID pandemic gave them a momentary respite, but we have witnessed the harm that too much tourism can do."
Aimed at site managers, tour guides, and tourists, the report highlights the need to recognize ecological requirements across all firefly life stages. To promote the breeding success of firefly adults, sites should minimize light pollution: bright lights from buildings, vehicles, flashlights, and even cell phones - all of which can disrupt firefly courtship rituals.
Protection of nearby habitats also plays an essential role. Fireflies spend most of their life cycle in a juvenile, larval stage. These juveniles require several months or even years to develop into their adult form and, depending on the species, spend this time living below ground, in leaf litter or sometimes underwater. The authors describe former firefly sites along mangrove rivers where commercial development and excessive motorboat traffic have degraded riverbank habitat that had been essential for supporting firefly larvae.
At some sites, the reproductive cycle of firefly populations is threatened by tourists inadvertently trampling female fireflies and degrading larval habitats. Females in many species can't fly, and so are particularly susceptible to tourist foot traffic. Learn more about the mating rituals of fireflies studied by the Tufts research team in this video.
The report noted the popularity of displays created by several kinds of synchronous fireflies found in Southeast Asia and North America, where hundreds or thousands of firefly males captivate females - and tourists, too - by flashing their lights together in unison. According to co-author Anchana Thancharoen, lecturer at Kasetsart University in Bangkok, "With such mesmerizing lights, the firefly display trees make tourists fall in love at first sight. Our aim with this call to action is to channel that love into support for conservation efforts."
INFORMATION:
Other recommendations by the authors include:
1) Tailored conservation practices to protect the habitats for all life stages to thrive
2) Involvement of local communities as ecological and economic stakeholders
3) Training programs for guides
4) Educational materials for visitors and best practices for transforming tourist behavior
Whether managed by local governments or run by commercial enterprises, well-managed tourism should educate global visitors to become allies in protecting firefly populations.
"There is also a larger opportunity here," said Lewis. "Fireflies hold a special fascination for people, and their fading lights make an obvious and visible case for conservation. But fireflies can also be a gateway bug to get tourists interested in conserving many other insects, which might not be so charismatic, yet still are essential building blocks for healthy ecosystems."
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-11
An eight-week programme of mindfulness meditation improves quality of life and reduces fear of activity in heart attack patients, according to research presented today at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
"A heart attack is a serious life-threatening event and survivors can suffer from low quality of life," said study author Dr. Canan Karadas of Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey. "One reason is a fear of movement, called kinesiophobia, which limits daily activity due to concerns of another heart attack."
"Mindfulness refers to the mental state achieved by focusing awareness on the present moment, ...
2021-03-11
The research was published on the journal Nature Catalysis on December 14, 2020.
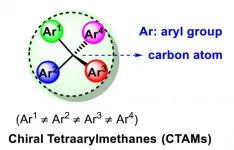
A strong bias towards linear and disc-shaped molecules has long been observed in drug molecules. In contrast, spherical molecules have been utilized on far fewer occasions, due to the lack of efficient access to the latter chemical space. Specifically, efficient strategies to synthesize tetraarylmethanes, a unique family of spherical molecules, have remained scarce.
Chiral tetraarylmethanes (CTAMs), a unique family of spherical molecules which bear four different aryl groups with defined stereochemistry, remain as a mystery due to the lack of efficient asymmetric synthesis. The challenge in asymmetric synthesis of CTAMs lies in not only the high barrier in making ...
2021-03-11
Giving at scale by the super-wealthy has done little to redistribute wealth from rich to poor, helping perpetuate social inequalities rather than remedying them, while paying considerable dividends to donors in the form of privilege and influence in society and politics, new research shows.
In the research paper 'Elite philanthropy in the United States and the United Kingdom in the new age of inequalities' researchers at the University of Bath School of Management and Newcastle University Business School also conclude that giving by the super-wealthy has failed significantly to benefit poor countries in the developing ...
2021-03-11
Pregnant women remain at increased risk of severe COVID-19, and their risk of being admitted to intensive care or needing invasive ventilation is higher than non-pregnant reproductive aged women with the virus, an ongoing global study has found.
Pregnant women with COVID-19 are at increased risk of severe COVID-19, particularly if they are from ethnic minority backgrounds, or if they have pre-existing conditions like obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes, concludes the research led by the University of Birmingham and World Health Organization (WHO).
Their research, ...
2021-03-11
New research indicates that lockdowns to help tackle the spread of COVID-19 could be linked to an increase in symptoms associated with eating disorders.
The longitudinal study, carried out by academics from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in Cambridge, England, and published in the journal Psychiatry Research, examined the behaviour and attitudes of 319 health club members during the summer of 2020.
The researchers followed up initial research into addictive or unhealthy behaviours, conducted in 2019, to investigate the effects of the first COVID-19 restrictions introduced in the spring of 2020.
Participants, with an average age of 37, completed the eating attitudes test, called EAT-26, which involved answering questions related to statements ...
2021-03-11
Osteosarcoma is a painful and aggressive bone tumour in dogs that is known to be more common in certain breeds than others. New research has now confirmed that larger breeds, such as Rottweiler, Great Dane and Rhodesian Ridgeback, have a greater risk of osteosarcoma than smaller breeds, as well as showing that breeds with shorter skulls and legs have lower osteosarcoma risk. The findings could inform future breed health reforms as well as studies into the way tumours develop from normal bone.
The study led by the University of Bristol Veterinary School in collaboration with Cardiff University and Royal Veterinary College (RVC) London, and using data from VetCompass™ and Veterinary Pathology Group (VPG) histology, looked at the epidemiology surrounding which dog breeds ...
2021-03-11
Women of the ruling class may have played an important role in the governance of El Argar, a society which flourished in the southeast of the Iberian Peninsula between 2200 and 1550 BCE, and which in the last two centuries of its existence, developed into the first state organisation of the western Mediterranean.
These are the conclusions reached by researchers from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) who led a study analysing the contents of a princely tomb (Grave 38), containing two individuals and a large amount of valuable items. The tomb was discovered in 2014 at the archaeological site of La Almoloya in Pliego, Murcia, beneath what was later identified to be the governing hall of a palatial building.
"La Almoloya ...
2021-03-11
Almost 60% of frontline health and social care workers (HSCWs) experienced a mental health disorder during the first COVID-19 lockdown, with many suffering "very high rates of distress", suggests a new study led by researchers at UCL and the University of Haifa, Israel.
Given the significantly high levels of mental health disorders across all HSCWs, the researchers (part of the UCL-led COVID Trauma Response Working Group*), are now calling for long-term planning to meet the needs of staff from across health and social care, including specialist trauma services to be set up for healthcare workers, similar to the specialist commissioned NHS psychological trauma services for military veterans.
The 'Frontline-COVID study', published ...
2021-03-11
Stormier weather will increasingly force fishers to choose between their safety and income, researchers say.
Climate change is causing more extreme weather in many locations. Storms will likely increase around the UK in the future, while many fishers in the UK also face economic insecurity.
The new study - led by the University of Exeter - worked with fishers in Cornwall to understand how they balance the risks and rewards of fishing in varying conditions.
Factors that made skippers more likely to risk fishing in high wind or waves included: being the main earner in their household, poor recent fishing success, and having a crew to support.
"Climate ...
2021-03-11
Parents of children with food allergies face significant worry, severe anxiety and post-traumatic stress - according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
Between six and eight per cent of children suffer a food allergy - with eggs, milk, and peanuts being the most common causes. They can cause vomiting, cramps, hives, swelling, eczema, breathing problems and in severe cases anaphylactic shock, which can lead to hospitalisation or death.
A new study published today finds that more than 80 per cent of parents face 'significant worry' about their child's food allergy, while ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Firefly tourism takes flight, sparking wonder and concern
First comprehensive review on the growing global phenomenon of firefly tourism