INFORMATION:
Support for the study was provided by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Lifestyle intervention is beneficial for most people with type 2 diabetes, but not all
2021-03-11
(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 11, 2021- For people who are overweight or obese and have type 2 diabetes, the first line of treatment is usually lifestyle intervention, including weight loss and increased physical activity. While this approach has cardiovascular benefit for many, it can be detrimental for people who have poor blood sugar control, according to a study conducted by researchers at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
In the study, published in the current issue of the journal Diabetes Care, the researchers re-evaluated the National Institutes of Health Action for Health in Diabetes (Look AHEAD) study that found intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) neither helped nor hurt people with diabetes.
"Contrary to the initial findings of Look AHEAD, our work found that lifestyle interventions reduced potential cardiovascular harm and optimized benefits for 85% of those in the trial," said the study's lead investigator, Michael P. Bancks, Ph.D., assistant professor of public health sciences at Wake Forest School of Medicine, part of Wake Forest Baptist Health.
"However, for those who had poor blood sugar control, lifestyle intervention increased the risk of major cardiovascular events. Based on our findings, doctors may want to consider alternative options, such as glucose-lowering drugs, before trying lifestyle modification for those people."
Look AHEAD randomized 5145 participants with type 2 diabetes (T2D) who were overweight or obese to 10 years of ILI or a control group that received diabetes support and education. ILI focused on weight loss through decreased caloric intake and increased physical activity.
In the Wake Forest School of Medicine study, the researchers divided the study participants into four subgroups: diabetes onset at older age, poor glycemic control, severe obesity and younger age at onset. These subgroups were determined based on diabetes diagnosis, body mass index, waist circumference, measure of blood sugar value (glycemic control) and the age of diabetes onset.
Bancks and his team examined each group's response to the intensive lifestyle intervention and its association with major cardiovascular events. In the subgroup with poor glycemic control, the intervention was associated with 85% higher risk of having a cardiovascular event as compared to the control group. Among the three other diabetes subgroups analyzed, ILI was not associated with an increased risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events.
"Although the interest in diabetes subgroups is growing, our study is one of the first to apply it to lifestyle intervention," Bancks said. "So for clinicians, determining which subgroup their patient most closely resembles should help them determine the best treatment option and reduce any potential harm for that individual."
These results provide support for further investigation into whether these findings apply to other diabetes complications, including cognitive issues, and to assess what interventions would be beneficial for those individuals, Bancks said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The world's oldest crater from a meteorite isn't an impact crater after all
2021-03-11
Several years after scientists discovered what was considered the oldest crater a meteorite made on the planet, another team found it's actually the result of normal geological processes.
During fieldwork at the Archean Maniitsoq structure in Greenland, an international team of scientists led by the University of Waterloo's Chris Yakymchuk found the features of this region are inconsistent with an impact crater. In 2012, a different team identified it as the remnant of a three-billion-year-old meteorite crater.
"Zircon crystals in the rock are like little ...
Unhealthy weight gains, increased drinking reported by Americans coping with pandemic stress
2021-03-11
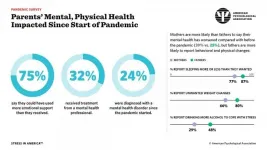
WASHINGTON -- As growing vaccine demand signals a potential turning point in the global COVID-19 pandemic, the nation's health crisis is far from over. One year after the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic, many adults report undesired changes to their weight, increased drinking and other negative behavior changes that may be related to an inability to cope with prolonged stress, according to the American Psychological Association's latest Stress in America™ poll.
APA's survey of U.S. adults, conducted in late February 2021 by The Harris Poll, shows that a majority of adults (61%) experienced undesired weight changes - weight gain ...
New report reveals how the U.S. can renew its leadership in global health R&D
2021-03-11
The U.S. Congress and Biden-Harris administration have a clear opportunity to supercharge global health research and development (R&D) in the wake of a pandemic that has revealed both the sector's chronic neglect and amazing potential, according to a detailed agency-by-agency action plan released today by the nonprofit Global Health Technologies Coalition (GHTC).
"The same core capabilities instrumental to defeating COVID-19 can also defeat diseases that have plagued humanity for generations--such as AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and Ebola--while targeting emerging pathogens of pandemic potential," said GHTC Director Jamie Bay Nishi. "Developing vaccines in ...
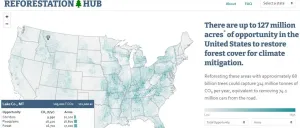
Mapping the best places to plant trees
2021-03-11
Reforestation could help to combat climate change, but whether and where to plant trees is a complex choice with many conflicting factors. To combat this problem, researchers reporting in the journal One Earth on December 18 have created the Reforestation Hub, an interactive map of reforestation opportunity in the United States. The tool will help foresters, legislators, and natural resource agency staff weigh the options while developing strategies to restore lost forests.
"Often the information we need to make informed decisions about where to deploy reforestation already exists, it's just scattered across a lot of different locations," says author Susan Cook-Patton, a Senior Forest Restoration Scientist at the Nature Conservancy. "Not everybody has the ...
Lifestyle research studies to reduce risk of Alzheimer's respond to COVID-19 challenges
2021-03-11
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on public health is staggering; more than one hundred million cases and two million deaths worldwide. In response, most countries and local governments have taken substantial measures -- such as travel restrictions and physical distancing -- to keep their citizens safe. Both the pandemic and related protective measures pose challenges for ongoing clinical research studies seeking to treat and prevent the world's greatest public health emergencies including COVID-19, but also Alzheimer's disease and other dementia.
In a new paper from the World-Wide FINGERS network in Alzheimer's ...
Updated guidance confirms crucial role of nurses for patients with acute ischemic stroke
2021-03-11
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- As integral members of stroke treatment teams, nurses coordinate patient assessment and collaborate care among multiple health care professionals to facilitate the best possible outcomes for patients with acute ischemic stroke. Nurses also advocate for patients and their caregivers to ensure they receive appropriate information and education to successfully navigate phases of treatment in the hospital and after discharge. A series of three new Scientific Statements, "Care of the Patient With Acute Ischemic Stroke," from the American Heart Association, published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association, provide the latest evidence-based guidance ...
Scientists move closer to developing 'game-changing' test to diagnose Parkinson's
2021-03-11
Results published today show it is possible to identify Parkinson's based on compounds found on the surface of skin. The findings offer hope that a pioneering new test could be developed to diagnose the degenerative condition through a simple and painless skin swab.
Scientists at The University of Manchester have developed a technique which works by analysing compounds found in sebum - the oily substance that coats and protects the skin - and identifying changes in people with Parkinson's Disease. Sebum is rich in lipid-like molecules and is one of the lesser studied biological fluids in the diagnosis of the ...
Lehigh U. researchers: 'One step closer to unlocking mysteries of the bio/nano interface'
2021-03-11
An interdisciplinary research team at Lehigh University has unraveled how functional biomaterials rely upon an interfacial protein layer to transmit signals to living cells concerning their adhesion, proliferation and overall development.
According to an article published today in Scientific Reports, the nanoscale features and properties of an underlying substrate do not impact the biological response of cells directly. However, these properties indirectly influence cell behavior through their control over adsorbed proteins.
In the article, "Nanostructure ...
Firefly tourism takes flight, sparking wonder and concern
2021-03-11
Firefly beetles rank among the world's most charismatic creatures, with luminous courtship displays that have now turned them into a popular attraction for wildlife tourists. In the first comprehensive review of firefly tourism, published in the journal Conservation Science and Practice, an international team of biologists led by a Tufts University researcher, reveal that an estimated 1 million people now travel each year to witness bioluminescent performances starring some two dozen firefly species around the world.
But the authors also point out that while this unique, insect-based tourism ...
Mindfulness meditation improves quality of life in heart attack survivors
2021-03-11
An eight-week programme of mindfulness meditation improves quality of life and reduces fear of activity in heart attack patients, according to research presented today at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
"A heart attack is a serious life-threatening event and survivors can suffer from low quality of life," said study author Dr. Canan Karadas of Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey. "One reason is a fear of movement, called kinesiophobia, which limits daily activity due to concerns of another heart attack."
"Mindfulness refers to the mental state achieved by focusing awareness on the present moment, ...