(Press-News.org) Chest pain is misdiagnosed in women more frequently than in men, according to research presented today at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The study also found that women with chest pain were more likely than men to wait over 12 hours before seeking medical help.
"Our findings suggest a gender gap in the first evaluation of chest pain, with the likelihood of heart attack being underestimated in women," said study author Dr. Gemma Martinez-Nadal of the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, Spain. "The low suspicion of heart attack occurs in both women themselves and in physicians, leading to higher risks of late diagnosis and misdiagnosis."
This study examined gender differences in the presentation, diagnosis, and management of patients admitted with chest pain to the chest pain unit of an emergency department between 2008 and 2019. Information was collected on risk factors for a heart attack including high blood pressure and obesity. The researchers recorded the physician's initial diagnosis after the first evaluation of each patient, which is based on clinical history, physical examination, and an electrocardiogram (ECG) and occurs before other examinations like blood tests.
"We had the first impression of the doctor as to whether the chest pain had a coronary cause or another origin such as anxiety or a musculoskeletal complaint," explained Dr. Martinez-Nadal.
A total of 41,828 patients with chest pain were included, of which 42% were women. The median age was 65 years in women and 59 years in men. Women were significantly more likely to present late to the hospital (defined as waiting 12 hours or longer after symptom onset): this occurred in 41% of women compared to 37% of men.
"This is worrying since chest pain is the main symptom of reduced blood flow to the heart (ischaemia) because an artery has narrowed," said Dr. Martinez-Nadal. "It can lead to a myocardial infarction which needs rapid treatment."
In the physician's initial diagnosis, acute coronary syndrome was more likely to be considered the cause of chest pain in men compared to women. Specifically, in 93% of patients, the ECG did not provide a definitive diagnosis. In those patients, the doctor noted a probable acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in 42% of cases - when analysed according to gender, probable ACS was noted in 39% of women and 44.5% of men (p END
Heart attack diagnosis missed in women more often than in men
2021-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Whooping cranes steer clear of wind turbines when selecting stopover sites
2021-03-11
As gatherings to observe whooping cranes join the ranks of online-only events this year, a new study offers insight into how the endangered bird is faring on a landscape increasingly dotted with wind turbines. The paper, published this week in Ecological Applications, reports that whooping cranes migrating through the U.S. Great Plains avoid "rest stop" sites that are within 5 km of wind-energy infrastructure.
Avoidance of wind turbines can decrease collision mortality for birds, but can also make it more difficult and time-consuming for migrating flocks to find safe and suitable rest and refueling locations. The study's insights into migratory behavior ...
Stress reduction as a path to eating less fast food
2021-03-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Overweight low-income mothers of young kids ate fewer fast-food meals and high-fat snacks after participating in a study - not because researchers told them what not to eat, but because the lifestyle intervention being evaluated helped lower the moms' stress, research suggests.
The 16-week program was aimed at preventing weight gain by promoting stress management, healthy eating and physical activity. The methods to get there were simple steps tucked into lessons on time management and prioritizing, many demonstrated in a series ...
A touch of silver
2021-03-11
In the field of robotics, metals offer advantages like strength, durability, and electrical conductivity. But, they are heavy and rigid--properties that are undesirable in soft and flexible systems for wearable computing and human-machine interfaces.
Hydrogels, on the other hand, are lightweight, stretchable, and biocompatible, making them excellent materials for contact lenses and tissue engineering scaffolding. They are, however, poor at conducting electricity, which is needed for digital circuits and bioelectronics applications.
Researchers in Carnegie Mellon University's Soft Machines Lab have developed a unique silver-hydrogel composite that has high electrical ...
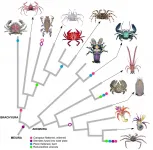
How does a crustacean become a crab?
2021-03-11
Crabs are living the meme life on social media lately. The memes joke that everything will eventually look like a crab. But it's actually based in some truth.
The crab shape has evolved so many times the evolutionary biologist L.A. Borradaile coined the term carcinization in 1916 to describe the convergent evolution process in which a crustacean evolves into a crab-like form from a non-crab-like form. Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura and are considered "true crabs", most of which are carcinized. "False crabs" are of the ...
Mindfulness program in campus dorms, groups improved students' mental health
2021-03-11
As experts nationwide point to a mental health crisis among teens and young adults, a pilot program teaching mindfulness and coping techniques to students at the University of Washington has helped lower stress and improve emotional well-being.
New studies by the psychology researchers who created the program find that the strategies, offered first in residence halls and later through classes and other organized campus groups, have provided participants with successful methods for coping with stress, managing their emotions and learning self-compassion.
Researchers say the results show the potential for preventive mental health services offered in an accessible, peer-group environment.
"This program is not a substitute ...
Deforestation favors an increase in the diversity of antibiotic-resistant soil bacteria
2021-03-11
In Brazil, a study conducted by researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo (USP) and collaborators showed that deforestation in the Amazon causes an increase in the diversity of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. An article on the study, published in Soil Biology and Biochemistry, compares the microorganisms that live in the soil of native forest with those found in pasture and croplands. The researchers found a far larger number of genes considered markers of antibiotic resistance in deforested than forested areas.
“Bacteria produce substances with which to attack each other in a competition for resources that’s ...
How India's rice production can adapt to climate change challenges
2021-03-11
URBANA, Ill. ¬- As the global population grows, the demand for food increases while arable land shrinks. A new University of Illinois study investigates how rice production in India can meet future needs by adapting to changing climate conditions and water availability.
"Rice is the primary crop in India, China, and other countries in Southeast Asia. Rice consumption is also growing in the U.S. and elsewhere in the world," says Prasanta Kalita, professor in the Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering at U of I and lead author on the study.
"If you look at where they traditionally grow rice, it is countries that have ...
Climate change damaging North America's largest temperate rainforest, harming salmon
2021-03-11
New research released in Bioscience found that a remote region of North America's largest temperate rainforest is experiencing changes to its ecosystem due to climate change. Brian Buma, a researcher and professor of integrated biology at University of Colorado Denver, co-leads the research network that outlined the changes in a new paper.
North America's largest remaining temperate rainforest, located in Southeast Alaska, is one of the most pristine and intact ecosystems. The entire ecosystem stretches well over 2,000 km from north to south and stores more carbon ...
Preterm birth, prolonged labor influenced by progesterone balance
2021-03-11
New research by the National Institutes of Health found that unbalanced progesterone signals may cause some pregnant women to experience preterm labor or prolonged labor. The study in mice -- published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences -- provides novel insights for developing treatments.
During pregnancy, the hormone progesterone helps to prevent the uterus from contracting and going into labor prematurely. This occurs through molecular signaling involving progesterone receptor types A and B, referred to as PGR-A and PGR-B. In this ...
HAWC Gamma Ray Observatory discovers origin of highest-energy cosmic rays in the galaxy
2021-03-11
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 11, 2021--A long-time question in astrophysics appears to finally be answered, thanks to a collection of large, high-tech water tanks on a mountainside in Mexico. The High-Altitude Water Cherenkov (HAWC) data shows that the highest-energy cosmic rays come not from supernovae, but from star clusters.
"The origin of the highest-energy cosmic rays in the galaxy has been an open question in astrophysics for more than 60 years," said Patrick Harding, a Los Alamos National Laboratory astrophysicist doing research using HAWC. "Very few regions of the galaxy have both the power to produce high-energy ...