Confined magnetic colloidal system for controllable fluid transport
2021-03-12
(Press-News.org) Colloidal suspensions of microscopic particles show complex and interesting collective behaviors. In particular, the collective dynamics of colloids is fundamental and ubiquitous for materials assembly, robotic motion, microfluidic control, and in several biological scenarios. The collective dynamics of confined colloids can be completely different from that of free colloids: for instance, confined colloids can self-organize into vortex structures, coherent motion, or different phase behaviors. On one hand, due to the complexity of colloidal suspensions, how to finely tune the collective dynamics of confined colloids remains elusive. On the other hand, since the microscale confinement is on the same length scale as the colloidal size, it is difficult to determine how the colloids interplay with each other and the geometrical constraints.
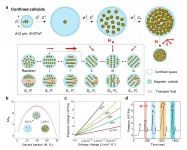
To study the colloidal collective in confinements, prior work has been focused on the microscopic visualization and simulation method, lacking direct evidence to characterize the mechanical property of colloidal interaction. Can this mechanical property be probed in a direct way or expressed as feedback of force in real-time? With the help of liquid gating technology, the answer could be yes. The leading research field "Liquid gating technology" was selected as the "2020 Top Ten Emerging Technologies In Chemistry" announced by International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Liquid gating technology allows certain liquids to selectively open and close pores on-demand. Especially, liquid gating membranes can respond to pressure changes, which also indicate transmembrane fluid transport capability. Therefore, utilizing the pressure-driven intrusion fluids as efficient causes, the mechanics of the confined colloids can be determined in real-time. In a new research article published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at Xiamen University present a new paradigm of the liquid gating system that confines the magnetic colloidal suspension in a porous matrix. This confined magnetic colloid system (CMCS) can probe the mechanical properties of the colloidal suspension in real-time, showing the ability to allow or stop the microscale flow or dynamically manipulate the fluid transport.
Interestingly, it seems that "freedom is not free". Firstly, the colloidal suspensions are trapped by the porous matrix. However, the confined colloids are also free in their limited space because their collective dynamics is vastly controllable via the magnetic field. The collective configuration of the confined colloids is statistically and thermodynamically characterized by the colloidal entropy. Meanwhile, the interplay between the confined colloids and the interplay between the colloidal suspension and geometrical constraints are simultaneously indicated by the pressure value. Notably, the pressure change is in a linear relationship with the entropy change. Both of them are prominently affected by the geometrical constraints, packing fraction of colloids, and the strengths and directions of magnetic fields. Moreover, as a proof of concept, this system has been demonstrated for the applications of dynamic and preprogrammed fluid transport, remote drug release, microfluidic logic, and chemical reaction, enabling sustainable antifouling behavior.
Beyond the magnetic field, the reported strategy of entropy regulation of confined colloids is also applicable to other remote external stimuli, such as acoustic field, light field, electric field, and so on. This work would enlighten the exploitation for fundamental research of colloidal science, and applications ranging from fluid transport, multiphase separation, logic microfluidics, to programmable cargo transport. The findings described here would also deepen the understanding of phenomena such as swarm intelligence, cellular collective, pollutant treatment by granular particles, and stop-and-go in traffic jamming.
INFORMATION:
This research received funding from the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Overseas Expertise Introduction Project for Discipline Innovation, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China, CAS Key Laboratory of Bio-inspired Materials and Interfacial Science, Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
See the article:
Zhizhi Sheng, Mengchuang Zhang, Jing Liu, Paolo Malgaretti, Jianyu Li, Shuli Wang, Wei Lv, Rongrong Zhang, Yi Fan, Yunmao Zhang, Xinyu Chen and Xu Hou
Reconfiguring confined magnetic colloids with tunable fluid transport behavior
Natl Sci Rev, DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa301
https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa301
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country's rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-12
As the world continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, an international team of researchers have published a review of the best techniques to collect airborne aerosols containing viruses.
In the review, which was published by the Science of the Total Environment journal, a team led by the University of Surrey concluded that the most effective way to collect and detect airborne pathogens, particularly viruses, was to use cyclone sampling techniques.
For example, the sampler draws the air through the cyclone separator. It then uses centrifugal forces to collect the particles on a sterile cone containing the liquid collection vessel, such as DMEM (Dulbecco's minimal essential ...
2021-03-12
Photovoltaics decisively contributes to sustainable energy supply. The efficiency of solar cells in directly converting light energy into electrical energy depends on the material used. Metal-halide perovskites are considered very promising materials for solar cells of the next generation. With these semiconductors named after their special crystal structure, a considerable increase in efficiency was achieved in the past years. Meanwhile, perovskite solar cells have reached an efficiency of up to 25.5 percent, which is quite close to that of silicon ...
2021-03-12
Proteins are the key component in all modern forms of life. Haemoglobin, for example, transports the oxygen in our blood; photosynthesis proteins in the leaves of plants convert sunlight into energy; and fungal enzymes help us to brew beer and bake bread. Researchers have long been examining the question of how proteins mutate or come into existence in the course of millennia. That completely new proteins - and, with them, new properties - can emerge practically out of nothing, was inconceivable for decades, in line with what the Greek philosopher Parmenides said: "Nothing can emerge from nothing" (ex nihilo nihil fit). Working with colleagues from the USA and ...
2021-03-12
The Cabeza de los Gatos waste rock pile, left from mining activities in the town of Tharsis (Huelva), underwent a rehabilitation process consisting of remodelling the slope of the pile, applying liming materials and then a layer of soil. Finally, trees and shrubs typical of the area were planted and a hydroseeding with a mixture of shrub and herbaceous seeds was applied. Twelve years later, a study led by researchers from IRNAS-CSIC, in collaboration with Sabina Rossini Oliva, a researcher from the University of Seville and the Environment and Water Agency of Andalusia (AMAYA), has proven the effectiveness of this sort of rehabilitation.
"The results obtained show that the steps taken were successful. Now, ...
2021-03-12
People with high levels of emotional intelligence are less likely to be susceptible to 'fake news', according to research at the University of Strathclyde.
The study invited participants to read a series of news items on social media and to ascertain whether they were real or fictitious, briefly describing the reasons for their answers. They were also asked to complete a test to determine their levels of emotional intelligence (EQ or emotional quotient) and were asked a number of questions when considering the veracity of each news item.
Researchers found that those who identified the types of news correctly were most likely to score highly in the EQ tests. There was a similar correlation between correct identification and educational attainment.
The ...
2021-03-12
In asthma, the airways become hyperresponsive. Researchers from Uppsala University have found a new mechanism that contributes to, and explains, airway hyperresponsiveness. The results are published in the scientific journal Allergy.
Some 10 per cent of Sweden's population suffer from asthma. In asthmatics, the airways are hyperresponsive (overreactive) to various types of stimuli, such as cold air, physical exertion and chemicals. The airways become constricted, making breathing difficult.
To diagnose asthma, a "methacholine test" is commonly used to determine whether a person is showing signs of airway hyperresponsiveness. Methacholine binds to what are known as muscarinic receptors in the smooth muscle cells lining the inside ...
2021-03-12
The researchers say this is a big step in tackling smouldering peat fires, which are the largest fires on Earth. They ignite very easily, are notoriously difficult to put out, and release up to 100 times more carbon into the atmosphere than flaming fires, contributing to climate change.
The fires, known as 'zombie fires' for their ability to hide and smoulder underground and then reanimate as new flames days or weeks after the wildfire had been extinguished, are prevalent in regions like Southeast Asia, North America, and Siberia.
They are driven by the burning of soils rich in organic content like peat, which is a large natural reservoir of carbon. Worldwide, peat fires account for millions of tonnes of carbon released into the atmosphere each year.
Firefighters currently use millions ...
2021-03-12
A new model of aging takes into account not only genetics and environmental exposures but also the tiny changes that randomly arise at the cellular level.
University Professor Caleb Finch introduced the "Tripartite Phenotype of Aging" as a new conceptual model that addresses why lifespan varies so much, even among human identical twins who share the same genes. Only about 10 to 35 percent of longevity can be traced to genes inherited from our parents, Finch mentioned.
Finch authored the paper introducing the model with one of his former graduate students, Amin Haghani, who received his PhD in the Biology of Aging from the USC ...
2021-03-12
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden can now show that a new examination method identifies high-risk plaques in the blood vessels surrounding the heart, that cannot be seen solely with traditional angiograms. This type of plaque, rich in fat, could potentially cause recurring heart attacks in patients with heart disease. The study is published in the The Lancet.
"We have been working on this study for ten years. This creates a unique opportunity to treat plaques before they cause a heart attack", says David Erlinge, professor of cardiology at Lund University and Consultant in ...
2021-03-12
During 1995-2015, fullerene derivatives had been the dominating electron acceptors in organic solar cells (OSCs) owing to their performance superior to other acceptors. However, the drawbacks of fullerenes, such as weak visible absorption, limited tunability of electronic properties and morphological instability, restrict further development of OSCs toward higher efficiencies and practical applications. Therefore, the development of new acceptors beyond fullerenes is urgent in the field of OSCs.
Professor Zhan Xiaowei from the College of Engineering at Peking University is one of the pioneers engaging in development of nonfullerene acceptors in the world. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Confined magnetic colloidal system for controllable fluid transport