(Press-News.org) A discovery by University of Queensland pain researchers may allow some future cancer patients, including children with leukaemia, to avoid their chemotherapy's worst and most debilitating side effects.
Professor Irina Vetter and Dr Hana Starobova thought "turning off" the inflammation that is one of the body's natural reactions to the chemotherapy drug vincristine might reduce its accompanying pain and unpleasant symptoms.
"We found the anti-inflammatory drug anakinra substantially reduced the awful nerve symptoms for which vincristine chemotherapy is known," Professor Vetter said.
"Importantly, it did not reduce the effectiveness of the chemo."
Anakinra is an existing rheumatoid and juvenile arthritis treatment and the Institute for Molecular Bioscience researchers plan to test it soon on human chemotherapy patients taking vincristine.
"Vincristine is used to treat cervical, brain and lung cancers, leukaemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas," Professor Vetter said.
She said the finding was specific to vincristine and anakinra, although early findings suggested anakinra may help relieve symptoms of some other chemotherapy drugs.
"Unfortunately chemo's side effects are sometimes so terrible that people interrupt their treatment or end it, putting them at risk of succumbing to their cancer," Professor Vetter said.
"Reducing the chemo's unpleasant symptoms ultimately will save lives and a lot of patient suffering."
The Kids' Cancer Project part-funded the research and the charity's chief executive, Owen Finegan, said the researchers' choice to test a known and approved drug meant relatively fast translation to clinical use.
"This discovery will flow through to patients much more quickly than if the researchers had developed a completely new drug," he said.
"This is likely to bring better treatment for kids with cancers including acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, sarcoma, medulloblastoma and neuroblastoma.
"We are also delighted that these findings - initiated to help children - will also benefit adults."
The researchers made the discovery while studying how vincristine causes sensory nerves to function abnormally.
Dr Starobova said neuropathy was one of the chemotherapy drug's most unpleasant and severe side-effects, causing tingling and numbness in hands and feet, pain, and muscle weakness leading to limping.
"Unfortunately these symptoms can persist long after treatment," Dr Starobova said.
"The only way to ease them is to lower the vincristine dose, but this lowers the treatment's effectiveness against the cancer.
"Where chemotherapy is concerned, neuropathic pain results from immune cells infiltrating the nerves and inflammation running wild."
Claire Bermingham of Lennox Head said her son Archer, 4, still suffered from his 2019 vincristine treatment for leukaemia and doctors estimated the side-effects would last eight years.
"Archer has peripheral neuropathy, foot drag, headaches, jaw pain and occasional raspy voice," Mrs Bermingham said.
"He can't take stairs, hold a pen, write his name, use scissors or do lots of other things children his age can do.
"People think once treatment is over and the cancer is in remission, that it's all over - that's not the reality."
Mrs Bermingham said she was delighted to hear about the discovery at the Institute for Molecular Bioscience.
"It's great that researchers are prioritising kinder, gentler cancer treatments for children," she said.
Professor Vetter said inflammation was a natural response in the body to injury or infection, but unchecked it could cause its own issues.
Since the finding, she and Dr Starobova have joined forces with their IMB colleague and inflammation expert Professor Kate Schroder.
"Kate's group focuses on inflammasomes - the molecular machines that trigger the immune response," Professor Vetter said.
"Working together allows us to accelerate this research."
Their next step will focus on how vincristine activates immune cells.
INFORMATION:
The research is published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine and funded by the NHMRC.
Anakinra is a biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug (bDMARD), a therapeutic class of cytokine blockers that came into use in the 1990s.
A study by a research team from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) and China's first digital-only bank WeBank has found that security, service quality and system quality are the most important factors for customers who use mobile banking.
Two in five respondents (40%) said that the security they felt while carrying out transactions on mobile applications was their most important consideration.
This was followed by the level of service quality (25%), which referred to whether the banking applications could fulfil users' needs, such as carrying out transactions and easy access to credit card services.
System quality, which considers the performance of the application, including ...
Researchers at UniSA have developed a cost-effective new technique to monitor soil moisture using a standard digital camera and machine learning technology.
The United Nations predicts that by 2050 many areas of the planet may not have enough fresh water to meet the demands of agriculture if we continue our current patterns of use.
One solution to this global dilemma is the development of more efficient irrigation, central to which is precision monitoring of soil moisture, allowing sensors to guide 'smart' irrigation systems to ensure water is applied at the optimum time and rate.
Current methods for sensing soil moisture are problematic - buried sensors are susceptible to ...
Dr Daniel Montesinos is a Senior Research Fellow at the Australian Tropical Herbarium, at James Cook University in Cairns. He is studying weeds to better understand (among other things) how they might respond to climate change.
He said most invasive plants are characterised by their rapid pace when it comes to taking up nutrients, growing, and reproducing - and they're even faster in the regions they invade.
"New experiments comparing populations from distant regions show a clear trend for already-fast invasive plants to rapidly adapt even faster traits in their non-native regions," Dr Montesinos said.
This is further pronounced in the tropics and sub-tropics.
"Even though invasives' growth rates are already among the highest for plants, when they invade new territory ...
A new concept of on-demand drug delivery system has emerged in which the drugs are automatically released from in vivo medical devices simply by shining light on the skin.
A research team led by Professor Sei Kwang Hahn of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Kilwon Cho of the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH have together developed an on-demand drug delivery system (DDS) using an organic photovoltaic cell coated with upconversion nanoparticles. This newly developed DDS allows nanoparticles to convert skin-penetrating near-infrared (NIR) light into visible light so that drug release can be controlled in medical ...
An international team of researchers, affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a novel technology that could improve the learning ability of artificial neural networks (ANNs).
Professor Hongsik Jeong and his research team in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST, in collaboration with researchers from Tsinghua University in China, proposed a new learning method to improve the learning ability of ANN chips by challenging its instability.
Artificial neural network chips are capable of mimicking the structural, functional and biological features of human neural networks, and thus have been considered the technology of the future. In this study, the research team demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed learning method ...
A chromatin-regulating enzyme has been shown by in-depth interdisciplinary investigations to be a key driver of a common type of lung cancer. Drugs that target the enzyme could improve treatment and survival rates for this particular cancer.
"Squamous cell carcinoma represents nearly one third of all lung cancers in humans," says KAUST structural biologist Lukasz Jaremko, who led the research along with colleagues at Stanford University and The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, U.S. "Our joint structural and dynamics investigations, including enzymatic activity studies, genetic analyses, and mouse model and human cell results, ...
Basic, acidic, basic again: for pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella, the human digestive tract is a sea change. So how do the bacteria manage to react to these changes? A team of researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology in Marburg led by Andreas Diepold has now provided a possible explanation: pathogenic bacteria can change components of their injection apparatus on the fly - like changing the tires on a moving car - to enable a rapid response.
Some of the best-known human pathogens - from the plague bacterium Yersinia pestis to the diarrhea pathogen Salmonella - use a tiny hypodermic needle to inject disease-causing ...
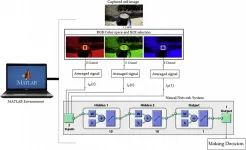
Despite pandemic-driven restrictions on movement, there were over 12,000 accidents in Madrid in 2020, leading to 31 fatalities. In Barcelona, there were more than 5,700 collisions, causing 14 deaths. Pedestrian and vehicle safety is a priority, which is why a research project at the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) is harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) to make decisions that will make cities safer. The researchers have looked into the correlation between the complexity of certain urban areas and the likelihood of an accident occurring there.
According to the researchers, the data they have gathered can be used to train neural networks to detect probable ...
Last December, the Parliament of Catalonia unanimously approved the incorporation into its legislation of second-order violence against those who give their support to victims of violence against women. A recent study compiles testimonies of victims, and analyses this form of intimidation
To tackle violence against women, it is essential for victims to have the support of those surrounding them and to prevent them from being isolated. But what happens if the people around them are not protected? The work of Jose Ramón Flecha García, founder of the Community of Research on Excellence for All (CREA), and various academic teams, has led to the approval in the Catalan parliament of the first legislation on the Second Order of Sexual Harassment (SOSH).
The following point ...
Robotics researchers are developing exoskeletons and prosthetic legs capable of thinking and moving on their own using sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
The system combines computer vision and deep-learning AI to mimic how able-bodied people walk by seeing their surroundings and adjusting their movements.
"We're giving robotic legs vision so they can control themselves," said Brokoslaw Laschowski, a PhD candidate in systems design engineering who leads a University of Waterloo research project called ExoNet.
Exoskeletons and prosthetic devices operated by motors already exist, but users must manually ...