INFORMATION:
The article is available as open access in Lancet Healthy Longevity:
Lancet Healthy Longev 2021 Published Online March 25, 2021
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00024-6
Physicians and scientists join forces to develop the longevity medicine curriculum
Physicians and scientists highlight the importance of longevity medicine education and collaborate on the first longevity medicine course for physicians
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) 16th of March, Tuesday, 2021 -- Longevity medicine is a rapidly evolving branch of preventative precision medicine that is specifically focused on promoting healthspan and lifespan, utilizing aging biomarkers commonly referred to as aging clocks. Over the past decade advances in AI and machine learning enabled the development of deep aging clocks (DACs) and other novel tools to track the rate of aging. In parallel novel preventative and therapeutic interventions have been discovered or progressed into clinical trials. Many medical and public health professionals do not have time to read the thousands of research papers covering this new field and actively engage in cutting-edge innovation in preventative medicine. And there are few educational resources that outline the benefits of longevity medicine. However, in order for the field to evolve, it is important that these materials are easily accessible for the broad medical community and presented at the level acceptable by the general medical practitioners.
In the comment titled "Longevity medicine: upskilling the physicians of tomorrow" (Lancet Healthy Longevity, 2021) Evelyne Bischof, MD, Morten Scheibye-Knudsen, MD, PhD, Richard Siow, PhD, Alexey Moskalev, PhD, summarise current findings on the main types of deep aging clocks, longevity medicine and reflect on the necessary education in this field.
Multiple institutions providing medical education are now actively seeking collaborations with artificial intelligence experts to create educational content that will help medical professionals acquire new skills in artificial intelligence for healthcare. However, it was not until 2020 when the first educational curriculum in longevity medicine for physicians was created by the team of scientists and clinicians, led by the artificial intelligence and longevity scientist and entrepreneur, Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD.
In connection with the article calling for more educational resources scientists launched the first longevity medicine course for physicians.
The course provided the physicians and other medical professionals with the introduction to the theoretical and practical basics of longevity medicine, which includes molecular mechanisms, theories of aging, biomarkers of aging, and geroprotector regimens. This course, as well as similar courses, provide medical and public health professionals with the baseline knowledge required to understand aging research, knowledge about longevity therapies available related to senescence-related processes, and the skills to examine biomarkers of aging and other age testing mechanisms. The course discusses advances in research in drug design, machine learning, omics, differential diagnosis, biogerontology, geroprotective interventions and healthcare organisations while also educating medical clinicians on how to implement them on a daily basis.
Physicians and medical professionals can register for this course at Udemy at no charge during the promotional periods, take the course at their own pace at any time, and receive a certificate of completion. The next promotion will transpire from 16th to 24th March 2021 on Udemy Platform (coupon codes: LONGEVITYMEDICINE, FREELONGEVITY2021) and students registering for this course will be able to start the course at any time and receive a certificate of completion.
The authors also agreed to collaborate on a course to be available free of charge to physicians and the general public at https://www.longevity.degree/
"Longevity physicians are looking for ways to reduce the gap between the current parameters, such as the current biological age, and the parameters of optimal maximum physical performance, such as the ideal biological age, predicted by deep learning. It is essential that practicing doctors have access to the appropriate longevity medicine education through a credible curriculum", said Evelyne Bischof, MD.
"The emergence of reliable markers for human aging now allows us to understand what interventions reduce the rate of aging. We are on the cusp of a new era in medicine where age-associated diseases and perhaps aging itself can be slowed or even halted. Education about interventions leading to healthy aging is paramount for allowing everyone a healthier and longer life", said Morten Scheibye-Knudsen, MD, PhD.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
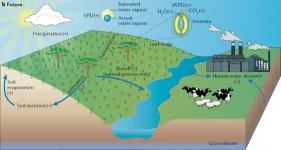
Toward a more comprehensive understanding of aridity changes over global drylands
2021-03-16
Global drylands are experiencing faster-than-average warming and are also among the most vulnerable regions to climate change. Meteorological metrics all point to an emerging trend of increased surface aridity, raising concerns of land desertification and degradation. However, recent satellite observations also show lusher drylands, in apparent contradiction to the image of drylands becoming drier. In a new Review Article published in Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, an international team comprehensively examined global dryland aridity changes with evidence from the literature and various sources of Earth observations and numerical ...
Study shows how varying climate conditions impact vulnerable species
2021-03-16
New findings on the diet of Arctic foxes, determined by the condition of their teeth, show how varying climate conditions in the Arctic affect the animals that live there.
In a study published in Polar Biology, Peter Ungar, Distinguished Professor of anthropology at the University of Arkansas, and several co-authors analyzed tooth breakage and wear - both gross and micro - of Arctic foxes from Russia's Yamal Peninsula.
Studying the effect of varying climate conditions within this region helps scientists understand the impact of climate change on ...
Commercial truck electrification is within reach
2021-03-16
When it comes to electric vehicles, particularly for heavy-duty trucks, the limitations of battery technology are often seen as the main barrier to widespread adoption. However, a new analysis concludes that it's the lack of appropriate policies around adoption incentives, charging infrastructure, and electricity pricing that prevents widespread electrification of commercial trucking fleets.
Researchers from the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California, Los Angeles published a new study that makes the case for prioritizing public policy to help move long-haul trucking from diesel to electric. Doing so will mean huge gains in addressing the ...
Roof-tiles in imperial China: Creating Ximing Temple's lotus-pattern tile ends
2021-03-16
Kanazawa, Japan -- Any visitor to China will have noticed the spectacular roofs on buildings dating from imperial times. However, the question of how these roof tiles were produced has attracted relatively little attention from archaeologists. Now, a team of researchers has conducted a major study of tile ends unearthed at the Ximing Temple in Xi'an, yielding exciting insights into their production.
In a study published in Archaeological Research in Asia, researchers from Kanazawa University and the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences have revealed the significance of minute variations in the tile ends used in the roof of the famous Ximing Temple in Xi'an, built during the ...
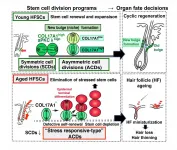
The bald truth - altered cell divisions cause hair thinning
2021-03-16
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify a novel mechanism underlying hair thinning and loss during aging
Tokyo, Japan - Hair grows from stem cells residing in hair follicles. During aging, the capability of hair follicles to grow hair is successively lost, leading to hair thinning and ultimately hair loss. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and the University of Tokyo identified a novel mechanism by which hair follicles lose their regenerative capabilities.
Hair follicles are mini-organs from which new hair constantly grows. The basis for new hair growth is the proper function of hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs). HFSCs undergo cyclic symmetric and asymmetric cell divisions ...
Genetic discovery gives insight into causes of eye disease
2021-03-16
A genetic defect could hold the key to preventing or delaying the onset of a debilitating eye disease that can lead to vision loss and blindness.
MacTel (macular telangiectasia type 2) affects one in 1,000 Australians. Symptoms include slow loss of vision, distorted vision and trouble reading. Because early signs of the disorder are subtle, it is difficult to diagnose.
Researchers have identified an additional seven regions in the human genome that increase the risk of developing the condition, including a rare DNA mutation in the PHGDH gene, which will help clinicians to better diagnose and treat ...
The valuable contribution of stress to the thermal stability of nanograined polycrystalline alloys
2021-03-16
Nanograined metals and alloys, whose grain size is less than 100 nm, exhibit extremely high strength and high ductility, possessing excellent mechanical properties. Nanograined materials, however, have a large number of grain boundaries and hence high total grain boundary energy. At a temperature higher than a critical temperature, grains in nanograined materials will grow spontaneously to reduce the grain boundary energy, leading to thermal instability of the materials. A common approach to enhance the thermal stability is via grain boundary energy segregation, which thermodynamically lowers the grain boundary energy and kinetically pins ...
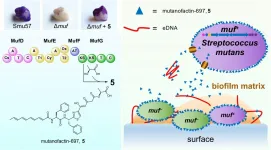
HKUST researchers unlock the micro-molecular physiochemical mechanism of dental plaque formation
2021-03-16
An inter-disciplinary team of researchers led by Prof. Qian Peiyuan, Chair Professor at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)'s Department of Ocean Science and Division of Life Science has unraveled how a novel microbial small molecule released by Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) - a bacterium commonly found in the human oral cavity - is connected to dental caries development using a synthetic biology approach, offering new insights to the health impact of the human oral microbiota and facilitating future research on the prevention of tooth decay. The research findings were recently published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature Chemical Biology and reported by Nature as one of the research highlights.
Every wetted surface on our ...
State of the climate over the three gorges region of the Yangtze river in 2019
2021-03-16
The Three Gorges project, completed in 2009, is one of the world's largest hydropower projects. It has brought important social and economic benefits in flood control, power generation, shipping and water resources redistribution.
But how does such a large-scale water conservancy project affect the local climate, and is the response to climate change a relatively vulnerable one? The Three Gorges Project has been repeated questioned, especially whenever rainstorms, floods and drought hit the area around the reservoir area or its neighboring areas, since ...
Researchers discover intact plant fossils beneath Greenland's ice sheet for the first time
2021-03-16
Following a relocation of ice cores to the Copenhagen suburb of Rødovre in 2017, University of Copenhagen researchers found unopened boxes of ice cores dating back to 1966--the first ice cores drilled on Earth.
Analyses of the long-forgotten ice have now been completed and are presented in a new study with groundbreaking results.
Within the cores, which come from deep within the ice sheet at Camp Century, Greenland, the UCPH researchers and their Belgian and American colleagues became the first ever to find these millions of years old macrofossils.
The fossils are large enough to be seen without a microscope.
"We pinched ourselves over the treasure we'd found! Because within the cores, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Physicians and scientists join forces to develop the longevity medicine curriculumPhysicians and scientists highlight the importance of longevity medicine education and collaborate on the first longevity medicine course for physicians