The bald truth - altered cell divisions cause hair thinning
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify a novel mechanism underlying hair thinning and loss during aging
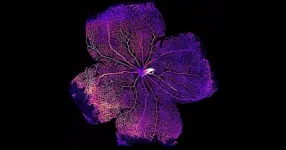
Tokyo, Japan - Hair grows from stem cells residing in hair follicles. During aging, the capability of hair follicles to grow hair is successively lost, leading to hair thinning and ultimately hair loss. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and the University of Tokyo identified a novel mechanism by which hair follicles lose their regenerative capabilities.
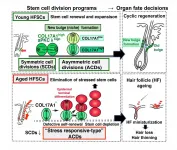
Hair follicles are mini-organs from which new hair constantly grows. The basis for new hair growth is the proper function of hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs). HFSCs undergo cyclic symmetric and asymmetric cell divisions (SCDs and ACDs). SCDs generate two identical cells that go on to have the same fate, while ACDs generate a differentiating cell and a self-renewing stem cell. The combination ensures that the stem cell population continues to exist, yet how those contribute to the loss of HFSC function due to aging is not yet completely understood.
"For proper tissue function, symmetric and asymmetric cell divisions have to be in balance," says corresponding author of the study Emi Nishimura. "Once stem cells preferentially undergo one of either or, worse yet, deviate from the typical process of either type of cell division, the organ suffers. In this study, we wanted to understand how stem cell division plays into hair grows during aging."
To achieve their goal, the researchers investigated stem cell division in HFSCs in young and aged mice by employing two different types of assays: Cell fate tracing and cell division axis analyses. In the former, HFSCs were marked with a fluorescent protein so they could be followed over time, while in the latter the angle of HFSC division was measured. Strikingly, the researchers were able to show that while HFSCs in young mice underwent typical symmetric and asymmetric cell divisions to regenerate hair follicles, during aging they adopted an atypical senescent type of asymmetric cell division.
But why does the mode of cell division change so drastically during aging? To answer this question, the researchers focused on hemidesmosomes, a class of protein that connect the cells to the extracellular matrix (ECM; proteins surrounding cells). Cell-ECM have long been known to confer polarity to cells, i.e., that the cells can sense their localization within a given space through the action of specific proteins. The researchers found that during aging both hemidesmosomal and cell polarity proteins become destabilized, resulting in the generation of aberrantly differentiating cells during division of HFSCs. As a result, HFSCs become exhausted and lost (leading to hair thinning and hair loss) over time.
"These are striking results that show how hair follicles lose their ability to regenerate hair over time," says first author of the study Hiroyuki Matsumura. "Our results may contribute to the development of new approaches to regulate organ aging and aging-associated diseases."
INFORMATION:
The article, "Distinct types of stem cell divisions determine organ regeneration and aging in hair follicles" was published in Nature Aging at DOI: 10.1038/s43587-021-00033-7
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-16
A genetic defect could hold the key to preventing or delaying the onset of a debilitating eye disease that can lead to vision loss and blindness.
MacTel (macular telangiectasia type 2) affects one in 1,000 Australians. Symptoms include slow loss of vision, distorted vision and trouble reading. Because early signs of the disorder are subtle, it is difficult to diagnose.
Researchers have identified an additional seven regions in the human genome that increase the risk of developing the condition, including a rare DNA mutation in the PHGDH gene, which will help clinicians to better diagnose and treat ...
2021-03-16
Nanograined metals and alloys, whose grain size is less than 100 nm, exhibit extremely high strength and high ductility, possessing excellent mechanical properties. Nanograined materials, however, have a large number of grain boundaries and hence high total grain boundary energy. At a temperature higher than a critical temperature, grains in nanograined materials will grow spontaneously to reduce the grain boundary energy, leading to thermal instability of the materials. A common approach to enhance the thermal stability is via grain boundary energy segregation, which thermodynamically lowers the grain boundary energy and kinetically pins ...
2021-03-16
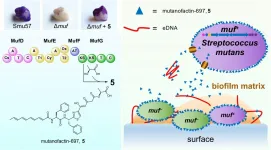
An inter-disciplinary team of researchers led by Prof. Qian Peiyuan, Chair Professor at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)'s Department of Ocean Science and Division of Life Science has unraveled how a novel microbial small molecule released by Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) - a bacterium commonly found in the human oral cavity - is connected to dental caries development using a synthetic biology approach, offering new insights to the health impact of the human oral microbiota and facilitating future research on the prevention of tooth decay. The research findings were recently published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature Chemical Biology and reported by Nature as one of the research highlights.
Every wetted surface on our ...
2021-03-16
The Three Gorges project, completed in 2009, is one of the world's largest hydropower projects. It has brought important social and economic benefits in flood control, power generation, shipping and water resources redistribution.
But how does such a large-scale water conservancy project affect the local climate, and is the response to climate change a relatively vulnerable one? The Three Gorges Project has been repeated questioned, especially whenever rainstorms, floods and drought hit the area around the reservoir area or its neighboring areas, since ...
2021-03-16
Following a relocation of ice cores to the Copenhagen suburb of Rødovre in 2017, University of Copenhagen researchers found unopened boxes of ice cores dating back to 1966--the first ice cores drilled on Earth.
Analyses of the long-forgotten ice have now been completed and are presented in a new study with groundbreaking results.
Within the cores, which come from deep within the ice sheet at Camp Century, Greenland, the UCPH researchers and their Belgian and American colleagues became the first ever to find these millions of years old macrofossils.
The fossils are large enough to be seen without a microscope.
"We pinched ourselves over the treasure we'd found! Because within the cores, ...
2021-03-16
Sugar is added to many common foodstuffs, and people in Switzerland consume more than 100 grams of it every day. The high calorie content of sugar causes excessive weight and obesity, and the associated diseases. But does too much sugar have any other harmful effects if consumed regularly? And if so, which sugars in particular?
Even moderate amounts of sugar increase fat synthesis
Researchers at the University of Zurich (UZH) and the University Hospital Zurich (USZ) have been investigating these questions. Compared to previous studies, which mainly examined the consumption ...
2021-03-16
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Nearly every older adult was prescribed a prescription drug that increased their risk of falling in 2017, according to new University at Buffalo research.
The study found that the percentage of adults 65 and older who were prescribed a fall- risk-increasing drug climbed to 94% in 2017, a significant leap from 57% in 1999. The research also revealed that the rate of death caused by falls in older adults more than doubled during the same time period.
Even minor falls may be dangerous for older adults. Falls that are not fatal can still result in injuries - such as hip fractures and head traumas - that may drastically lower remaining quality of life. Each year, nearly $50 billion is spent on medical costs related to fall injuries ...
2021-03-16
From science to implementation: How do we know if humankind is moving in the right direction towards global sustainability? The ambitious aim of the SDGs is a global call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure all people enjoy peace and prosperity by 2030. To monitor progress towards these goals, a set of over 220 indicators is used, but there is a danger that one can no longer see the forest for the trees. A single comprehensive indicator to assess the overall progress is needed. In a new paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), IIASA researchers and colleagues from the University of Vienna, the Vienna Institute of Demography (Austrian Academy of Sciences), and the Bocconi ...
2021-03-16
Researchers from Louisiana State University have introduced a smart quantum technology for the spatial mode correction of single photons. In a paper featured on the cover of the March 2021 issue of Advanced Quantum Technologies, the authors exploit the self-learning and self-evolving features of artificial neural networks to correct the distorted spatial profile of single photons.
The authors, PhD candidate Narayan Bhusal, postdoctoral researcher Chenglong You, graduate student Mingyuan Hong, undergraduate student Joshua Fabre, and Assistant Professor Omar S. Magaña?Loaiza of LSU--together with collaborators Sanjaya Lohani, Erin M. Knutson, ...
2021-03-16
ITHACA, N.Y. - Using light from the Big Bang, an international team led by Cornell University and the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has begun to unveil the material which fuels galaxy formation.
"There is uncertainty on the formation of stars within galaxies that theoretical models are unable to predict," said lead author Stefania Amodeo, a Cornell postdoctoral researcher in astronomy in the College of Arts and Sciences, who now conducts research at the Observatory of Strasbourg, France. "With this work, we are providing tests for galaxy formation models to comprehend galaxy and star formation."
The research, "Atacama Cosmology Telescope: Modeling the Gas Thermodynamics ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The bald truth - altered cell divisions cause hair thinning