Simple blood test could replace surgery for some brain tumour patients
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) A research breakthrough shows that a simple blood test could reduce, or in some cases replace, the need for intrusive surgery when determining the best course of treatment for patients with a specific type of brain tumour.
Researchers at the Brain Tumour Research Centre of Excellence at the University of Plymouth have discovered a biomarker which helps to distinguish whether meningioma - the most common form of adult primary brain tumour - is grade I or grade II.
The grading is significant because lower grade tumours can sometimes remain dormant for long periods, not requiring high risk surgery or harsh treatments such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Tumours classified as grade II can progress to become cancerous and more aggressive treatment may be needed in order to try to control their spread.
At the moment, meningioma patients are usually put on watch and wait, undergo radiotherapy or have surgery in an attempt to remove the tumour. Between 70 and 85% of meningioma cases are lower grade so, if the blood test - or liquid biopsy - is carried out these patients may well be spared surgery or radiotherapy.
The team at Plymouth, led by Professor Oliver Hanemann, has published its work on this novel biomarker known as the protein Fibulin-2 (FBLN2) in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. FBLN2 has not previously been shown to play a role in meningioma development, although it has been linked to other types of cancer such as forms in the lung, liver, breast and pancreas. The team therefore believes that this study is the first to link the FBLN2 protein as a biomarker for meningioma.
The results build on the important work of the Plymouth centre to identify non-invasive biomarkers of different grades of meningioma tumours. More information on an earlier paper, "GATA-4, a potential novel therapeutic target for high-grade meningioma, regulates miR-497, a potential novel circulating biomarker for high-grade meningioma" can be found here https://www.braintumourresearch.org/media/news/news-item/2020/08/19/news-on-meningioma-research-from-our-plymouth-centre.
Using tumour samples, cancer cells grown in the laboratory and liquid biopsies from patients, the scientists were able to distinguish grade I from grade II tumours. In a smaller sub-study, the researchers have shown that levels of the biomarker could differentiate between good (slower growing) and bad (faster growing) grade tumours as defined by genetic make-up.
Prof Hanemann said: "In this study, we identified FBLN2 as a novel biomarker that can distinguish grade II from grade I meningiomas. Higher levels of this biomarker were found in tumour samples from grade II meningioma compared with the grade I form. We also showed that higher levels of FBLN2 can be detected in blood samples from grade II meningioma patients, compared to those from grade I meningioma patients. The identification of FBLN2 as a biomarker for meningioma has significant potential to improve the diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and follow-up of meningiomas."
Hugh Adams, spokesman for Brain Tumour Research, which funded the study said: "This is an exciting breakthrough which could see patients spared the ordeal of neurosurgery at what is already likely to be one of the most difficult times of their life. In the UK, 16,000 people are diagnosed with a brain tumour each year and more children and adults under the age of 40 are lost to brain tumours than any other cancer."
Victoria Bradley, aged 50, from Plymouth, was diagnosed with a meningioma in 2017 and underwent surgery at Derriford Hospital six weeks later. She has lifelong side effects including debilitating seizures. No longer able to work as an overseas holiday representative, Victoria is now developing a mindfulness and meditation app to help others with brain tumours and epilepsy.
"My diagnosis and operation has changed everything about my life," she said. "Going through neurosurgery is a massive thing. I live in constant fear, no longer feel comfortable going out on my own and always, always, have an emergency alarm with me to call help in case I have a seizure.
"It is absolutely wonderful and incredible to think that, one day, patients like me might not have to go through surgery."
It is hoped the findings will contribute to the development of more personalised treatment options for patients with meningioma. Indeed, there exists a lack of consensus currently on the best management for grade II meningioma. FBLN2 could become a valuable tool for identifying and treating meningioma, accessible through a non-invasive blood test. Further research is required to assess the accuracy of diagnosing meningioma using a liquid biopsy for FBLN2 in comparison to current methods.
INFORMATION:
The Plymouth centre is part of a network of Brain Tumour Research Centres of Excellence. It is funded by Brain Tumour Research which is the only national charity in the UK singularly focused on finding a cure for brain tumours through campaigning for an increase in the national investment into research to £35 million per year, while fundraising to create a sustainable network of brain tumour research centres in the UK.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
Many athletes, from football players to equestrians, rely on helmets to protect their heads from impacts or falls. However, a loose or improperly fitted helmet could leave them vulnerable to traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), a leading cause of death or disability in the U.S. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sensors have developed a highly sensitive pressure sensor cap that, when worn under a helmet, could help reveal whether the headgear is a perfect fit.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1.6 to 3.8 million sports- and recreation-related TBIs occur each year in the U.S. Field data suggest that loose or improperly fitted helmets can contribute ...
2021-03-17
March 17, 2021-- A new study published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society reveals how socioeconomic factors partially explain the increased odds that Black and Hispanic Americans have of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
In "Association of Race and Ethnicity With COVID-19 Test Positivity and Hospitalization Is Mediated by Socioeconomic Factors," Hayley B. Gershengorn, MD, associate professor, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and co-authors ...
2021-03-17
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute demonstrated for the first time that blocking "cell drinking," or macropinocytosis, in the thick tissue surrounding a pancreatic tumor slowed tumor growth--providing more evidence that macropinocytosis is a driver of pancreatic cancer growth and is an important therapeutic target. The study was published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Now that we know that macropinocytosis is 'revved up' in both pancreatic cancer cells and the surrounding fibrotic tissue, blocking the process might provide a 'double whammy' to pancreatic tumors," ...
2021-03-17
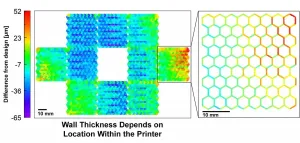
Researchers at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign developed software to improve the accuracy of 3D-printed parts, seeking to reduce costs and waste for companies using additive manufacturing to mass produce parts in factories.
"Additive manufacturing is incredibly exciting and offers tremendous benefits, but consistency and accuracy on mass-produced 3D-printed parts can be an issue. As with any production technology, parts built should be as close to identical as possible, whether it is 10 parts or 10 million," said Professor Bill King, Andersen Chair in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering and leader of the project.
The team's ...
2021-03-17
- The increasing complexity of treatments for lung cancer and language differences can make it difficult for patients to communicate with their medical teams
- Risks of jeopardising the treatment and care journey as well as recent progress in patient empowerment.
Lugano, Switzerland; Denver, CO, USA, 17 March 2021 - More than one in 10 patients with lung cancer do not know what type of tumour they have, according to data from a 17-country study carried out by the Global Lung Cancer Coalition (GLCC) to be presented at the European Lung Cancer Conference (ELCC) ...
2021-03-17
What would a volcano - and its lava flows - look like on a planetary body made primarily of metal? A pilot study from North Carolina State University offers insights into ferrovolcanism that could help scientists interpret landscape features on other worlds.
Volcanoes form when magma, which consists of the partially molten solids beneath a planet's surface, erupts. On Earth, that magma is mostly molten rock, composed largely of silica. But not every planetary body is made of rock - some can be primarily icy or even metallic.
"Cryovolcanism is volcanic activity on icy worlds, and we've seen it happen on Saturn's moon Enceladus," says Arianna Soldati, assistant professor of marine, earth and atmospheric sciences at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the ...
2021-03-17
TORONTO, ON - American adults 65 years old and older have better vision than that age group did nearly a decade ago, according to a recent study published in the journal Ophthalmic Epidemiology.
In 2008, 8.3% of those aged 65 and older in the US reported serious vision impairment. In 2017 that number decreased to 6.6% for the 65-plus cohort. Put another way: if vision impairment rates had remained at 2008 levels, an additional 848,000 older Americans would have suffered serious vision impairment in 2017.
"The implications of a reduction in vision impairment are significant," ...
2021-03-17
Cancer develops when changes occur with one or more genes in our cells. A change in a gene is called a fault or a mutation.
The inherited gene mutations found in this study, are passed from parent to child and are common in the population. However, each one individually does not significantly raise cancer risk.
Instead, these mutations collectively act to raise the risk of cancer developing. They do not directly cause cancer, instead they most likely interact with many other risk factors or random mutations that accumulate over a person's lifetime.
Cancers caused by inherited faulty genes were previously thought to be very rare, compared with mutations that happen by chance as we ...
2021-03-17
Fields and farms with more variety of insect pollinator species provide more stable pollination services to nearby crops year on year, according to the first study of its kind.
An international team of scientists led by the University of Reading carried out the first ever study of pollinator species stability over multiple years across locations all around the world, to investigate how to reduce fluctuations in crop pollination over time.
They found areas with diverse communities of pollinators, and areas with stable populations of dominant species, suffered fewer year-to-year fluctuations ...
2021-03-17
Living for nearly 2 months in simulated weightlessness has a modest but widespread negative effect on cognitive performance that may not be counteracted by short periods of artificial gravity, finds a new study published in END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Simple blood test could replace surgery for some brain tumour patients