Solar cells: Losses made visible on the nanoscale
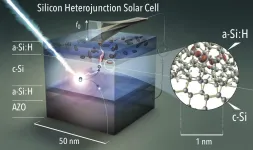
Using a conductive atomic force microscope, they scanned the solar cell surfaces and detected tiny, nanometre-sized channels for the detrimental dark currents, which are due to disorder in the a-Si:H layer.
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) Silicon solar cells are now so cheap and efficient that they can generate electricity at prices of less than 2 cent/kWh. The most efficient silicon solar cells today are made with less than 10 nanometres thin selective amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) contact layers, which are responsible for separating the light-generated charges . Efficiencies of over 24% are achieved at HZB with such silicon heterojunction solar cells and are also part of a tandem solar cell that lead to a recently reported efficiency record of 29.15 % (A. Al-Ashouri, et al. Science 370, (2020)). The current world record from Japan for a single junction silicon solar cell is also based on this heterocontact (26.6%: K. Yoshikawa, et al. Nature Energy 2, (2017)).
There is still considerable efficiency potential related to such heterocontact systems, however, it is not yet understood in detail how these layers enable charge carrier separation and what their nanoscopic loss mechanisms are. The a-Si:H contact layers are characterised by their intrinsic disorder, which on the one hand enables excellent coating of the silicon surface and thus minimises the number of interfacial defects, but on the other hand also has a small disadvantage: it can lead to local recombination currents and to the formation of transport barriers.
For the first time, a team at HZB and the University of Utah has experimentally measured on an atomic level how such leakage currents form between c-Si and a-Si:H, and how they influence the solar cell performance. In a joint effort, a team led by Prof. Christoph Boehme at the University of Utah, and by Prof. Dr. Klaus Lips at HZB, they were able to resolve the loss mechanism at the interface of the above mentioned silicon heterocontact on the nanometre scale using ultrahigh vacuum conductive atomic force microscopy (cAFM).
The physicists were able to determine with near atomic resolution where the leakage current penetrates the selective a-Si:H contact and creates a loss process in the solar cell. In cAFM these loss currents appear as nanometre-sized current channels and are the fingerprint of defects associated with the disorder of the amorphous silicon network. "These defects act as stepping stones for charges to penetrate the selective contact and induce recombination, we refer to this" as trap-assisted quantum mechanical tunnelling", explains Lips. "This is the first time that such states have been made visible in a-Si:H and that we were able to unravel the loss mechanism under working conditions of the a solar cell of highest quality," the physicist reports enthusiastically.
The Utah/Berlin team was also able to showed that the channelled dark current fluctuates stochastically over time. The results indicate that a short-term current blockade is present, which is caused by local charge that is trapped in neighbouring defects which changes the energetic positioning of the tunnelling states (stepping stones). This trapped charge can also cause the local photovoltage at a current channel to rise to above 1V, which is far above what one would be able to use with a macroscopic contact. "At this transition from the nano to the macro worldwe find the exciting physics of heterojunctions and the key on how to further improve the efficiency of silicon solar cells in an even more targeted way," says Dr. Bernd Stannowski, who is responsible for the development of industrial silicon heterojunction solar cells at HZB.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
Tropical Cyclone (TC) is an intense atmospheric vortex with a warm core and low pressure structure, and generates over the tropical or subtropical warm ocean. The problem of TC genesis has been paid great attention by scientists since the 1950s, but due to the lack of the observation data over sea, this problem has become the most difficult and challenging topic in the researches of TC.
Cumulus convections are considered to be the most basic element in the TC generation process. The formation of TC in the Northwest Pacific is often associated with the mesoscale convective system (MCS) or mesoscale convective complex (MCC). Meanwhile, in the stratiform ...
2021-03-17
Not least because of the COVID-19 pandemic, conspiracy theories are more topical than ever. They are reported and discussed in almost all media and communication channels. But what influence do they have on our behavior? Scientists led by behavioral economist Loukas Balafoutas investigated this question in a recently published study. The result: We don't need to believe in conspiracy theories for them to have an impact on us. Merely being confronted with them suffices.
Previous studies have shown that beliefs in conspiracy theories have an influence on the behavior of their adherents. For example, they lead to lower voter turnout or a lower willingness to get vaccinated. For years now, conspiracy theories have been ...
2021-03-17
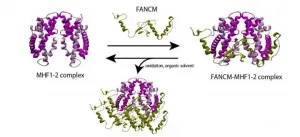
One of the most vital functions performed by the cells in our body is DNA repair, a task so crucial to our well-being that failing to execute it can lead to consequences as dreadful as cancer. The process of DNA repair involves a complex interplay between several gene pathways and proteins. One such pathway is the "Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway," whose genes participate in DNA repair. FANCM, a component of this pathway, is tasked with the elimination of harmful DNA "inter-strand cross-links," and interacts with another component called MHF in order to function. The importance of the FANCM-MHF complex is well-documented: its loss can result in chromosomal ...
2021-03-17
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are among the major global health problems. Particularly problematic is the high number of chronic courses of the disease, causing the deaths of more than 800.000 people globally every year. So far, there is no therapy to cure the condition. "With the discovery of a new hepatitis B virus in donkeys and zebras capable of causing prolonged infections, we now have the opportunity for a better understanding of the chronic course of the disease and thus also for mitigation or prevention of severe clinical consequences," explains Prof. Dr. Jan Felix Drexler, DZIF ...
2021-03-17
A new study uncovers which cell types can be infected by SARS-CoV-2 due to their viral entry factors. The study also suggests that increased gene expression of these viral entry factors in some individuals partially explains the differences of COVID-19 severity reported in relation to age, gender and smoking status. The study evolved from the Human Cell Atlas Lung Biological Network with main contributions from Helmholtz Zentrum München, the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, the Wellcome Sanger Institute and University Medical Center Groningen.
COVID-19 does not affect everyone in the same way. While the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 primarily ...
2021-03-17
The health of women aged 65 and over appears to be related, in addition to their own socioeconomic characteristics, with that of their partners, as a result of traditional gender norms. This is one of the main conclusions of research led by Jordi Gumà, a researcher at the UPF Department of Political and Social Sciences, conducted in conjunction with Jeroen Spijker, a Ramon y Cajal I3 researcher at the Centre for Demographic Studies of the Autonomous University of Barcelona (CED-UAB), focusing on the case of Spain.
The study, published in Gaceta Sanitaria, analyses the health differences among the Spanish ...
2021-03-17
An international team of scientists from the University of Turku, Finland and PennState University, USA have solved a long-standing mystery of how living organisms distinguish RNA and DNA building blocks during gene expression paving the way for the design of new antiviral drugs. The new insights were published in the journal Nature Communications.
All cellular organisms use two types of nucleic acids, RNA and DNA to store, propagate and utilize their genetic information. The synthesis of DNA is carried out by enzymes called DNA polymerases and is needed to accurately transfer the genetic information from generation to generation. ...
2021-03-17
Our immune system is very successful when it comes to warding off viruses and bacteria. It also recognizes cancer cells as potential enemies and fights them. However, cancer cells have developed strategies to evade surveillance by the immune system and to prevent immune response.
In recent years, fighting cancer with the help of the immune system has entered into clinical practice and gained increasing importance as a therapeutical approach. Current therapies apply so-called immune checkpoint inhibitors. Immune checkpoints are located on the surface ...
2021-03-17
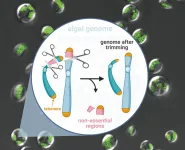
A single-celled alga undergoes genome surgery to remove non-essential parts. This can lead to a most efficient cellular factory for producing sustainable biofuels from sunlight and carbon dioxide.
Researchers from the Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have stripped hundred-kilobase genome from a type of oil-producing microalgae, knocking out genes non-essential for it to function. By doing so, they have created a "genome scalpel" that can trim microalgal genomes rapidly and creatively.
The 'minimal genome' microalgae produced is potentially useful as a model organism for further study of the molecular and biological function of every gene, or as a 'chassis' strain for synthetic biologists to augment for customized ...
2021-03-17
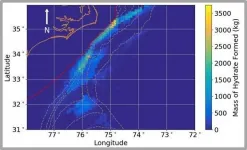
RALEIGH, N.C. -- Methane hydrate, an ice-like material made of compressed natural gas, burns when lit and can be found in some regions of the seafloor and in Arctic permafrost.
Thought to be the world's largest source of natural gas, methane hydrate is a potential fuel source, and if it "melts" and methane gas is released into the atmosphere, it is a potent greenhouse gas. For these reasons, knowing where methane hydrate might be located, and how much is likely there, is important.
A team of researchers from Sandia National Laboratories and the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory have developed a new system to model the likelihood of finding methane ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Solar cells: Losses made visible on the nanoscale
Using a conductive atomic force microscope, they scanned the solar cell surfaces and detected tiny, nanometre-sized channels for the detrimental dark currents, which are due to disorder in the a-Si:H layer.