COVID-19 denial depends on a population's trust in social institutions
Meanwhile, in Western Europe, people trust their governments more than in other EU countries
2021-03-18
(Press-News.org) An international team of scholars studied how the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted Europeans' stress levels and their trust in their national governments and the healthcare systems. They found that respondents were most stressed by the state of the national economy, and only after that, by the risk of catching COVID-19 and possibly being hospitalized. The results of the study were published in Royal Society Open Science.
The authors of the study represent over 50 universities. Among them is Dmitrii Dubrov, Junior Research Fellow at the HSE Center for Sociocultural Research, who developed and organized the global survey, COVIDiSTRESS. The researchers studied the psychological consequences of the current pandemic-related crisis, as reflected in stress levels. Over 150,000 respondents from over 50 countries participated in the study. The results (below) include answers from 75,570 respondents in 27 countries of the European Union (EU), who were surveyed from March 30 to April 20, 2020.
The general level of respondents' stress was measured on a 10-grade scale developed by psychologists Cohen, Kamarck, and Mermelstein (1983). This scale illustrates people's stress levels over the course of a recent week. The study participants were asked, for example, whether they experienced a lack of control over events, felt pressure due to growing difficulties, or disappointment due to unexpected change. Scores over 2.4 points were considered moderate, while those over 3.7 were considered high.
'Stress is a natural human reaction to negative change. We wanted to find out how humans would behave under stress, during the pandemic, whether they would follow recommendations by the WHO and authorities on how to protect oneself and others from COVID-19,' explains Dmitrii Dubrov, Junior Research Fellow at the HSE Centre for Sociocultural Research.
In many EU countries, levels of stress were moderate or even low. Poland and Portugal demonstrated the highest levels of stress in Europe, while the lowest rates were registered in Denmark and the Netherlands. Women worried more about the pandemic's consequences than men. The respondents were 74.18% female and 24.63% male.
The study participants also talked about the reasons of stress. The results showed that Europeans are most of all concerned about the state of the national economy, with the risk of catching COVID-19 and being hospitalized coming in second place. A total of 24 factors were indicated, including concerns about family and friends, work, or feeling isolated.
The respondents were also asked about their trust in the six key institutions, such as the healthcare system, the WHO, the police, social services, and national governments. Europeans demonstrate the highest levels of trust in their national healthcare systems and the WHO. Trust in national governments was lower than in other institutions. Finland and Denmark demonstrated the highest levels of trust in their governments. On the contrary, people in Bulgaria and Poland were much less inclined to trust their respective national governments.
The participants also evaluated the adequacy of anti-COVID measures implemented by their governments. Citizens of Slovenia and Slovakia believed the national measures to be excessive, while people in Hungary and France thought they were insufficient. Populations in countries were people trust their governments' efforts better, also better comply with social distancing guidelines.
'We have learned that COVID-19 denial depends on people's trust in social institutions, a belief that the government won't leave them on their own with their problems. Institutional trust in impacted by many factors, such as the level of corruption in the country. The results of our study can be used to prepare recommendations on how governments should communicate with people in situations of uncertainty. As we discovered here, the problem is global, which means that systematic work with citizen's demands is needed,' Dmitrii Dubrov said.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-18
An international study led by the University Complutense of Madrid (UCM) proposed new computational image processing methods that improve the analysis and three-dimensional reconstruction of biological macromolecules.
Currently, determining the composition (i.e., the sequence of amino acids) of macromolecules such as proteins is relatively simple; however, determining the shape in which they are ordered in a three-dimensional structure is not. The new methodology, published in Nature Communications, improves the visualization of the 3D reconstructions obtained through cryogenic electron microscopy, as well as their quality.
"This study helps us broaden our understanding of proteins ...
2021-03-18
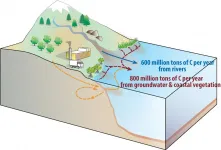
Every year 600-900 million tons of carbon flow through rivers to the ocean either as particles or in dissolved form. Researchers have known for a long time that this does not represent the total amount of carbon that gets transported from the land to the ocean. But the remaining contributors mostly from coastal ecosystems, such as carbon-rich mangrove forests, and from groundwater discharge into the ocean have been notoriously difficult to measure.
A new study published in the journal Global Biogeochemical Cycles and spearheaded by Dr. Eun Young Kwon, project leader at the IBS Center for Climate Physics South Korea provides new estimates of this elusive component of the global carbon cycle. The study makes use of the existence of two stable carbon isotopes, 12C and 13C, with the latter ...
2021-03-18
Statisticians have calculated the probability of ships of different Polar Ship Categories becoming beset in ice along the Northern Sea Route. Their data will help assess the risks of maritime traffic in the Arctic.
The results of the new study, published recently in the Cold Regions Science and Technology journal, will support safer maritime transport planning and the prevention of oil spills. The results will also benefit authorities that regulate maritime traffic by providing a foundation for statutes and legislation. A comprehensive approach to computing helps shipping companies plan transport routes.
Tankers more common on the Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route is attracting more tankers and cargo ships travelling from Russia and ...
2021-03-18
Powerful and squat stegosaurs are now one of the most recognisable dinosaurs: they are easily identified by the spines on the tail and the bony plates on the back - osteoderms. The representatives of this group lived about 165-125 million years ago, during the Jurassic and early Cretaceous periods. They were five to seven metres long and had a disproportionately small head. Their teeth were therefore quite small - about a centimetre in height and about the same in width.
Palaeontologists from St Petersburg University worked together with colleagues from: the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences; the ...
2021-03-18
The ocean covers about 70% of the Earth's surface area and is the largest reservoir of energy. Researchers have been exploring the approach for harnessing ocean energy to solve the world energy crisis and pollution problems caused by thermal power generation. The nanogenerator, including piezoelectric, triboelectric, and pyroelectric nanogenerators, is one of the key technologies for mechanical energy conversion. The triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) makes use of the triboelectric effect and electrostatic induction to harvest mechanical energy based on contact or sliding electrification.
However, conventional TENG device is often based on solid/solid contact, and it is hard to ensure the contact intimacy of the two tribo-materials. In the meanwhile, the material surfaces will wear or become ...
2021-03-18
Research from the University of Kent's School of Biosciences has revealed that a molecule produced by the human immune system can severely diminish the potency of certain antibiotics.
This may explain why antibiotics effective in laboratory settings can be less effective at clearing infections in humans.
The research findings, which have been published in the journal Archives of Microbiology, reveal that nitric oxide, a molecule produced by our immune systems, can render aminoglycoside antibiotics ineffective when used against E. coli strains isolated from ...
2021-03-18
Geopolitical boundaries can have a profound effect on the protection of threatened species. A case in point is the native cycads of the United States. A recent review paper written by researchers at the Western Pacific Tropical Research Center at the University of Guam highlights extinction risks of cycad species that occur in U.S. controlled lands and the profound effect geopolitical boundaries has had on the protection of these threatened species. The paper appears in the December 2020 issue of the MDPI journal Diversity.
Cycads are the most threatened plant order worldwide. This is due to a combination of factors including habitat loss, poaching predation by invasive species, and lack of appropriate ...
2021-03-18
Shipping provides the very foundation for world trade, by moving an estimated 11 billion tonnes of goods a year from where they are produced to where they will be used. From TVs to toasters, soap to sugar -- much of it moves over the waves.
Yet for ships plying the open ocean and for offshore industries, waves present an enormous challenge --because they can increase operational risks, reduce operating efficiency, and be dangerous if large enough and not handled well -- and they can be difficult to predict.
Ships can access information about wave heights, directions and frequency, but those data may be expensive to obtain or delayed because of satellite communication limitations, says Zhengru ...
2021-03-18
Undocumented women in Finland access pregnancy care later than others. Yet, screening of infectious diseases at the early stages of pregnancy would be particularly important to these women, a new study carried out in Helsinki, Finland, shows. Conducted by the University of Eastern Finland and the University of Helsinki, the study on undocumented women's pregnancy care and childbirth was published in BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.
Undocumented pregnant women constitute a vulnerable group of people who lack equal access to pregnancy care. Previous ...
2021-03-18
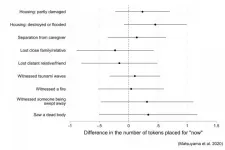
Study finds that children who experienced housing loss in the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake are more inclined to opt for short-term gratification
Tokyo - Living through a tragic event might make us more inclined to live for the moment, but not always in a good way. Research is looking into the psychological after-effects among children who survived the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, and a recent study may have made a connection: the children may forgo greater long-term reward for short-term pleasure.
Among the traumatic experiences in the quake and subsequent tsunami that killed almost 16,000 people, some survivors witnessed people washed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] COVID-19 denial depends on a population's trust in social institutions
Meanwhile, in Western Europe, people trust their governments more than in other EU countries